File:Biogeography of oral microbiota.png
Original file (1,681 × 1,286 pixels, file size: 643 KB, MIME type: image/png)
Summary
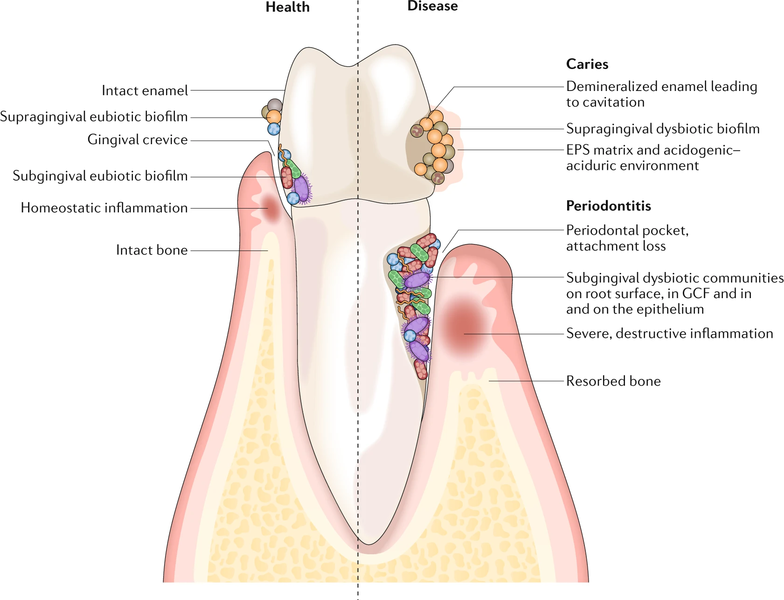
Figure 1: Microbial colonization occurs on all available surfaces, and microorganisms can also penetrate epithelial tissues and cells. The microbiota assembles into biofilm communities on the abiotic and biotic surfaces. In health (left), eubiotic biofilms maintain a homeostatic balance with the host. In disease (right), caries and periodontitis ensue when biofilms become dysbiotic, resulting in increased levels and duration of low pH challenge and the induction of destructive inflammatory responses, respectively. EPS, extracellular polymeric substance; GCF, gingival crevicular fluid.
Lamont RJ, Koo H, Hajishengallis G. 2018. The oral microbiota: dynamic communities and host interactions. Nature Reviews Microbiology 16:745-759.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 01:34, 31 August 2021 |  | 1,681 × 1,286 (643 KB) | A.reis (talk | contribs) | Figure 1: Microbial colonization occurs on all available surfaces, and microorganisms can also penetrate epithelial tissues and cells. The microbiota assembles into biofilm communities on the abiotic and biotic surfaces. In health (left), eubiotic biofilms maintain a homeostatic balance with the host. In disease (right), caries and periodontitis ensue when biofilms become dysbiotic, resulting in increased levels and duration of low pH challenge and the induction of destructive inflammatory re... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
There are no pages that use this file.
