Thermos Thermophilus: Difference between revisions
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
==Cell structure and metabolism== | ==Cell structure and metabolism== | ||
{| border="1" | |||
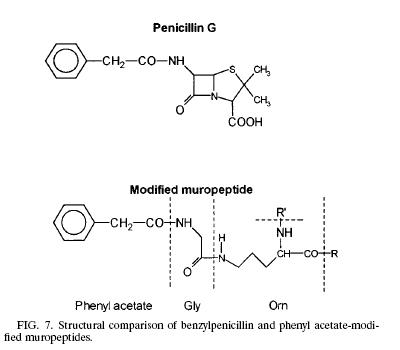
!Like any other Gram negative bacteria, Thermus Thermophilus composed of an outer membrane, mainly phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides, which made it ineffective to hold the crystal violet color during gram stain; a thin layer of peptidoglycan covering the plasma membrane and a cytoplasmic membrane. The peptidoglycan (murein) is responsible for the cell’s rigid structure. There are a total of 29 muropeptides composed of more than 85% of the total murein in the organism. Scientists dissected the composition of the Thermus Thermophilus murein and found the presence of Ala, Glu, Gly, Orn, N-acetyl glucosamine, and N-acetylmuramic. In addition to the amino acid and sugar mentioned above, T. Thermophilus also contains phenyl acetic acid at the N terminal of Glysine. The presence of phenyl acetic acid in the muropeptides is 23.7% relative to the total muropeptides. The process of how and why the phenyl acetic acid incorporated into the muropeptides is still unknown but scientists think that the aromatic phenyl ring could be facilitating the interaction between the noncovalent and hydrophobic molecules from the surrounding environment. Other hypothesis also arises linking the phenyl acetic acid to the structure of penicillin.('''1''')!! Modified Muropeptide & Penicillin[[Image:Modified_Muropeptide_and_penicillin.jpg|frame|none|]] | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Revision as of 20:59, 29 August 2007
A Microbial Biorealm page on the genus Thermos Thermophilus
Classification
Higher order taxa
Higher order taxa: Bacteria (Domain): Deinococcus-Thermus (Phylum): Deinococci (Class): Thermales (Order): Thermacaea (Family): Thermus (Genus) [1] link to find]
Species
Thermophilus (Species): Strain (HB27, HB8)
|
NCBI: Taxonomy |
Genus species
Description and significance
| Thermus Thermophilus is a Gram-negative bacterium that was isolated in 1971, Japan. They spawn in thermal spring ranging from 50-82C. The biological machines from these organisms have a higher stability than other organisms due to the environment that they have to live in. In general, thermophiles are anaerobes that can live in hot environment with low oxygen solubility due to the temperature with the exception of thermus, they are aerobic chemorganotroph. Thermus Thermophilus contains two strains, HB8 and HB27; both were found in Japan’s thermal environment with optimum environment 68C and the pH 7.0. The HB8 strain can live in either anaerobe and aerobe; where as the HB27 can only strive in aerobe environment. HB8 survive anaerobeically in the presence of nitrate through nitrate reductase production. However the HB27 was unable to growth in the same environment as the HB8 due to the inability to produce nitrate reductase. | Thermus Thermophilus |
|---|
Genome structure
The Thermus Thermophilus bacterium contain Circular DNA and a megaplasmid. The DNA has 1,894,877 base pair where 1476627 base pair (69.40%) are G+C content. The high percentage of G+C content allow the bacterium to strive in extreme thermo environment where it's own genetic information would not be denatured by the surrounding environment. Also, the megaplasmid contain 232,605 nucleotides with 69% G+C content. In addition, it contained a total of 2210 protein encoding genes and 53 RNA genes. (2)
|
NCBI: Genome structure |
Cell structure and metabolism
| Like any other Gram negative bacteria, Thermus Thermophilus composed of an outer membrane, mainly phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides, which made it ineffective to hold the crystal violet color during gram stain; a thin layer of peptidoglycan covering the plasma membrane and a cytoplasmic membrane. The peptidoglycan (murein) is responsible for the cell’s rigid structure. There are a total of 29 muropeptides composed of more than 85% of the total murein in the organism. Scientists dissected the composition of the Thermus Thermophilus murein and found the presence of Ala, Glu, Gly, Orn, N-acetyl glucosamine, and N-acetylmuramic. In addition to the amino acid and sugar mentioned above, T. Thermophilus also contains phenyl acetic acid at the N terminal of Glysine. The presence of phenyl acetic acid in the muropeptides is 23.7% relative to the total muropeptides. The process of how and why the phenyl acetic acid incorporated into the muropeptides is still unknown but scientists think that the aromatic phenyl ring could be facilitating the interaction between the noncovalent and hydrophobic molecules from the surrounding environment. Other hypothesis also arises linking the phenyl acetic acid to the structure of penicillin.(1) | Modified Muropeptide & Penicillin |
|---|
Ecology
Describe any interactions with other organisms (included eukaryotes), contributions to the environment, effect on environment, etc.
Pathology
How does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
Application to Biotechnology
Does this organism produce any useful compounds or enzymes? What are they and how are they used?
Current Research
Enter summaries of the most recent research here--at least three required
References
Edited by student of Rachel Larsen