Tobamovirus
Baltimore Classification
Higher order taxa
Viruses; ssRNA positive-strand viruses, no DNA stage; (no assigned family); Tobamovirus
Species
Tobacco mosaic virus, Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus, Frangipani mosaic virus, Turnip vein-clearing virus (examples)
Description and Significance
Genome Structure
The genome of Tobamovirus is usually monomeric or polymeric, not segmented, and contains a single molecule of linear, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA. Minor species of non-genomic nucleic acid may also be found in virions. The encapsidated nucleic acid is mainly of genomic origin but virions may also contain nucleic acid of host origin and subgenomic mRNA including host rRNA found in the short particles of some species. The genome is sequenced and the complete sequence is about 6450 nucleotides long. The genome has a base ratio of 23-24.32-25.8 % guanine; 24.6-27.92-29.8 % adenine; 18-19.02-20.6 % cytosine; and 26.3-28.72-31.6 % uracil. The 5'-end of the genome has a methylated nucleotide cap and the cap sequence type is m7G5'ppp5 ('Gp). The 3'-terminus has a tRNA-like structure that accepts histidine. (source: ICTVdB Descriptions)
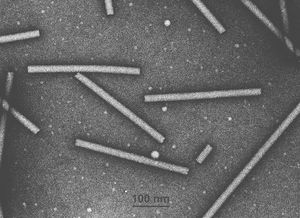
Virion Structure of a Tobamovirus
The virions of tobamovirus consist of a non-enveloped capsid. The capsid is elongated with helical symmetry and is rod shaped and straight. It has a herring-bone pattern with a low percentage in population clear predominate lengths. The axial canal could be distinct with a diameter of 2-3.257-4 nm and the basic helix could be obvious or obscure. The pitch of the helix is 2.3-2.314-2.4 nm. (source: ICTVdB Descriptions)
