Ashbya gossypii: Difference between revisions
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
<br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br> | ||
==Cell Structure and Metabolism== | ==Growth, Cell Structure and Metabolism== | ||
===Growth=== | |||
''Ashbya gossypii'' has isotropic growth, where the haploid spore germinates to form a germ bubble. Two germ tubes then grow from opposite sites of the germ bubble. Apical growth follows, which allows fungi to extend into their environment and release enzymes from the tips for nutrient intake. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 04:51, 8 November 2013
Classification
Higher Order Taxa:
Fungi, Ascomycota, Saccharomycetes, Saccharomycetales, Saccharomycetaceae
Species:
A. gossypii
Description and Significance
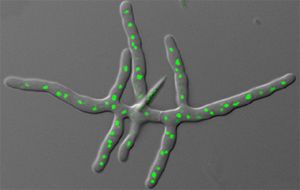
Ashbya gossypii (Eremothecium gossypii) is a filamentous fungus, meaning that it is an infectious agent of the fungus kingdom consisting of a long series of attached cells. It is closely related to unicellular yeasts, especially Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a yeast with which it shares more than 90% of its genome.
Ashbya gossypii is an effective fungus in which to study the growth of long and multinucleate (more than one nucleus) fungal cells. It has a small genome, haploid nuclei, and efficient gene targeting methods, characteristics that make it favorable in studies.
Genome Structure
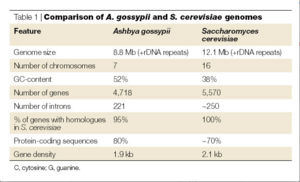
The genome for Ashbya gossypii is the smallest genome of a free-living eukaryote thus far, coming up to only 9.2 megabases. It contains a total of 4718 protein-coding genes. As mentioned above, more than 90% of its genes are similar to that of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The comparison of these genes reveals shared homology and synteny (the condition of two or more genes being located on the same chromosome) between the two species.
Growth, Cell Structure and Metabolism
Growth
Ashbya gossypii has isotropic growth, where the haploid spore germinates to form a germ bubble. Two germ tubes then grow from opposite sites of the germ bubble. Apical growth follows, which allows fungi to extend into their environment and release enzymes from the tips for nutrient intake.
Ecology
Pathology
Ashbya gossypii is a pathogen in certain crops that causes stigmatomycosis. (Ashby and Novell, 1926.) This fungal disease, discovered in cotton, affects the development of hair cells in cotton bolls. It can then transfer to citrus fruits, causing dry rot disease in which the fruits dry out and collapse.
References
- Jaspersen Lab, 2007. "Sue Jasperseon, Ph.D, Profile." Stowers Institute for Medical Research.
- Wikipedia Article "A. gossypii," March 2013. "Ashbya gossypii."
- Ashbya Genome Database, September 2013. "Ashbya gossypii." EnsemblFungi.
