Campylobacteriosis: Difference between revisions
From MicrobeWiki, the student-edited microbiology resource
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment of Campylobacteriosis is done by managing the symptoms and any complications until the symptoms subside. Symptoms mainly include diarrhea leading to dehydration, and vomiting. Antibiotics can be used but are not usually administered unless serious complications arise. A majority of people recover from the symptoms within a week; however, some cases have known to take up to approximately 10 days. | |||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention== | ||
Revision as of 15:39, 15 July 2013
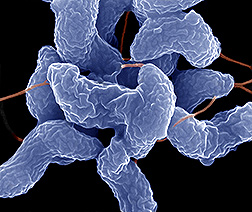
Spiral rod Campylobacter jejunum. From: Wikipedia.org [1]
Etiology/Bacteriology
Taxonomy
| Domain = Bacteria | Phylum = Proteobacteria | Class = Epsilon Proteobacteria | Order = Campylobacterales | Family = Campylobacteraceae | Genus = Campylobacter | Species = jejuni
Description
Alt text
Caption
Caption
Pathogenesis
Transmission
Infectious Dose, Incubation, Colonization
Epidemiology
Virulence Factors
Clinical features
Symptoms
Morbidity and Mortality
Diagnosis
Treatment
Treatment of Campylobacteriosis is done by managing the symptoms and any complications until the symptoms subside. Symptoms mainly include diarrhea leading to dehydration, and vomiting. Antibiotics can be used but are not usually administered unless serious complications arise. A majority of people recover from the symptoms within a week; however, some cases have known to take up to approximately 10 days.
Prevention
Risk Avoidance
Immunization
Host Immune Response
References
References
Created by Halen Borron, Kelley Raines, and Evan Robinson, students of Tyrrell Conway at the University of Oklahoma.
