Endomycorrhizal fungi: Difference between revisions
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
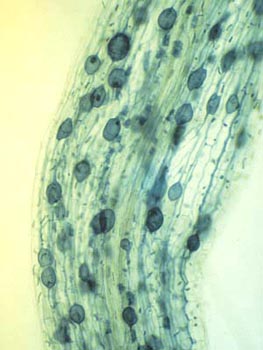
Endomycorrhizal fungi (more commonly referred to as endomycorrhizae) is one of the major types of known mycorrhizae which differs from the another type of mycorrhizae, ectomycorrhizae, in structure. Unlike ectomycorrhizae which form a system of hyphae that grow around the cells of the root, the hyphae of the endomycorrhizae not only grow inside the root of the plant but penetrate the root cell walls and become enclosed in the cell membrane as well. This makes for a more invasive symbiotic relationship between the fungi and the plant. The penetrating hyphae create a greater contact surface area between the hyphae of the fungi and the plant. This heightened contact facilitates a greater transfer of nutrients between the two. Endomycorrhizae have further been classified into five major groups: arbuscular, ericoid, arbutoid, monotropoid, and orchid mycorrhizas.<br><br> | |||
Compose a title for your page. Type your exact title in the Search window, then press Go. The MicrobeWiki will invite you to create a new page with this title.<br><br> | Compose a title for your page. Type your exact title in the Search window, then press Go. The MicrobeWiki will invite you to create a new page with this title.<br><br> | ||
Open the class template page in "edit." Copy ALL the editable text. Then go to YOUR OWN page; edit tab. PASTE into your own page, and edit.<br><br> | Open the class template page in "edit." Copy ALL the editable text. Then go to YOUR OWN page; edit tab. PASTE into your own page, and edit.<br><br> | ||
Revision as of 22:43, 7 November 2013
Introduction
Endomycorrhizal fungi (more commonly referred to as endomycorrhizae) is one of the major types of known mycorrhizae which differs from the another type of mycorrhizae, ectomycorrhizae, in structure. Unlike ectomycorrhizae which form a system of hyphae that grow around the cells of the root, the hyphae of the endomycorrhizae not only grow inside the root of the plant but penetrate the root cell walls and become enclosed in the cell membrane as well. This makes for a more invasive symbiotic relationship between the fungi and the plant. The penetrating hyphae create a greater contact surface area between the hyphae of the fungi and the plant. This heightened contact facilitates a greater transfer of nutrients between the two. Endomycorrhizae have further been classified into five major groups: arbuscular, ericoid, arbutoid, monotropoid, and orchid mycorrhizas.
Compose a title for your page. Type your exact title in the Search window, then press Go. The MicrobeWiki will invite you to create a new page with this title.
Open the class template page in "edit." Copy ALL the editable text. Then go to YOUR OWN page; edit tab. PASTE into your own page, and edit.
At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki. The insertion code consists of:
Double brackets: [[
Filename: PHIL_1181_lores.jpg
Thumbnail status: |thumb|
Pixel size: |300px|
Placement on page: |right|
Legend/credit: http://jpkc.sdau.edu.cn/zbgpp/vocabulary/endomycorrhiza.htm
Closed double brackets: ]]
Other examples:
Bold
Italic
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
Section 1
Include some current research, with at least one image.
Section 2
Include some current research, with a second image.
Conclusion
Overall text length should be at least 1,000 words (before counting references), with at least 2 images. Include at least 5 references under Reference section.
References
Edited by [Author Name], student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 116 Information in Living Systems, 2013, Kenyon College.