Onchocerciasis (Onchocerca volvulus): Difference between revisions
From MicrobeWiki, the student-edited microbiology resource
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention== | ||
[[File:Walkingblind.jpeg|250px|thumb|right center|Children lead men affected by Onchocerciasis. Published in the Atlas of Tropical and Extraordinary Diseases via the National Museum of Health and Medicine. https://www.flickr.com/photos/medicalmuseum/3969963699/in/album-72157622366709345/]] | |||
==Host Immune Response== | ==Host Immune Response== | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 13:19, 26 July 2015

University of Oklahoma Study Abroad Microbiology in Arezzo, Italy[1]
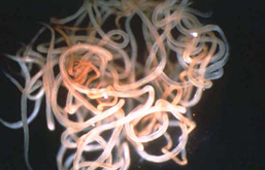
Picture of Adult Onchocerca volvulus worms from the World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/apoc/media/adult_worms.JPG
Etiology/Bacteriology
Taxonomy
| Domain = Animalia | Phylum = Nematoda | Class = Secernentea | Order = Spirurida | Family = Onchocecidae | Genus = Onchocerca | species = O. volvulus
Description
Pathogenesis

A known vector of Onchocerca volvulus the Simulium Blackfly feeds on a human. Courtesy of WHO via the Natural History Museum. http://www.nhm.ac.uk/nature-online/species-of-the-day/scientific-advances/disease/simulium-yahense/index.html
Clinical Features
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention

Children lead men affected by Onchocerciasis. Published in the Atlas of Tropical and Extraordinary Diseases via the National Museum of Health and Medicine. https://www.flickr.com/photos/medicalmuseum/3969963699/in/album-72157622366709345/
