The Temperature Relationship of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: Difference between revisions
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- Do not edit this line-->{{Curated}} | <!-- Do not edit this line-->{{Curated}} | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
[[Image:F4.large.jpg|thumb| | [[Image:F4.large.jpg|thumb|250px|right|Composite line drawing of a longitudinal section of a <i>Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis</i> zoospore.<ref name=Berger2005>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16465834/ Berger et al. 2005. Life cycle stages of the amphibian chytrid <i>Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis</i>. Inter-Research. 68:52-63]</ref>]] | ||
<br>By [Eva Brazer]<br> | <br>By [Eva Brazer]<br> | ||
Revision as of 22:12, 29 April 2020
Introduction
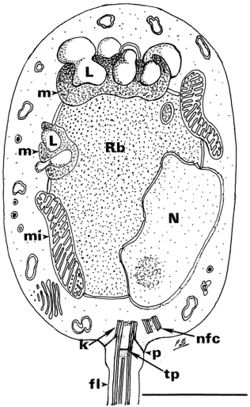
By [Eva Brazer]
Amphibian species around the world are experiencing unprecedented population decline due to the emerging infectious disease chytridiomycosis, which is caused by the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd).[2] The chytrid pathogen is considered an emerging infectious disease because it was discovered and described only in the last twenty years, and has continued to spread globally causing devastating effects.[3] Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis has been documented in hundreds of amphibian species, and reports of infection in new species and geographic locations continue to accumulate rapidly.[4]
Effect on Amphibians
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Every point of information REQUIRES CITATION using the citation tool shown above.
Effect of Temperature
Phylogeny
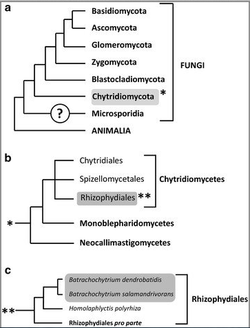
Scientific classification
Kingdom: Fungi
Division: Chytridiomycota
Class: Chytridiomycetes
Order: Rhizophydiales
Genus: Batrachochytrium
Species: B. dendrobatidis
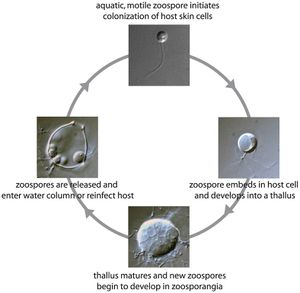
Life Cycle
Effect of Temperature
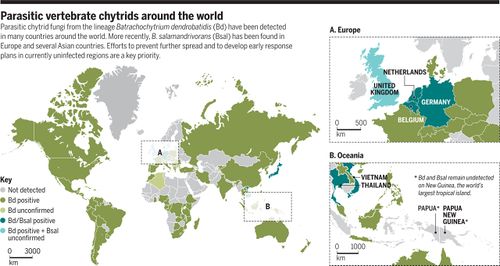
Geographic Distribution
Effect of Temperature
Climate Change
Conclusion
References
- ↑ Berger et al. 2005. Life cycle stages of the amphibian chytrid Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. Inter-Research. 68:52-63
- ↑ Weldon et al. 2004. Origin of the Amphibian Chytrid Fungus. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 10(12):2100-2105
- ↑ Piotrowski et al. 2004. Physiology of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, a Chytrid Pathogen of Amphibians. Mycologia. 96:9-15
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Rosenblum et al. 2010. The Deadly Chytrid Fungus: A Story of an Emerging Pathogen. PLoS Pathogens. 6(1):e1000550
- ↑ Rooij et al. 2015. Amphibian chytridiomycosis: A review with focus on fungus-host interactions. Veterinary Research. 46(1):137.
- ↑ Bower et al. 2017. Amphibians on the brink: Preemptive policies can protect amphibians from devastating fungal diseases. Science. 357:454-455
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski, 2018, Kenyon College.
