Thiomargarita namibiensis food storage: Difference between revisions
Slonczewski (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (41 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
The bacteria Thiomargarita namibiensis was discovered in 1997 by Heidi N. Schulz off the coast of Walvis Bay, Namibia, Africa. Thiomargarita namibiensis is currently the largest known bacteria (up to 0.3 mm in diameter). Thiomargarita namibiensis is a sulfide eating bacteria and although it mainly consumes sulfides, Thiomargarita namibiensis also consumes significant amounts of nitrates. A separate strand of the Thiomargarita namibiensis was also found off the coast of the Gulf of Mexico in 2005 but this strand does not does not divide along a single axis and because of that, it is unable to form large chains. The Thiomargarita namibiensis is closely related to a much smaller bacteria called Thioploca which live in vertical sheaths and have to move up and down in order to obtain the nutrients that they need. Thiomargarita namibiensis does not need to do that in order to obtain required nutrients. The Thiomargarita namibiensis are rarely seen individually and most often are grouped together in extremely tight, dense clusters that can be up to forty-seven grams per square meter. Having such a high density has enabled these bacteria to oxidize the highly toxic sulfides in its environments off the coast of Namibia. | |||
<ref>[https://www.nature.com/articles/ismej201166 Jake V Bailey, Verena Salman, Gregory W Rouse, Heide N Schulz-Vogt, Lisa A Levin & Victoria J Orphan "<I>Thiomargarita namibiensis</i> Dimorphism in methane seep-dwelling ecotypes of the largest known bacteria" June 23, 2011.]</ref> | |||
[[Image:Sulphide_bacteria_crop.jpg|thumb| | ====Reproduction==== | ||
In order to maintain a high surface area-to-volume ratio many bacteria have developed morphologies in order to maintain their cytoplasm no less than a micron away from its outside environment. There are two types of bacteria that are exceptions to this rule of diffusion, one of which is the Thiomargarita namibiensis mainly because of its extremely large volume compared to other bacteria. However many bacteria, including the Thiomargarita namibiensis, goes through a process of binary fission in order to reproduce. Binary fission is when a single organism/cell divides into two more entities. The Thiomargarita namibiensis goes through the process of binary fission on a single plane and during this process it does not separate at all causing a chain of cells to form. | |||
<ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4484965/ Petra Ann Levin and Esther R. Angert "<I>Thiomargarita namibiensis</i> Small but Mighty: Cell Size and Bacteria" July 2015.]</ref> | |||
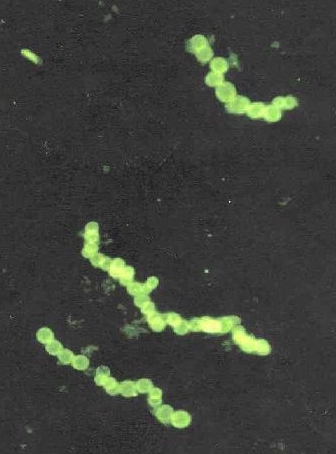
[[Image:Sulphide_bacteria_crop.jpg|thumb|500px|right|Stained micrograph of the Thiomargarita namibiensis bacteria in 2007. Taken by NASA. [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Sulphide_bacteria_crop.jpg].]] | |||
==Metabolism== | |||
The Thiomargarita namibiensis is a non-photosynthetic chemolithotroph. Although it it currently not possible to cultivate the Thiomargarita namibiensis in the lab, scientists at Harvard University have found that the bacteria is able to thrive best under anaerobic and hypoxic conditions. This information may help further the research on how to be able to cultivate this bacteria in the lab. For example, under hypoxic conditions, the scientists at Harvard University were able to find that the Thiomargarita namibiensis uses acetate, citrate, and hydrogen sulfide in order to maintain and steady metabolism. The Thiomargarita namibiensis is capable of using nitrogen as the terminal electron acceptor during the Electron Transport Chain. Throughout this process, it oxidizes hydrogen sulfide (H<sub>2</sub>S)</sub> into elemental sulfur (S<sub>2</sub>). The sulfur molecules are then deposited in their periplasms which provides the bacteria with the characteristic of a white shimmer. Furthermore, this "white" glow allowed for scientists to give it the nickname of "The Sulfur Pearl of Namibia". When the nitrate concentrations in the surrounding environment become low, the Thiomargarita namibiensis uses the excess nutrients that it has stored in its vacuoles instead. In the recent years there has been research done which shows that the Thiomargarita namibiensis is able to go through the respiration process if the oxygen levels are plentiful in its current environment. <ref>[https://www.sciencemag.org/news/1999/04/giant-sulfur-eating-microbe-found Bernice Wuethrich "<I>Thiomargarita namibiensis</i> Giant Sulfur-Eating Microbe Found" 1999.]</ref> | |||
<ref>[https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2014AGUFM.B14C..02B/abstract Bailey J., Flood B., Ricci E. "<I>Thiomargarita namibiensis</i> Metabolism in the Uncultivated Giant Sulfide-Oxidizing Bacterium Thiomargarita Namibiensis Assayed Using a Redox-Sensitive Dye" December 2014.]</ref> | |||
<br><br> | |||
<ref>[ | |||
< | |||
== | ==Structure and Food Storage== | ||
===Structure=== | |||
The Thiomargarita namibiensis grows in horizontal rows of up to sixteen single ball-shaped cells. Due to physical limitations from this specific structure, the bacteria does not have a very good range of motion. The ball-like structure that the Thiomargarita namibiensis has allows for them to be able to store extra nutrients in their vacuoles for later consumption. The Thiomargarita namibiensis also has a cytoplasm that runs along the perimeter of the cell so as to amplify the extra space for the vacuoles. The bacteria also holds the current record for having the largest volume, being about three million times larger than the average bacteria. The cells of the Thiomargarita namibiensis are held together in a chain formation by mucus that surrounds each individual cell. Scientists have yet to find an exact gradient change in the uptake of oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfates but they have been able to gain more knowledge about the bacteria by looking at the changes in uptake rates over time. | |||
<ref>[https://bio.libretexts.org/Courses/University_of_California_Davis/BIS_2A_(2018)%3A_Introductory_Biology_(Singer)/MASTER_RESOURCES/Cellular_Structure_of_Bacteria_and_Archaea*%23 Biology LibreTexts "<I>Thiomargarita namibiensis</i> Cellular Structure of Bacteria and Archaea" June 2, 2019.]</ref> | |||
<ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC129903/ Heide N. Schulz and Dirk de Beer "<I>Thiomargarita namibiensis</i> Uptake Rate of Oxygen and Sulfide Measured with Individual Thiomargarita namibiensis Cells by Using Microelectrodes" November 2002.]</ref> | |||
<br></br> | |||
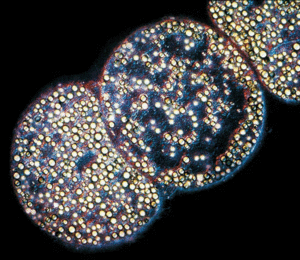
[[Image:The-Largest-Bacteria-in-the-World-2.gif|thumb|300px|right|Micrograph of vacuoles inside a cell of the Thiomargarita namibiensis. Taken by SoftPedia News. [https://news.softpedia.com/news/The-Largest-Bacteria-in-the-World-62520.shtml].]] | |||
===Food Storage=== | |||
The Thiomargarita namibiensis is able to store food and other nutrients inside of its vacuoles for up to months at a time. Their ability to store food is affected by two different aspects: the size of the individual cell as well as the amount of nutrients that is available in the surrounding environment. When the bacteria undergoes cellular reproduction, it will sometimes produce string-like chains of up to sixteen cells that are all interconnected. This process, specifically in the Thiomargarita namibiensis, was discovered by scientists in hydrocarbon seeps at depth ranging from 900 to 1,600 meters below the ocean surface in the Gulf of Mexico. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the Thiomargarita namibiensis is able to go through the respiration process via an "anaerobic lung", but only when there is a plentiful amount of oxygen in the surrounding environment. Having this extra boost allows for the bacteria to be able to have a higher uptake of nutrients and be able to store more in its vacuoles for later use. The vacuoles in the Thiomargarita namibiensis takes up about 98% of the internal volume of the cell. <br> | |||
<ref>[https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/1999-04/M-TLBS-160499.php MAX-PLANCK-GESELLSCHAFT "<I>Thiomargarita namibiensis</i> The Largest Bacterium: Scientist Discovers New Bacterial Life Form Off The African Coast" 1999.]</ref> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
<br>Edited by [ | <br>Edited by [Lauren Barrabee], student of [mailto:slonczewski@kenyon.edu Joan Slonczewski] for [http://biology.kenyon.edu/courses/biol116/biol116_Fall_2013.html BIOL 116 Information in Living Systems], 2020, [http://www.kenyon.edu/index.xml Kenyon College]. | ||
<!--Do not edit or remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Joan Slonczewski at Kenyon College]] | <!--Do not edit or remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Joan Slonczewski at Kenyon College]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:59, 24 December 2020
Introduction
The bacteria Thiomargarita namibiensis was discovered in 1997 by Heidi N. Schulz off the coast of Walvis Bay, Namibia, Africa. Thiomargarita namibiensis is currently the largest known bacteria (up to 0.3 mm in diameter). Thiomargarita namibiensis is a sulfide eating bacteria and although it mainly consumes sulfides, Thiomargarita namibiensis also consumes significant amounts of nitrates. A separate strand of the Thiomargarita namibiensis was also found off the coast of the Gulf of Mexico in 2005 but this strand does not does not divide along a single axis and because of that, it is unable to form large chains. The Thiomargarita namibiensis is closely related to a much smaller bacteria called Thioploca which live in vertical sheaths and have to move up and down in order to obtain the nutrients that they need. Thiomargarita namibiensis does not need to do that in order to obtain required nutrients. The Thiomargarita namibiensis are rarely seen individually and most often are grouped together in extremely tight, dense clusters that can be up to forty-seven grams per square meter. Having such a high density has enabled these bacteria to oxidize the highly toxic sulfides in its environments off the coast of Namibia. [1]
Reproduction
In order to maintain a high surface area-to-volume ratio many bacteria have developed morphologies in order to maintain their cytoplasm no less than a micron away from its outside environment. There are two types of bacteria that are exceptions to this rule of diffusion, one of which is the Thiomargarita namibiensis mainly because of its extremely large volume compared to other bacteria. However many bacteria, including the Thiomargarita namibiensis, goes through a process of binary fission in order to reproduce. Binary fission is when a single organism/cell divides into two more entities. The Thiomargarita namibiensis goes through the process of binary fission on a single plane and during this process it does not separate at all causing a chain of cells to form. [2]
Metabolism
The Thiomargarita namibiensis is a non-photosynthetic chemolithotroph. Although it it currently not possible to cultivate the Thiomargarita namibiensis in the lab, scientists at Harvard University have found that the bacteria is able to thrive best under anaerobic and hypoxic conditions. This information may help further the research on how to be able to cultivate this bacteria in the lab. For example, under hypoxic conditions, the scientists at Harvard University were able to find that the Thiomargarita namibiensis uses acetate, citrate, and hydrogen sulfide in order to maintain and steady metabolism. The Thiomargarita namibiensis is capable of using nitrogen as the terminal electron acceptor during the Electron Transport Chain. Throughout this process, it oxidizes hydrogen sulfide (H2S) into elemental sulfur (S2). The sulfur molecules are then deposited in their periplasms which provides the bacteria with the characteristic of a white shimmer. Furthermore, this "white" glow allowed for scientists to give it the nickname of "The Sulfur Pearl of Namibia". When the nitrate concentrations in the surrounding environment become low, the Thiomargarita namibiensis uses the excess nutrients that it has stored in its vacuoles instead. In the recent years there has been research done which shows that the Thiomargarita namibiensis is able to go through the respiration process if the oxygen levels are plentiful in its current environment. [3]
[4]
Structure and Food Storage
Structure
The Thiomargarita namibiensis grows in horizontal rows of up to sixteen single ball-shaped cells. Due to physical limitations from this specific structure, the bacteria does not have a very good range of motion. The ball-like structure that the Thiomargarita namibiensis has allows for them to be able to store extra nutrients in their vacuoles for later consumption. The Thiomargarita namibiensis also has a cytoplasm that runs along the perimeter of the cell so as to amplify the extra space for the vacuoles. The bacteria also holds the current record for having the largest volume, being about three million times larger than the average bacteria. The cells of the Thiomargarita namibiensis are held together in a chain formation by mucus that surrounds each individual cell. Scientists have yet to find an exact gradient change in the uptake of oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfates but they have been able to gain more knowledge about the bacteria by looking at the changes in uptake rates over time.
[5]
[6]
Food Storage
The Thiomargarita namibiensis is able to store food and other nutrients inside of its vacuoles for up to months at a time. Their ability to store food is affected by two different aspects: the size of the individual cell as well as the amount of nutrients that is available in the surrounding environment. When the bacteria undergoes cellular reproduction, it will sometimes produce string-like chains of up to sixteen cells that are all interconnected. This process, specifically in the Thiomargarita namibiensis, was discovered by scientists in hydrocarbon seeps at depth ranging from 900 to 1,600 meters below the ocean surface in the Gulf of Mexico. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the Thiomargarita namibiensis is able to go through the respiration process via an "anaerobic lung", but only when there is a plentiful amount of oxygen in the surrounding environment. Having this extra boost allows for the bacteria to be able to have a higher uptake of nutrients and be able to store more in its vacuoles for later use. The vacuoles in the Thiomargarita namibiensis takes up about 98% of the internal volume of the cell.
[7]
References
- ↑ Jake V Bailey, Verena Salman, Gregory W Rouse, Heide N Schulz-Vogt, Lisa A Levin & Victoria J Orphan "Thiomargarita namibiensis Dimorphism in methane seep-dwelling ecotypes of the largest known bacteria" June 23, 2011.
- ↑ Petra Ann Levin and Esther R. Angert "Thiomargarita namibiensis Small but Mighty: Cell Size and Bacteria" July 2015.
- ↑ Bernice Wuethrich "Thiomargarita namibiensis Giant Sulfur-Eating Microbe Found" 1999.
- ↑ Bailey J., Flood B., Ricci E. "Thiomargarita namibiensis Metabolism in the Uncultivated Giant Sulfide-Oxidizing Bacterium Thiomargarita Namibiensis Assayed Using a Redox-Sensitive Dye" December 2014.
- ↑ Biology LibreTexts "Thiomargarita namibiensis Cellular Structure of Bacteria and Archaea" June 2, 2019.
- ↑ Heide N. Schulz and Dirk de Beer "Thiomargarita namibiensis Uptake Rate of Oxygen and Sulfide Measured with Individual Thiomargarita namibiensis Cells by Using Microelectrodes" November 2002.
- ↑ MAX-PLANCK-GESELLSCHAFT "Thiomargarita namibiensis The Largest Bacterium: Scientist Discovers New Bacterial Life Form Off The African Coast" 1999.
Edited by [Lauren Barrabee], student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 116 Information in Living Systems, 2020, Kenyon College.
