Jordan.Arredondo
Classification
Domain: Bacteria; Kingdom: Eubacteria; Phylum: Firmicutes; Class: Bacilli; Order: Bacillales; Family: Bacillaceae; Genus: Bacliiius;
NCBI link to find]
Species
|
NCBI: Taxonomy |
Genus species: Bacillus Cereus
Habitat Information
B. cereus is found all around the world, makes a necessary switch from single cellular to multicellular once in the soil to help with translocation. Found near vegetative growth and has optimum growth conditions as follows:
1.) 28 - 35 degress celsius
2.) Oxygen
3.) Sediment
4.) Food products act as a host
Description and Significance
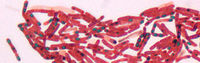
This organism is a large, rod-shaped, endospore forming gram positive bacteria, which in the endospore form, might lay dormant for decades or maybe longer. Bacillus Cereus is said to be most closely related to Bacillus Anthracis, which causes Anthrax!!! Also related to Bacillus thuringiensis, which is found in some insect pesticides. Without stating where, the bacteria was first isolated in 1969 from a man with a fatal case of pneumonia, samples taken from his blood and lung fluid.
Genome Structure
This circular chromosome measures 5,411,809 nt in length and sequenced by a shotgun sequencing method, with 5481 genes, 5234 protein coding, 147 structural RNAs. The genome measures anywhere between 5.4 and 6.3 in size. A cluster within the genome encodes for an arginine deiminiase metabolic pathway that is said to have a role in it's survival with the resistance from acidic type conditions. The arginine deiminase produces ammonia and that is what protects the cells from high acidic environments until the levels rose to level out.
Include S Ribosomal sequence that you obtained from PCR and sequencing here.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
To maintain the cell's shape, a thick peptidoglycan makes up the inner membrane. This organism is motile, using a flagella for swimming and swarming. In a single cell it uses a swimming motion with a shorter flagellated rods and when the organism uses a swarming function, the flagellum has been seen to be 3 to 4 times longer. This is a facultative anaerobe that can use oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor, and uses methods of anaerobic respiration for energy as well. In aerobic respiration, the organism reduces equivalents produced from glycolysis and the Kreb's cycle, reoxidizing them by the electron transport chain. In anaerobic respiration, the organism uses fermentation to make energy.
Pathology
B. cereus produces beta-lactamase, which was one of the first reported enzymes to destroy penicillin. Not all strains produce toxins, in fact some are used as an antifungal compound and have been useful for farming, suppressing fungi in crop diseases. This organism also contributes to the normal flora of our intestines, and gut microflora in invertebrates. Plants also benefit from the organism since it inhibits some plant diseases caused by protest pathogens by naturally producing two antibiotics, zwittermicin A and Kanosamine.
SInce 1955, B. cereus has been recognized as a cause of food poisoning in humans, but has never really become noticeable in food poisoning cases overall. It is stated that in 2003 only two food borne diseases were reported to the CDC positive for B. cereus. As a food borne illness some of the symptoms are caused, consist of abdominal cramps, diarrhea and has an incubation time of 8-16 hours, that is considered the long incubation forming versus the short incubation forming which has an incubation period of 8 hours with symptoms of abdominal cramps, nausea and vomiting. An illness in both short and long incubation is said to last about 24 hours.
B. cereus produces one emetic toxin and three different enterotoxins. The third enterotoxin (EntK) which is a single component protein is stated as the one that's involved in food poisoning. Holes are made in the membranes of the affected cells by all three of the cytotoxic enterotoxins. One of the three enterotoxins, non-hemolytic enterotoxin (Nhe) is the one responsible for causing diarrhea in food poisoning cases.
A few of the virulence factors include: HBL that can result in blindness and detachment of the retina, gangrene, cellulitis, and septic meningitis and endocarditis.
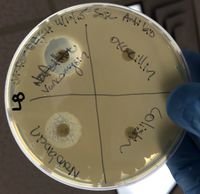
From a blood culture study in 1988, by Weber et al. showed the following about susceptibility and resistance during microdilution:
All strains showed susceptible to imipenem, vancomycin, chloramphenicol, gentamicin and ciprofloxacin (shown to be highly effective in B. cereus wound infections) Many strains were susceptible to erythromycin and tetracycline, most strains were resistant to clindamycin, cefazolin, and cefotaxime and all B. cereus isolates were also shown to be resistant to penicillin, oxacillin and cephalosporins, but not to mezlocillin.
References
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2863360/
https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Bacillus_cereus
http://textbookofbacteriology.net/B.cereus.html
http://www.mn.uio.no/farmasi/english/research/groups/lamda/research-projects/bacillus.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2843090
http://textbookofbacteriology.net/Bacillus_3.html
Author
Page authored by Jordan Arredondo, student of Prof. Kristine Hollingsworth at Austin Community College.