Vibrio parahaemolyticus: Difference between revisions
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
==Application to Biotechnology== | ==Application to Biotechnology== | ||
<b>Compound Production.</b> No useful compounds or enzymes | <b>Compound Production.</b> No useful compounds or enzymes have been found to be produced by ''V. parahaemolyticus'', according to the latest research. | ||
==Current Research== | ==Current Research== | ||
Revision as of 10:27, 3 May 2007
A Microbial Biorealm page on the genus Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Classification
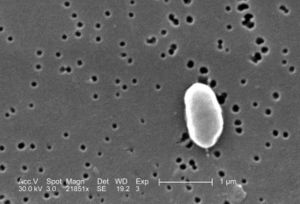
Higher order taxa
Bacteria (domain); Proteobacteria (phylum); Gammaproteobacteria (class); Vibrionales (order); Vibrionaceae (family); Vibrio (genus); Vibrio parahaemolyticus (species)
Species
|
NCBI: Taxonomy |
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Description and significance
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a gram negative bacterium that is typically found in warm estuarine seawaters due to its halophilic (salt-requiring) characteristics. It is the number one leading cause of sea-food associated bacterial gastroenteritis in the United States.
V. parahaemolyticus causes diarrhea upon ingestion. While the overwhelming majority of people acquire the infection by eating raw or undercooked seafood (particularly shellfish and oysters), an open wound exposed to warm seawater can facilitate V. parahaemolyticus infection.
Isolation of V. parahaemolyticus is possible from cultures of stool, wound, or blood. Isolation from stool preferably involves a medium that contains thiosulfate, citrate, bile salts, and sucrose (TCBS agar).
Genome structure
Shotgun sequencing of Vibrio parahaemolyticus AQ3810 is unfinished. To this date, 2 plasmids (pO3K6 and pSA19) and 2 chromosomes (chromosome I and chromosome II) are completely sequenced. The importance of plasmids to the organism's lifestyle is unknown at this point.
Vibrio parahaemolyticus AQ3810 (unfinished)
DNA structure: other
Length: 5,771,228 nt
Replicon Type: chromosome
Created: 2007/01/11
Vibrio parahaemolyticus plasmid pO3K6, complete sequence
DNA structure: circular
Length: 8,784 nt
Replicon Type: plasmid
Replicon Name: pO3K6
Created: 2000/06/29
Vibrio parahaemolyticus plasmid pSA19, complete sequence
DNA structure: circular
Length: 4,839 nt
Replicon Type: plasmid
Replicon Name: pSA19
Created: 1996/05/23
Vibrio parahaemolyticus RIMD 2210633 chromosome II, complete sequence
DNA structure: circular
Length: 1,877,212 nt
Replicon Type: chromosome
Replicon Name: II
Created: 2003/03/10
Vibrio parahaemolyticus RIMD 2210633 chromosome I, complete sequence
DNA structure: circular
Length: 3,288,558 nt
Replicon Type: chromosome
Replicon Name: I
Created: 2003/03/10
Cell structure and metabolism
Cell Structure. V. parahaemolyticus is a gram negative bacterium, meaning that it has an outer membrane, inner membrane, and a thin cell wall made out of peptidoglycan that is located in the periplasm. The gram negative cell wall may contain lipopolysaccharides, which is an important feature of pathogens and is composed of O-antigen repeating subunits, core polysaccharide, and lipid A anchor.
Ecology
Cause and Symptoms. V. parahaemolyticus is the leading cause of seafood-associated gastroenteritis in the United States. Human ingestion of V. parahaemolyticus causes various symptoms, including diarrhea, abdominal cramping, myalgias, self-reported fever, headache, vomiting, diarrhea with mucus, and bloody diarrhea (McLaughlin et al., 2005) In addition to self-limited gastroenteritis, V. parahaemolyticus infections also occur through wound exposure to organism, primary septicemia, and other infection sites (Daniels et al., 2000).
Hosts. V. parahaemolyticusis most commonly found in oysters and shellfish, including human-controlled oyster farms. Doubling time of V. parahaemolyticus at ideal conditions is one of the shortest times known for bacteria (8 to 9 minutes). The fast replication rate implies that contaminated oysters with a small colony of V. parahaemolyticus will only need a few hours to grow to an infectious dose (Daniels et al., 2000).
Virulence factors. Thermostable direct hemolysin (encoded by tdh genes) and thermostable direct hemolysin-related hemolysin (encoded by trh genes). Encoding of thermostable direct hemolysin virulence factors can cause beta-hemolysis of human erythrocytes, also known as the Kanagawa phenomenon. A strong link between possession of the tdh gene and incidents of gastroenteritis has been established in Japanese studies. Therefore, detection of tdh and trh genes is often used to determine the pathogenicity of V. parahaemolyticus strains (Martinez-Urtaza et al., 2004).
Application to Biotechnology
Compound Production. No useful compounds or enzymes have been found to be produced by V. parahaemolyticus, according to the latest research.
Current Research
McLaughlin et al (2005).
Martinez-Urtaza et al (2004).
Daniels et al (2000).
References
CDC Public Health Image Library
Edited by Hau-Chen Lee, student of Rachel Larsen and Kit Pogliano
