Akkermansia muciniphila: Difference between revisions
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Description and Significance== | ==Description and Significance== | ||
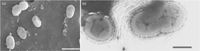
[[File:microbewikiakkerman.jpg|200px|thumb|left|Image of Figure 1. ''Akkermansia muciniphila'']] | [[File:microbewikiakkerman.jpg|200px|thumb|left|Image of Figure 1. ''Akkermansia muciniphila'' [7]]] | ||
''Akkermansia muciniphila'' is an anaerobic, Gram-negative, non-motile, non-spore-forming, oval-shaped bacterium, as seen in Figure 1 [7]. It is present in the human intestinal tract in high quantities, ranging from 39% to 84% of the total bacterial population. ''A.muciniphila'' is associated with the protective mucus lining of the intestines. Its presence in the mucus layer of the intestinal tract is particularly important because ''A.muciniphila'' is able to degrade host mucin into short chain fatty acids, or other products, to regulate the biological functions of the host [2]. The high content of ''Akkermansia muciniphila'' is thought to play a major role in the health of the intestinal mucus, as well as regulate host immune responses and lipid metabolism [5]. Several studies have observed that a decrease of Akkermansia muciniphila in the mucus is correlated with higher rates of obesity, increased inflammation, and an increase in Type 2 diabetes symptoms [1,3,11]. | ''Akkermansia muciniphila'' is an anaerobic, Gram-negative, non-motile, non-spore-forming, oval-shaped bacterium, as seen in Figure 1 [7]. It is present in the human intestinal tract in high quantities, ranging from 39% to 84% of the total bacterial population. ''A.muciniphila'' is associated with the protective mucus lining of the intestines. Its presence in the mucus layer of the intestinal tract is particularly important because ''A.muciniphila'' is able to degrade host mucin into short chain fatty acids, or other products, to regulate the biological functions of the host [2]. The high content of ''Akkermansia muciniphila'' is thought to play a major role in the health of the intestinal mucus, as well as regulate host immune responses and lipid metabolism [5]. Several studies have observed that a decrease of Akkermansia muciniphila in the mucus is correlated with higher rates of obesity, increased inflammation, and an increase in Type 2 diabetes symptoms [1,3,11]. | ||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 27: | ||
==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ||
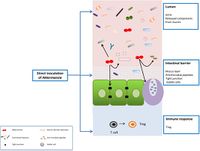
''Akkermansia muciniphila'' is able to use mucin as its sole source of carbon, nitrogen, and energy. It is an obligate chemo-organotroph, as evidenced by a study that found no growth on a basal medium supplemented with vitamins and purged with H2/CO2. After previous research hypothesized that ''A. muciniphila'' survived solely on the mucin in the host intestine, it was found that only a mucin medium was needed to culture ''A. muciniphila''. ''Akkermansia muciniphila'' was found to produce acetate, propionate, and ethanol from mucin fermentation [7]. [[File:akkermansia.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Image of Figure 2. ''Akkermansia muciniphila'' Function]] | ''Akkermansia muciniphila'' is able to use mucin as its sole source of carbon, nitrogen, and energy. It is an obligate chemo-organotroph, as evidenced by a study that found no growth on a basal medium supplemented with vitamins and purged with H2/CO2. After previous research hypothesized that ''A. muciniphila'' survived solely on the mucin in the host intestine, it was found that only a mucin medium was needed to culture ''A. muciniphila''. ''Akkermansia muciniphila'' was found to produce acetate, propionate, and ethanol from mucin fermentation [7]. [[File:akkermansia.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Image of Figure 2. ''Akkermansia muciniphila'' Function [6]]] | ||
==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ||
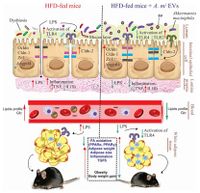
[[File:obesity.jpg|200px|thumb|left|Image of Figure 3.''Akkermansia muciniphila'' and obesity]] | [[File:obesity.jpg|200px|thumb|left|Image of Figure 3.''Akkermansia muciniphila'' and obesity [1]]] | ||
''Akkermansia muciniphila'' colonizes the mucosa layer of the host's gut, where it uses mucin as its sole source of carbon and nitrogen [6]. Though many mucin degrading microbes in the intestinal layer of a host can be pathogenic, ''A. muciniphila'' has mostly positive associations with its host. Since ''A. muciniphila'' remains in the outer mucosal layer and does not penetrate through to the inner layer, colonization is beneficial because the bacteria promotes the natural turnover of the outer mucin layer [10]. | ''Akkermansia muciniphila'' colonizes the mucosa layer of the host's gut, where it uses mucin as its sole source of carbon and nitrogen [6]. Though many mucin degrading microbes in the intestinal layer of a host can be pathogenic, ''A. muciniphila'' has mostly positive associations with its host. Since ''A. muciniphila'' remains in the outer mucosal layer and does not penetrate through to the inner layer, colonization is beneficial because the bacteria promotes the natural turnover of the outer mucin layer [10]. | ||
Latest revision as of 23:16, 29 April 2020
Classification
Domain: Bacteria
Phylum: Verrucomicrobia
Class: Verrucomicrobiae
Order: Verrucomicrobiales
Family: Akkermansiaceae
Species
Akkermansia muciniphila
Description and Significance
Akkermansia muciniphila is an anaerobic, Gram-negative, non-motile, non-spore-forming, oval-shaped bacterium, as seen in Figure 1 [7]. It is present in the human intestinal tract in high quantities, ranging from 39% to 84% of the total bacterial population. A.muciniphila is associated with the protective mucus lining of the intestines. Its presence in the mucus layer of the intestinal tract is particularly important because A.muciniphila is able to degrade host mucin into short chain fatty acids, or other products, to regulate the biological functions of the host [2]. The high content of Akkermansia muciniphila is thought to play a major role in the health of the intestinal mucus, as well as regulate host immune responses and lipid metabolism [5]. Several studies have observed that a decrease of Akkermansia muciniphila in the mucus is correlated with higher rates of obesity, increased inflammation, and an increase in Type 2 diabetes symptoms [1,3,11].
Genome Structure
The complete genome of Akkermansia muciniphila has one circular chromosome of 2,664,102 bp with a G+C content of 55.8%.Akkermansia muciniphila has a total of 2,176 protein coding sequences and an overall coding capacity of 88.8% [7]. Once sequenced, the genome was found to contain many candidate mucinase-encoding genes, but did not seem to have any genes for encoding canonical mucus-binding domains [4,8]. Akkermansia muciniphila's genome did contain numerous phage-associated sequences, which indicates that viruses may have played a role in the evolution of the species.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Akkermansia muciniphila is able to use mucin as its sole source of carbon, nitrogen, and energy. It is an obligate chemo-organotroph, as evidenced by a study that found no growth on a basal medium supplemented with vitamins and purged with H2/CO2. After previous research hypothesized that A. muciniphila survived solely on the mucin in the host intestine, it was found that only a mucin medium was needed to culture A. muciniphila. Akkermansia muciniphila was found to produce acetate, propionate, and ethanol from mucin fermentation [7].
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Akkermansia muciniphila colonizes the mucosa layer of the host's gut, where it uses mucin as its sole source of carbon and nitrogen [6]. Though many mucin degrading microbes in the intestinal layer of a host can be pathogenic, A. muciniphila has mostly positive associations with its host. Since A. muciniphila remains in the outer mucosal layer and does not penetrate through to the inner layer, colonization is beneficial because the bacteria promotes the natural turnover of the outer mucin layer [10].
Several studies have found that Akkermansia muciniphila is linked to metabolic homeostasis and its presence in the intestine can help alleviate fat gain and type 2 diabetes as seen in experiments on mice and testing of human feces samples for A. muciniphila. Since A. muciniphila is located close to the animal host epithelial cells, it can stimulate significant regulatory responses. One study found that after exposure to A. muciniphila, the mice epithelial cell line activated TLR-2 expression and tight junction proteins, while reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines in the colon, as seen in Figure 3 [1]. This led to an increase in intestinal barrier integrity, and a decrease in inflammation which led to a decrease in obesity and type 2 diabetes symptoms.
Akkermansia muciniphila can also positively impact host response to cancer immunotherapy. A study found that consumption of antibiotics was associated with poorer response to immunotherapeutic PD-1 blockade. Fecal samples of cancer patients were tested to determine the levels of A. muciniphila present after antibiotic consumption and found that it was much lower in patients that had recently taken antibiotics, and that those patients also had a poorer response to the immunotherapy. To determine that lower levels of Akkermansia muciniphila did have a direct impact on response rate, oral supplements of the bacteria were given to antibiotic-treated mice and found that it restored their response to the immunotherapy. Based on this research, it is suggested that maintaining a healthy gut flora, including mainly Akkermansia muciniphila is important to increase the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapy [9].
References
Author
Page authored by Emma Schuster, student of Prof. Jay Lennon at IndianaUniversity.