Micrococcus luteus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (28 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Uncurated}} | {{Uncurated}} | ||
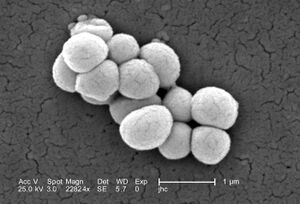
[[Image: | [[Image:M.luteus.jpeg|thumb|300px|right|A scanning electron microscope image of ''Micrococcus luteus''. Image credit: Janice Haney Carr, CDC.[https://phil.cdc.gov/Details.aspx?pid=9759]]] | ||
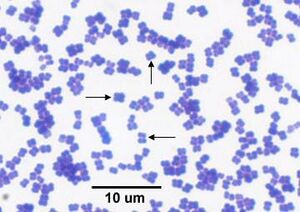
[[Image:M.luteus2.jpeg|thumb|300px|right|A light microscope image showing the tetrad formation of ''Micrococcus luteus''. Image Credit: Dr. E.I, Medical Labs. [https://www.medical-labs.net/micrococcus-luteus-930/]]] | |||
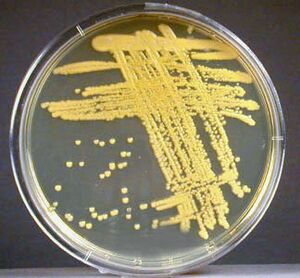
[[Image:M.luteus3.jpeg|thumb|300px|right|An image of ''Micrococcus luteus'' streaked onto CNA agar, displaying the distinct yellow color it is known for. Image Credit: Gary E. Kaiser, Ph.D. Professor of Microbiology at The Community College of Baltimore County. [https://cwoer.ccbcmd.edu/science/microbiology/Lab%20Manual/lab3/cnaml.html]]] | |||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 11: | ||
{| | {| | ||
| height="10" bgcolor="#FFDF95" | | | height="10" bgcolor="#FFDF95" | | ||
'''NCBI: [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id= | '''NCBI: [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=1270&lvl=3&lin=f&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock]''' | ||
|} | |} | ||
'' | ''Micrococcus luteus'' | ||
==Description and Significance== | ==Description and Significance== | ||
''Micrococcus luteus'' is a oligotrophic bacteria that can be found on the skin of humans and other mammals, some foods, soil, and water. This aerobic microorganism can withstand severe and unfavorable conditions, but is not spore-forming. Instead it uses resuscitation promoting factor (Rpf) to revive itself from dormancy. [https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/miclu/miclu.home.html#:~:text=Micrococcus%20luteus%20possesses%20unusual%20abilities,in%20its%20importance%20in%20biotechnology] | |||
''M. luteus'' is considered part of the normal microbiota and plays a role in breaking down the compounds in sweat which produces body-odor. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7176942/] | |||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
The “Fleming strain,” NCTC2665, is a single circular chromosome. It is one of the smallest actinobacterial genomes ever sequenced. It has 2,501,097 base pairs and G+C content of 73%. It Is thought that it can encode for 2,403 proteins. Despite its small size it contains 73 insertion sequence (IS) elements. However, it only encodes for four sigma factors and 14 response regulators. It is predicted that this is a result of keeping a strict niche of mammalian skin. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19948807/#:~:text=Micrococcus%20luteus%20(NCTC2665%2C%20%22Fleming,predicted%20to%20encode%202%2C403%20proteins] | |||
''M. luteus'' is differentiated into three clades. These clades are distinguished by differences in core and pan genomes. It is suspected that homologous recombination had an influence in the evolution of ''M. luteus.'' Gain and lose of function are evident in its path through evolution. [https://bmcgenomics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12864-021-07432-5] | |||
==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ||
''M. luteus'' are gram positive, non-motile, spherical cells that form tetrads and clusters. It utilizes sugars for energy and produces glutamic acid, thiosulphate, and polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB). It also supports the biosynthesis of alkene and carotenoids. [https://blog.microbiologics.com/environmental-isolate-case-files-micrococcus-luteus/#:~:text=Appearance%3A,in%20tetrads%20or%20irregular%20clusters] | |||
==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ||
''M. luteus'' is present on human skin and it forms a commensal relationship here. Under normal conditions ''M. luteus'' is non-pathogenic and has low virulence factors. However, it is also considered an opportunistic pathogen. This means that it can cause infections in immunocompromised patients or those with poor hygiene. ''M. luteus'' has been linked with several illnesses including meningitis, septic arthritis, endocarditis, chronic cutaneous infections in HIV positive patients, and catheter infections. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7176942/] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Carr JH. 2007. Public Health Image Library (PHIL). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://phil.cdc.gov/Details.aspx?pid=9759 | |||
Dr. E.I. 2013. Micrococcus luteus. Medical Laboratories. https://www.medical-labs.net/micrococcus-luteus-930/ | |||
Kaiser GE. 2018. Micrococcus luteus Gowing on Columbia CNA Agar. Biol 230 Lab Manual: Micrococcus Luteus on Columbia CNA Agar. https://cwoer.ccbcmd.edu/science/microbiology/Lab%20Manual/lab3/cnaml.html | |||
Khayyira AS, Rosdina AE, Irianti MI, Malik A. 2020. Simultaneous profiling and cultivation of the skin microbiome of healthy young adult skin for the development of therapeutic agents. Heliyon. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7176942/ | |||
Kundrat L. 2021. Environmental isolate case files: Micrococcus luteus. Microbiologics Blog. https://blog.microbiologics.com/environmental-isolate-case-files-micrococcus-luteus#:~:text=Appearance%3A,in%20tetrads%20or%20irregular%20clusters | |||
Li Y, Sun Z-Z, Rong J-C, Xie B-B. 2021. Comparative genomics reveals broad genetic diversity, extensive recombination and nascent ecological adaptation in Micrococcus luteus - BMC Genomics. BioMed Central. BioMed Central. Micrococcus luteus Fleming strain 2665. Home - micrococcus luteus fleming strain 2665. https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/miclu/miclu.home.html#:~:text=Micrococcus%20luteus%20possesses%20unusual%20abilities,in%20its%20importance%20in%20biotechnology | |||
Micrococcus luteus Fleming strain 2665. Home - micrococcus luteus fleming strain 2665. https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/miclu/miclu.home.html#:~:text=Micrococcus%20luteus%20possesses%20unusual%20abilities,in%20its%20importance%20in%20biotechnology | |||
Schoch CL, et al. Taxonomy browser (micrococcus luteus). National Center for Biotechnology Information. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?id=1270 | |||
Young M;Artsatbanov V;Beller HR;Chandra G;Chater KF;Dover LG;Goh EB;Kahan T;Kaprelyants AS;Kyrpides N;Lapidus A;Lowry SR;Lykidis A;Mahillon J;Markowitz V;Mavromatis K;Mukamolova GV;Oren A;Rokem JS;Smith MC;Young DI;Greenblatt CL;. 2009. Genome sequence of the Fleming strain of Micrococcus luteus, a simple free-living actinobacterium. Journal of bacteriology. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19948807/#:~:text=Micrococcus%20luteus%20(NCTC2665%2C%20%22Fleming,predicted%20to%20encode%202%2C403%20proteins. | |||
==Author== | ==Author== | ||
Page authored by | Page authored by Brittney Moore, student of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington. | ||
<!-- Do not remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington]] | <!-- Do not remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:40, 4 December 2022
Classification
Bacteria; Terrabacteria; Actinobacteria; Actinomycetia; Micrococcales; Micrococcaceae; Micrococcus
Species
|
NCBI: [4] |
Micrococcus luteus
Description and Significance
Micrococcus luteus is a oligotrophic bacteria that can be found on the skin of humans and other mammals, some foods, soil, and water. This aerobic microorganism can withstand severe and unfavorable conditions, but is not spore-forming. Instead it uses resuscitation promoting factor (Rpf) to revive itself from dormancy. [5]
M. luteus is considered part of the normal microbiota and plays a role in breaking down the compounds in sweat which produces body-odor. [6]
Genome Structure
The “Fleming strain,” NCTC2665, is a single circular chromosome. It is one of the smallest actinobacterial genomes ever sequenced. It has 2,501,097 base pairs and G+C content of 73%. It Is thought that it can encode for 2,403 proteins. Despite its small size it contains 73 insertion sequence (IS) elements. However, it only encodes for four sigma factors and 14 response regulators. It is predicted that this is a result of keeping a strict niche of mammalian skin. [7]
M. luteus is differentiated into three clades. These clades are distinguished by differences in core and pan genomes. It is suspected that homologous recombination had an influence in the evolution of M. luteus. Gain and lose of function are evident in its path through evolution. [8]
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
M. luteus are gram positive, non-motile, spherical cells that form tetrads and clusters. It utilizes sugars for energy and produces glutamic acid, thiosulphate, and polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB). It also supports the biosynthesis of alkene and carotenoids. [9]
Ecology and Pathogenesis
M. luteus is present on human skin and it forms a commensal relationship here. Under normal conditions M. luteus is non-pathogenic and has low virulence factors. However, it is also considered an opportunistic pathogen. This means that it can cause infections in immunocompromised patients or those with poor hygiene. M. luteus has been linked with several illnesses including meningitis, septic arthritis, endocarditis, chronic cutaneous infections in HIV positive patients, and catheter infections. [10]
References
Carr JH. 2007. Public Health Image Library (PHIL). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://phil.cdc.gov/Details.aspx?pid=9759
Dr. E.I. 2013. Micrococcus luteus. Medical Laboratories. https://www.medical-labs.net/micrococcus-luteus-930/
Kaiser GE. 2018. Micrococcus luteus Gowing on Columbia CNA Agar. Biol 230 Lab Manual: Micrococcus Luteus on Columbia CNA Agar. https://cwoer.ccbcmd.edu/science/microbiology/Lab%20Manual/lab3/cnaml.html
Khayyira AS, Rosdina AE, Irianti MI, Malik A. 2020. Simultaneous profiling and cultivation of the skin microbiome of healthy young adult skin for the development of therapeutic agents. Heliyon. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7176942/
Kundrat L. 2021. Environmental isolate case files: Micrococcus luteus. Microbiologics Blog. https://blog.microbiologics.com/environmental-isolate-case-files-micrococcus-luteus#:~:text=Appearance%3A,in%20tetrads%20or%20irregular%20clusters
Li Y, Sun Z-Z, Rong J-C, Xie B-B. 2021. Comparative genomics reveals broad genetic diversity, extensive recombination and nascent ecological adaptation in Micrococcus luteus - BMC Genomics. BioMed Central. BioMed Central. Micrococcus luteus Fleming strain 2665. Home - micrococcus luteus fleming strain 2665. https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/miclu/miclu.home.html#:~:text=Micrococcus%20luteus%20possesses%20unusual%20abilities,in%20its%20importance%20in%20biotechnology
Micrococcus luteus Fleming strain 2665. Home - micrococcus luteus fleming strain 2665. https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/miclu/miclu.home.html#:~:text=Micrococcus%20luteus%20possesses%20unusual%20abilities,in%20its%20importance%20in%20biotechnology
Schoch CL, et al. Taxonomy browser (micrococcus luteus). National Center for Biotechnology Information. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?id=1270
Young M;Artsatbanov V;Beller HR;Chandra G;Chater KF;Dover LG;Goh EB;Kahan T;Kaprelyants AS;Kyrpides N;Lapidus A;Lowry SR;Lykidis A;Mahillon J;Markowitz V;Mavromatis K;Mukamolova GV;Oren A;Rokem JS;Smith MC;Young DI;Greenblatt CL;. 2009. Genome sequence of the Fleming strain of Micrococcus luteus, a simple free-living actinobacterium. Journal of bacteriology. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19948807/#:~:text=Micrococcus%20luteus%20(NCTC2665%2C%20%22Fleming,predicted%20to%20encode%202%2C403%20proteins.
Author
Page authored by Brittney Moore, student of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington.
