Neptunomonas: Difference between revisions
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
Neptunomonas concharum was the species of choice when examining a the genome of this genus as a result of the extensive and complete genome sequencing conducted. The complete genome consisted of 3,561,992 bp, of which G-C base pairs made up 46%. 3273 protein coding sequences were found, with 69 tRNA genes, 15 complete rRNA genes (5 each for 5S, 16S, and 23S), and 4 ncRNAs. | Neptunomonas concharum was the species of choice when examining a the genome of this genus as a result of the extensive and complete genome sequencing conducted. The complete genome consisted of 3,561,992 bp, of which G-C base pairs made up 46%. 3273 protein coding sequences were found, with 69 tRNA genes, 15 complete rRNA genes (5 each for 5S, 16S, and 23S), and 4 ncRNAs. | ||
Bacteria containing prophage are more likely to show antibiotic resistance, greater environmental adaptability and improve adhesion. Concharum contained three incomplete prophage sequences. Additionally CRISPR/Cas systems play an important role in bacterial defence systems, fighting against viruses and other bacterial plasmid invasion, one credible CRISPR sequence containing 22 spacers was acknowledges in the genomic DNA. These sequences recognise some of the uniquely adapted sequences allowing concharum to function in toxic | |||
==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ||
Revision as of 21:43, 10 November 2023
Classification
Higher order taxa
Bacteria; Pseudomonadota; Gammaproteobacteria; Oceanospirillales; Oceanospirillaceae
NCBI: [1]
Genus
Neptunomonas
Description and Significance
Describe the appearance, habitat, etc. of the organism, and why you think it is important.
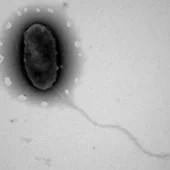
Appearance: The genus includes rod shaped (Bacillus) or slightly curved (vibrio) cells, with approximate sizes of 0.7–0.9 × 2.0–3.0 µm. Spherical (coccoid) body plans appear in older colonies, often associated with a loss of viability. They are capable of producing a capsid and are motile via a single flagellum. [1.]
Habitat: Often associated with historically polluted marine coastal sediment, such as the Puget sound (Washington, USA), the site of a wood treatment facility and the Mediterranean Sea (Milazzo Harbor, Italy), which has been impacted by municipal wastes.
In addition to these polluted sites, Neptunomonas is closely related (acting as endosymbionts) to the bone-eating polychaetes in the genus Osedax, which are inhabitants of whale carcasses within the deep sea. These endosymbionts are located within highly branched root tissues which burrow into the bones of these large carcasses, digesting them, releasing the organic carbon which can be used for nutrition. The specifics of this endosymbiosis is not fully known. [2.]
Genome Structure
Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence?
Neptunomonas concharum was the species of choice when examining a the genome of this genus as a result of the extensive and complete genome sequencing conducted. The complete genome consisted of 3,561,992 bp, of which G-C base pairs made up 46%. 3273 protein coding sequences were found, with 69 tRNA genes, 15 complete rRNA genes (5 each for 5S, 16S, and 23S), and 4 ncRNAs.
Bacteria containing prophage are more likely to show antibiotic resistance, greater environmental adaptability and improve adhesion. Concharum contained three incomplete prophage sequences. Additionally CRISPR/Cas systems play an important role in bacterial defence systems, fighting against viruses and other bacterial plasmid invasion, one credible CRISPR sequence containing 22 spacers was acknowledges in the genomic DNA. These sequences recognise some of the uniquely adapted sequences allowing concharum to function in toxic
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Metabolism: This species can receive and use resources from a wide range of carbon sources for metabolic engineering. They are aerobically respiring organisms, with selectivity anaerobic capabilities. Oxidising strains are commonly associated with polluted coastal marine sediments. Additionally, this organism is closely related to the endosymbionts of the bone-eating polychaetes in the genus Osedax, occurring in root structures produced by Osedax which penetrate the whale bone. Location and enzyme activity suggest Neptunomonas aid in the digestion of bones for the polychaete, however it is unknown yet if the resulting molecules are used in metabolic processes for the micro-organism.
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Habitat; symbiosis; biogeochemical significance; contributions to environment.
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
References
1. Hedlund B.P. "Neptunomonas". Neptunomonas. 2015. pp. 1–6.
Author
Page authored by Nathan Hicks, student of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington.