Acidilobus saccharovorans: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Uncurated}} | {{Uncurated}} | ||
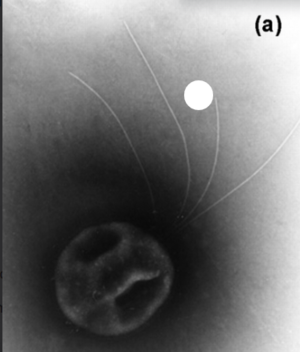
[[Image:A. saccharovorans.png|thumb|300px|right|Electron micrographs of <i>A.saccharovorans</i>. Image credit: | [[Image:A. saccharovorans.png|thumb|300px|right|Electron micrographs of <i>A.saccharovorans</i>. Image credit: Microbiology Society.]] | ||
Revision as of 20:43, 6 December 2023
Classification
Thermoproteota; Thermoprotei; Acidilobales; Acidilobaceae
Species
|
NCBI: [1] |
Acidilobus saccharovorans
Description and Significance
A. saccharovorans has a coccus shape with a bundle of flagella. This archaea also has a thick S-layer. A. saccharovorans was isolated from a terrestrial hot spring.
Genome Structure
A. saccharovorans consists of a circular genome with 1,496,453 base pairs. A. saccharovorans have no extrachromosomal elements and have one copy of the 16S-23S rRNA operon. There are 246 genes that are unique for A. saccharovorans.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Acidilobus saccharovorans is an anaerobic, organotrophic, thermoacidophilic archaeon. Glucose in A. saccharovorans is metabolized to pyruvate through the Embden-Meyerhof pathway or the Enter-Doudiroff pathway. A. saccharovorans may conserve energy by doing oxidative phosphorylation.
Ecology and Pathogenesis
A. saccharovorans are found on hot springs. They are believed to help with the complex oxidation of organic material.
References
Author
Page authored by Leah Rotte, student of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington.