Horseshoe Crab: the living fossil: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
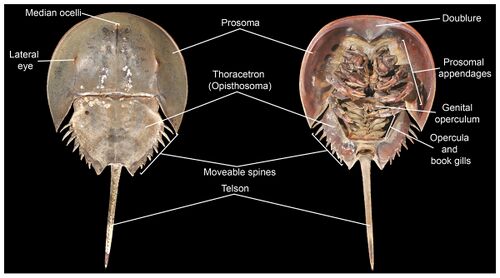
[[Image:Https---dfzljdn9uc3pi.cloudfront.net-2020-10431-1-fig-3-2x.jpg|thumb|500px|left|Figure 1. Front and back views of <i>Limulus polyphemus</i> showing general morphology <ref name=" abcd "></ref>]] | [[Image:Https---dfzljdn9uc3pi.cloudfront.net-2020-10431-1-fig-3-2x.jpg|thumb|500px|left|Figure 1. Front and back views of <i>Limulus polyphemus</i> showing general morphology <ref name=" abcd "></ref>]] | ||
==Phylogeny and Evolution== | ==Phylogeny and Evolution== | ||
Revision as of 04:59, 13 December 2024
Introduction
Witness to almost 500 million years of Earth's history, horseshoe crabs are the textbook definition of living fossils. Their alien-like primitive forms, featuring the iconic spine-like telson and horseshoe-shaped carapace, have remained virtually unchanged across their existence. While their resemblance to a horseshoe is difficult to challenge, “crab” is a misnomer for the creatures considering they are not even crustaceans. They are, in fact, more closely related to spiders and scorpions.
Present-day horseshoe crabs are all marine dwellers although forays into freshwater have been noted among long extinct groups. The mangrove horseshoe crab, at odds with the other three extant species, also inhabits the brackish waters found near mangrove forests.
Phylogeny and Evolution
Modern-day horseshoe crabs are chelicerate arthropods of the Limulidae family. Despite their name, they are not crustaceans at all and are, in fact, more closely related to arachnids. Of 88 formally described species, only 4 remain today and are the only surviving members of the order Xiphosura. The extant species include the Atlantic horseshoe crab Limulus polyphemus, and three Asiatic species: the Indo-Pacific horseshoe crab Tachypleus gigas, the tri-spine horseshoe crab Tachypleus tridentatus, and the mangrove horseshoe crab Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda.
The first Xiphosurans emerged some 470 million years ago in the Lower Ordovician period of the Paleozoic era, making horseshoe crabs one of the most ancestral species of animals still alive today. The Limulids, the family of modern horseshoe crabs, first appeared around 250 years ago in the Triassic period. Two rounds of evolutionary stasis have been identified in the Xiphosurans: the conservation of prosomal and opisthosomal growth rates near their origin in the Lower Ordivician and the conservation of shape in the Jurassic period owing to the emergence of the Limulids in the Triassic. Notwithstanding physiological changes, present-day crabs are larger in size than their ancestral counterparts and have their abdominal segments fused together.
Morphology
All horseshoe crabs share the same body plan: the cephalothorax or prosoma (head and chest fused together), the opisthosoma (the abdomen with the inclusion of the heart and respiratory organs, a distinctive feature of the chelicerates) and, the iconic feature of the horseshoe crab, the telson (the long tail-like spine jutting out from the abdomen). The prosoma is shrouded in a protective carapace bearing an uncanny resemblance to a horseshoe, giving the horseshoe crab its name. Unlike any other extant chelicerate, horseshoe crabs possess, among its ten eyes, two compound eyes that sit atop its carapace; they also have the largest rod and cone cells of any known animal.
Section titles are optional.
Include some current research, with at least one image.
Call out each figure by number (Fig. 1).
Sample citations: [2]
[3]
A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes.
For multiple use of the same inline citation or footnote, you can use the named references feature, choosing a name to identify the inline citation, and typing [5]
Second citation of Ref 1: [2]
Here we cite April Murphy's paper on microbiomes of the Kokosing river. [6]
Microbiome
Include some current research, with a second image.
Here we cite Murphy's microbiome research again.[6]
Conclusion
You may have a short concluding section.
Overall, cite at least 5 references under References section.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Lamsdell JC. The phylogeny and systematics of Xiphosura. PeerJ. 2020 Dec 4;8:e10431.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Hodgkin, J. and Partridge, F.A. "Caenorhabditis elegans meets microsporidia: the nematode killers from Paris." 2008. PLoS Biology 6:2634-2637.
- ↑ Bartlett et al.: Oncolytic viruses as therapeutic cancer vaccines. Molecular Cancer 2013 12:103.
- ↑ Lee G, Low RI, Amsterdam EA, Demaria AN, Huber PW, Mason DT. Hemodynamic effects of morphine and nalbuphine in acute myocardial infarction. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 1981 May;29(5):576-81.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 text of the citation
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Murphy A, Barich D, Fennessy MS, Slonczewski JL. An Ohio State Scenic River Shows Elevated Antibiotic Resistance Genes, Including Acinetobacter Tetracycline and Macrolide Resistance, Downstream of Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent. Microbiology Spectrum. 2021 Sep 1;9(2):e00941-21.
Edited by [Author Name], student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 116, 2024, Kenyon College.
