Chroococcus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{ | {{Curated}} | ||
{{Biorealm Genus}} | |||
[[Image:chroococcussmall.jpg]] | [[Image:chroococcussmall.jpg|frame|right|''Chroococcus turgidus''. Image courtesy of [http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/featuredmicroscopist/vanegmond/galleryindex.html Wim van Edmond]. Copyright 2000-2005.]] | ||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 14: | ||
''Chroococcus dispersus, C. submarinus, C. submarinus kopara-BM, C. turgidus'' | ''Chroococcus dispersus, C. submarinus, C. submarinus kopara-BM, C. turgidus'' | ||
{| | |||
| height="10" bgcolor="#FFDF95" | | |||
'''NCBI: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=70190&lvl=3&lin=f&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock Taxonomy] Genome''' | |||
|} | |||
==Description and Significance== | ==Description and Significance== | ||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
''Chroococcus'', like other cyanobacteria, has signifanct ecological implications as a productive microbe. ''Chroococcus'' uses an extensive quantity of atmospheric carbon for photosynthetic processes, creating free oxygen in the atmosphere. In addition, ''Chroococcus'' is part of the first genus to use water to access electrons and hydrogen for photosynthesis, which also produces more free oxygen to be used by other organisms. | ''Chroococcus'', like other cyanobacteria, has signifanct ecological implications as a productive microbe. ''Chroococcus'' uses an extensive quantity of atmospheric carbon for photosynthetic processes, creating free oxygen in the atmosphere. In addition, ''Chroococcus'' is part of the first genus to use water to access electrons and hydrogen for photosynthesis, which also produces more free oxygen to be used by other organisms. | ||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
Relatively few studies have been performed on the background genetics of ''Chroococcus'' as of yet. Although there are currently no known genome sequencing projects, there is hope of one beginning soon because of ''Chroococcus's'' significant implications as an oxygen production source. | Relatively few studies have been performed on the background genetics of ''Chroococcus'' as of yet. Although there are currently no known genome sequencing projects, there is hope of one beginning soon because of ''Chroococcus's'' significant implications as an oxygen production source. | ||
==Cell Structure and Metabolism== | ==Cell Structure and Metabolism== | ||
[[Image:Chroococcus.JPG | [[Image:Chroococcus.JPG|frame|left|''Chroococcus sp.'' Image courtesy of Dr. Morgan Vis of [http://vis-pc.plantbio.ohiou.edu/algaeindex.htm Ohio University.]]] | ||
'' Chroococcus '' | ''Chroococcus''cells are ovoid or rod-shaped unicells with a diametere ranging between 0.4 to 40µm (Ditty). Formerly thought of and named as a blue-green strain of algae, cyanobacteria shares a close resemblance with green eukaryotic algae. In addition to physical similarities, cynaobacteria and algae also share similar habitats, often growing together. | ||
''Chroococcus''is an autotrophic organism able to survive almost without any freshwater or oxygen source (Carboni). ''Chroococcus''produces oxygen and adenosine triphosphate through phtosynthetic methods using sunlight as the catalyst. | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
''Chroococcus ''is known to traditionally inhabit freshwater areas, but has also been identified in water sources of higher salinity. ''Chroococcus ''has also been found in plankton inhabiting water reserves (Komárek). ''Chroococcus ''is often incorrectly identified, therefore outlining a true habitat pattern is difficult. | ''Chroococcus ''is known to traditionally inhabit freshwater areas, but has also been identified in water sources of higher salinity. ''Chroococcus ''has also been found in plankton inhabiting water reserves (Komárek). ''Chroococcus ''is often incorrectly identified, therefore outlining a true habitat pattern is difficult. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 53: | ||
[http://courses.biology.utah.edu/williams/3370/annurev.genet.37.110801.pdf Ditty, J.L., S.B. Williams, and S.S. Golden. "A Cyanobacterial Circadian Timing Mechanism.Annu. Rev. Genet. 2003. 37: 513-43.] | [http://courses.biology.utah.edu/williams/3370/annurev.genet.37.110801.pdf Ditty, J.L., S.B. Williams, and S.S. Golden. "A Cyanobacterial Circadian Timing Mechanism.Annu. Rev. Genet. 2003. 37: 513-43.] | ||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db= | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=16233836&dopt=Abstract Hong J, Ma H, Otaki M."Controlling algal growth in photo-dependent decolorant sludge by photocatalysis." <span title="Journal of bioscience and bioengineering.">J Biosci Bioeng.</span> 2005 Jun;99(6):592-7.] | ||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=11575503&query_hl=3&itool=pubmed_DocSum Kirkwood AE, Nalewajko C, Fulthorpe RR."The occurrence of cyanobacteria in pulp and paper waste-treatment systems." <span title="Canadian journal of microbiology.">Can J Microbiol.</span> 2001 Aug;47(8):761-6. ]<br /><br />[http://www.cyanodb.cz/Chroococcus/Chroococcus.html Komárek, Jiří and Tomáš Hauer.1992. CyanoDB: The online database of cyanobacterial genera. Database of cyanoprokaryotes: Databse of Genera.] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=11575503&query_hl=3&itool=pubmed_DocSum Kirkwood AE, Nalewajko C, Fulthorpe RR."The occurrence of cyanobacteria in pulp and paper waste-treatment systems." <span title="Canadian journal of microbiology.">Can J Microbiol.</span> 2001 Aug;47(8):761-6. ]<br /><br />[http://www.cyanodb.cz/Chroococcus/Chroococcus.html Komárek, Jiří and Tomáš Hauer.1992. CyanoDB: The online database of cyanobacterial genera. Database of cyanoprokaryotes: Databse of Genera.] | ||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=12744080&query_hl=3&itool=pubmed_DocSum Rezanka T, Dor I, Prell A, Dembitsky VM."Fatty acid composition of six freshwater wild cyanobacterial species." <span title="Folia microbiologica.">Folia Microbiol (Praha).</span> 2003;48(1):71-5.] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=12744080&query_hl=3&itool=pubmed_DocSum Rezanka T, Dor I, Prell A, Dembitsky VM."Fatty acid composition of six freshwater wild cyanobacterial species." <span title="Folia microbiologica.">Folia Microbiol (Praha).</span> 2003;48(1):71-5.] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:00, 26 July 2010
A Microbial Biorealm page on the genus Chroococcus
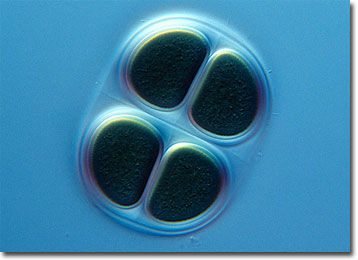
Classification
Higher order taxa:
Bacteria; Cyanobacteria; Chroococcales
Species:
Chroococcus dispersus, C. submarinus, C. submarinus kopara-BM, C. turgidus
|
NCBI: Taxonomy Genome |
Description and Significance
Chroococcus, a unicellular organism that is a genus of cyanobacteria, is blue-green in color and macroscopic colony mounded. Within the outside sheath, microscopic colonies are found with indistinct trichomes. Chroococcus are usually found in colonies of two, four, or eight cells with a transparent protective covering sheath containing photosynthetic pigments. Like all cyanobacteria, Chroococcus is a prokaryote and therefore lacks any of the membranous organelles of eukaryotes. Known for its underwater habitat, Chroococcus prefers the sludge of lake and river bottoms to call home.
Chroococcus, like other cyanobacteria, has signifanct ecological implications as a productive microbe. Chroococcus uses an extensive quantity of atmospheric carbon for photosynthetic processes, creating free oxygen in the atmosphere. In addition, Chroococcus is part of the first genus to use water to access electrons and hydrogen for photosynthesis, which also produces more free oxygen to be used by other organisms.
Genome Structure
Relatively few studies have been performed on the background genetics of Chroococcus as of yet. Although there are currently no known genome sequencing projects, there is hope of one beginning soon because of Chroococcus's significant implications as an oxygen production source.
Cell Structure and Metabolism
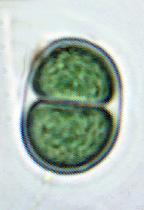
Chroococcuscells are ovoid or rod-shaped unicells with a diametere ranging between 0.4 to 40µm (Ditty). Formerly thought of and named as a blue-green strain of algae, cyanobacteria shares a close resemblance with green eukaryotic algae. In addition to physical similarities, cynaobacteria and algae also share similar habitats, often growing together.
Chroococcusis an autotrophic organism able to survive almost without any freshwater or oxygen source (Carboni). Chroococcusproduces oxygen and adenosine triphosphate through phtosynthetic methods using sunlight as the catalyst.
Ecology
Chroococcus is known to traditionally inhabit freshwater areas, but has also been identified in water sources of higher salinity. Chroococcus has also been found in plankton inhabiting water reserves (Komárek). Chroococcus is often incorrectly identified, therefore outlining a true habitat pattern is difficult.
References
Carboni, G. Microworlds. Nov 2004.
Davidson, M.W. Molecular Expressions: Featured Microscopist: Wim van Egmond. 01 Dec 2003.
Kirkwood AE, Nalewajko C, Fulthorpe RR."The occurrence of cyanobacteria in pulp and paper waste-treatment systems." Can J Microbiol. 2001 Aug;47(8):761-6.
Komárek, Jiří and Tomáš Hauer.1992. CyanoDB: The online database of cyanobacterial genera. Database of cyanoprokaryotes: Databse of Genera.
