Helicobacter: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{ | {{Curated}} | ||
{{Biorealm Genus}} | |||
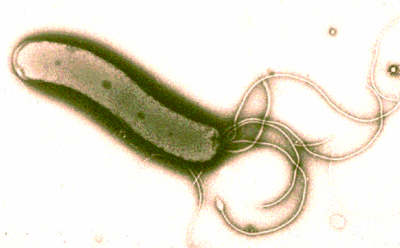
[[Image:h.pylori.gif|thumb|400px|right|''Helicobacter pylori''. From [http://www.shef.ac.uk/mbb/academic/staff/kelly.html Professor D. J. Kelly.]]] | [[Image:h.pylori.gif|thumb|400px|right|''Helicobacter pylori''. From [http://www.shef.ac.uk/mbb/academic/staff/kelly.html Professor D. J. Kelly.]]] | ||
| Line 18: | Line 13: | ||
''Candidatus H. bovis, Candidatus H.cebus, Candidatus H. suis, H. acinonychis, H. apodemus, H. aurati, H. bilis, H. bizzozeronii, H. canadensis, H. canis sp., H. cetorum, H. cholecystus, H. cinaedi, H. felis, H. fennelliae, H. ganmani, H. heilmannii sp., H. hepaticus sp., H. marmotae, H. mesocricetorum, H. muricola, H. muridarum, H. mustelae, H. pametensis, H. pullorum sp., H. pylori sp., H.rappini, H. rodentium, H. salomonis, H. suncus, H. trogontum, H. tursiopsae, H. typhlonius, H. winghamensis, H. sp.'' | ''Candidatus H. bovis, Candidatus H.cebus, Candidatus H. suis, H. acinonychis, H. apodemus, H. aurati, H. bilis, H. bizzozeronii, H. canadensis, H. canis sp., H. cetorum, H. cholecystus, H. cinaedi, H. felis, H. fennelliae, H. ganmani, H. heilmannii sp., H. hepaticus sp., H. marmotae, H. mesocricetorum, H. muricola, H. muridarum, H. mustelae, H. pametensis, H. pullorum sp., H. pylori sp., H.rappini, H. rodentium, H. salomonis, H. suncus, H. trogontum, H. tursiopsae, H. typhlonius, H. winghamensis, H. sp.'' | ||
{| | |||
| height="10" bgcolor="#FFDF95" | | |||
'''NCBI: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=209&lvl=3&lin=f&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock Taxonomy] Genome: '''[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/framik.cgi?db=Genome&gi=307 ''H. hepaticus''] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/framik.cgi?db=Genome&gi=128 ''H. pylori 26695''] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/framik.cgi?db=Genome&gi=139 ''H. pylori J99''] | |||
|} | |||
==Description and Significance== | ==Description and Significance== | ||
Latest revision as of 20:24, 6 August 2010
A Microbial Biorealm page on the genus Helicobacter
Classification
Higher order taxa:
Bacteria; Proteobacteria; delta/epsilon subdivisions; Epsilonproteobacteria; Campylobacterales; Helicobacteraceae
Species:
Candidatus H. bovis, Candidatus H.cebus, Candidatus H. suis, H. acinonychis, H. apodemus, H. aurati, H. bilis, H. bizzozeronii, H. canadensis, H. canis sp., H. cetorum, H. cholecystus, H. cinaedi, H. felis, H. fennelliae, H. ganmani, H. heilmannii sp., H. hepaticus sp., H. marmotae, H. mesocricetorum, H. muricola, H. muridarum, H. mustelae, H. pametensis, H. pullorum sp., H. pylori sp., H.rappini, H. rodentium, H. salomonis, H. suncus, H. trogontum, H. tursiopsae, H. typhlonius, H. winghamensis, H. sp.
|
NCBI: Taxonomy Genome: H. hepaticus H. pylori 26695 H. pylori J99 |
Description and Significance
Helicobacter is a Gram-negative, slow-growing organism. H. pylori has importance as a common human pathogen.
Genome Structure
Helicobacter pylori is composed of a single circular chromosome with 1,667,867 base pairs, containing about 1590 coding regions (TIGR, 2004).
Cell Structure and Metabolism
Helicobacter is a spiral shaped organism with flagella. It has a potent multisubunit urease enzyme that enables it to survive in acidic pH conditions and colonize the gastric environment (TIGR, 2004). H. pylori utilizes the enzyme urease to convert urea into bicarbonate and ammonia to combat the low acidity of the stomach. The mixing of the two extreme pH levels creates a neutralized protective cloud around the H. pylori, allowing it to survive in the stomach (Helicobacter Foundation, 2004).
Ecology
Helicobacter is able to live in the acidity of the stomach and duodenum, living on the mucus lining of the stomach, causing several health problems for the host (Helicobacter Foundation, 2004). Helicobacter can also be seen in animals such as cheetahs, dogs, cats, and ferrets (J. Solnick et al. 2004).
Pathology
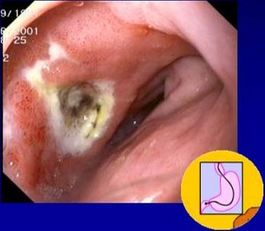
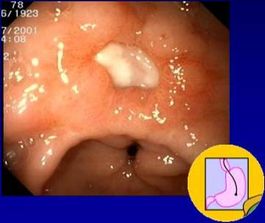
Until the discovery of Helicobacter in 1982, ulcers were thought to be caused by stress. Now it is known that ulcers, in addition to gastritis, are caused by a bacterial infection of H. pylori. Though relatively easy to treat with antibiotics, H. pylori can be a risk factor for gastric cancer if it becomes a long-term infection (D. J. Kelly, 2004).
The body's natural defenses cannot combat H. pylori because white and killer T cells cannot easily get through the stomach lining. The defense cells eventually die, spilling their superoxide radicals on stomach lining cells, on which H. pylori can feed (Helicobacter Foundation, 2004).
References
Kelly, D. J. 2004.The University of Sheffield. The Biology of Helicobacter pylori
The Helicobacter Foundation. 2004. Helicobacter pylori
The Institute for Genomic Research: TIGR Microbial Database. 2004. Helicobacter pylori background.
