Vibrio fischeri NEU2011: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
The bacteria form mutually symbiotic relationships with various species of fish and squids with their ability to produce bioluminescence. The production of bioluminescence is enabled by the proteins that are encoded in a set of genes referred to as the lux operon. Light is produced when an enzyme, luciferase, oxidizes luciferin, a substrate molecule. This reaction releases free energy in the form of blue-green light at 480nm-490nm(blue-green). The reaction that occurs in ''Vibrio fischeri'' is as follows: | The bacteria form mutually symbiotic relationships with various species of fish and squids with their ability to produce bioluminescence. The production of bioluminescence is enabled by the proteins that are encoded in a set of genes referred to as the lux operon. Light is produced when an enzyme, luciferase, oxidizes luciferin, a substrate molecule. This reaction releases free energy in the form of blue-green light at 480nm-490nm(blue-green). The reaction that occurs in ''Vibrio fischeri'' is as follows: | ||
FMNH2 + RCHO + O2 --> FMN + RCOOH + H2O + hv(490nm) | FMNH2 + RCHO + O2 --> FMN + RCOOH + H2O + hv(490nm) | ||
The bioluminescence quantum yield has been estimated to be 10-30% according to Encyclopedia of Life Sciences. | The bioluminescence quantum yield has been estimated to be 10-30% according to Encyclopedia of Life Sciences (Davis, Aubrey). | ||
==Pathology== | ==Pathology== | ||
Revision as of 02:16, 1 April 2011
A page on the microorganism Vibrio fischeri
Classification
Higher order taxa
Vibrio fischeri
- Kingdom: Bacteria
- Phylum: Proteobacteria
- Class: Gamma Proteobacteria
- Order: Vibrionales
- Family: Vibrionaceae
- Genus: Vibrio
- Species: V. fischeri
Description and Significance
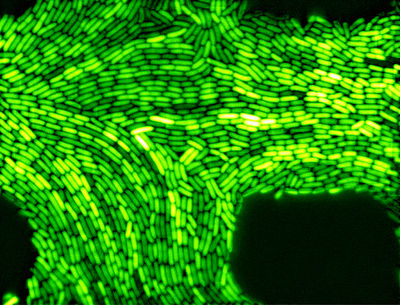
Vibrio Fischeri is a member of the phylum proteobacteria. These bacteria are motile, gram-negative rods that are found in temperate and subtropical waters. These heterotrophic bacteria use flagella as a means of movement and they are most famous for their bioluminescence properties. V. Fischeri is mainly found living in symbiosis with various deep sea marine animals such as monocentrid fishes and bobtail squid. V. Fischeri is found within unique light-organs or as part of the normal gut of these marine animals (V. Fischeri).
V. Fischeri can also be found living as free bacteria in small quantities surviving on decaying organic matter. V. Fischeri use proteins coded by a set of genes called the lux operon to produce bioluminescence. The light is produced in a chemical reaction where luciferin is oxidized by the enzyme luciferase. As a result of the oxidation, a blue-green light is emitted. The symbiotic relationship between a strain of the V. Fischeri and its host, the bobtail squid Euprymna scolopes, has been studied extensively. The bobtail squid acquires these bacteria from its surroundings and uses it as a protection from predators. Within several hours of being ingested, these bacteria begin to change. They decrease in size, lose their flagella, and begin to emit light. These bacteria help to eliminate the squid’s shadow caused by the moonlight above (Vibrio Fischeri-Euprymna). The isolation and cloning of the lux gene from V. Fischeri, and their use as a reporter gene, have provided scientists with many valuable research techniques. The lux gene has enabled scientists to visually study and examine many living organisms at a cellular level. Likewise, V. Fischeri cells have been made commercially available to ecotoxicologists to detect contaminants in the environment more quickly and cheaper than most other available methods (Madigan M).
Genome Structure
The genome of V.fisheri contains 4273718 nucleotides, 3817 protein genes and 165 RNA genes. The chromosomes I and II are circular. The sequence of the chromosome 1 is NC_006840 and its lenght is equal to 2897536. The sequence of the chromosome II is NC_006842 and its lenght is equal to 1330333. The ES114 strain is characterized by a circular plasmid known as pES100. The number of taxonomy of the Vibrio fisheri is 312309 (KEGG).
Ecology
Past studies have demonstrated that Vibrio fischeri is successful at adapting to a variety of ecological niches. They are commonly present as planktonic cells in seawater or sediments, and as saprophytes. V. fischeri are usually found in very low quantities in almost all oceans of the world, preferentially found in temperate and sub-tropical waters. They populate fecal materials. In higher concentration, V. fischeri have cooperative associations with certain deep sea marine life within special light-organs. Indeed, they can form associations with specialized symbiotic organs of marine squids and fishes (Nealson).
Although many studies have reported specific niches and predictable patterns in geographical distribution for luminous bacterial species the factors underlying their ecological dynamics is not well understood yet (Feldman). Additionally the bacteria can be pathogenic to certain species of marine invertebrates, some of which are commercially farmed in aquaculture. This disease is known as luminous vibriosis (Orndorff).
Cell Structure and Metabolism
Vibrio fischeri is a Gram-negative bioluminescent oxidase-positive marine bacterium composed of a cell wall with an outer membrane consisting of inner cytoplasmic membrane covered by peptidoglycan layer followed by periplasmic space to the lipopolysaccharides. They are straight rod with 0.8-1.3 um in diameter and 1.8-2.4um in length. The bacteria has 1-3 polar unsheathed flagella.
This bacterium is capable of respiratory and fermentative metabolism because it is a chemoorganotroph. Vibrio fischeri is a facultative anaerobe. It cannot dentrify, implying that it cannot use nitrogen in its metabolism.
The bacteria form mutually symbiotic relationships with various species of fish and squids with their ability to produce bioluminescence. The production of bioluminescence is enabled by the proteins that are encoded in a set of genes referred to as the lux operon. Light is produced when an enzyme, luciferase, oxidizes luciferin, a substrate molecule. This reaction releases free energy in the form of blue-green light at 480nm-490nm(blue-green). The reaction that occurs in Vibrio fischeri is as follows:
FMNH2 + RCHO + O2 --> FMN + RCOOH + H2O + hv(490nm)
The bioluminescence quantum yield has been estimated to be 10-30% according to Encyclopedia of Life Sciences (Davis, Aubrey).
Pathology
Vibrio fischeri itself is non-pathogenic and is classified as a mutualistic symbiont. The V. fischeri species is known for its beneficial association with the light organ of the bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes (Vibrio fischeri-Encyclopedia).
In the genus of Vibrio, are several dozen species known to participate in a diversity of pathogenic interactions with other organisms. Among these species are Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Vibrio vulnificus, and Vibrio harveyi,. V. cholerae, V. parahaemolyticus, and V. vulnificus are best known are causing illness in humans. Vibrio infections are characterized in humans as a foodborne illness. This would be due to the consumption of contaminated seafood or the exposure of an open wound to tainted seawater. Symptoms present themselves as gastroenteritis issues such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and headaches. Infections due to open wound sites would include swelling at the site, pain, erythema, and necrosis. In addition to these ailments,V. vulnificus is also responsible for causing septicemia in an infected individual. Of the pathogenic species present in humans, V. vulnificus is linked with the highest fatality rate (Fox).
Vibrio harveyi is pathogenic to certain species of marine invertebrates and is known as luminous vibriosis. Luminous vibriosis can be found in sharks, seabass, seahorses, lobster, and shrimp. This disease forms plaques in the mouth, innards, and appendages. This causes the loss of limb function and soon after death of the organism. Luminous vibriosis is the leading cause of death for commercially farmed shrimp and other aquaculture (Orndorff).
References
- Davis, Aubrey. Biology (BIMM) 101 Lab Manual. p. ii. AS Soft Reserves, Winter 2007. Hoi Ho, Thong Huy Do, Tony Tran Ho, Derek Lee. "Vibrio infections." 2007 January. Emedicine Specialties. http://www.emedicine.com/med/topic2375.htm
- Feldman K A, Buck J D. Distribution and characterization of luminescent bacteria in a temperate estuary. Estuaries. 1984;7:93–97.
- KEGG. Vibrio Fischeri Genome Information. Web. 18 Feb. 2001. http://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_organism?org=vfi.
- Koropatnick, Tanya. "Squid/Vibrio." SERC. Nov. 2006. Web. 21 Feb. 2011. http://serc.carleton.edu/microbelife/topics/marinesymbiosis/squid-vibrio/.
- Madigan M, Martinko J (editors) (2005). Brock Biology of Microorganisms (13th ed.). Prentice Hall.
- Nealson KH, Hastings JW.PMID: 396467 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]PMCID: PMC281490
- Orndorff S A, Colwell R R. Distribution and identification of luminous bacteria from the Sargasso Sea. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980;39:983–987.
- "V. Fischeri." The University of Nottingham. Web. 13 Feb. 2011. http://www.nottingham.ac.uk/quorum/fischerimain.htm.
- "Vibrio Fischeri - Encyclopedia Article - Citizendium." Welcome to Citizendium - Citizendium. 16 Feb. 2010. Web. 27 Mar. 2011. http://en.citizendium.org/wiki/Vibrio_fischeri.
- "Vibrio Fischeri - Euprymna Scolopes Symbiosis." Integrated Genomics. Aug. 2007. Web. 14 Feb. 2011. http://web.uconn.edu/mcbstaff/graf/VfEs/VfEssym.htm.