Vibrio parahaemolyticus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
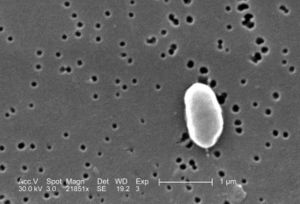
[[Image:V_parahaemolyticus.jpg|thumb|right | [[Image:V_parahaemolyticus.jpg|thumb|right|caption]] | ||
===Higher order taxa=== | ===Higher order taxa=== | ||
Revision as of 20:19, 1 May 2007
A Microbial Biorealm page on the genus Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Classification
Higher order taxa
Bacteria (domain); Proteobacteria (phylum); Gammaproteobacteria (class); Vibrionales (order); Vibrionaceae (family); Vibrio (genus); Vibrio parahaemolyticus (species)
Species
|
NCBI: Taxonomy |
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Description and significance
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is typically found in coastal waters due to its halophilic (salt-requiring) characteristics. It is found in higher concentrations during the summer.
V. parahaemolyticus causes diarrhea upon ingestion. While the overwhelming majority of people acquire the infection by eating raw or undercooked seafood (particularly shellfish and oysters), an open wound exposed to warm seawater can facilitate V. parahaemolyticus infection.
Isolation of V. parahaemolyticus is possible from cultures of stool, wound, or blood. Isolation from stool preferably involves a medium that contains thiosulfate, citrate, bile salts, and sucrose (TCBS agar).
Describe the appearance, habitat, etc. of the organism, and why it is important enough to have its genome sequenced. Describe how and where it was isolated. Include a picture or two (with sources) if you can find them.
Genome structure
Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence? Does it have any plasmids? Are they important to the organism's lifestyle?
Cell structure and metabolism
Describe any interesting features and/or cell structures; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Ecology
Describe any interactions with other organisms (included eukaryotes), contributions to the environment, effect on environment, etc.
Pathology
How does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
Human ingestion of V. parahaemolyticus causes various symptoms, including diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, headache, fever, and chills.
Application to Biotechnology
Does this organism produce any useful compounds or enzymes? What are they and how are they used?
Current Research
Enter summaries of the most recent research here--at least three required
References
Edited by Hau-Chen Lee, student of Rachel Larsen and Kit Pogliano