Ashbya gossypii: Difference between revisions
From MicrobeWiki, the student-edited microbiology resource
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
'''''Ashbya gossypii''' | '''''Ashbya gossypii''' | ||
('''''Eremothecium gossypii''''') | ('''''Eremothecium gossypii''''') | ||
is a filamentous fungus | is a filamentous fungus, meaning that it is an infectious agent of the fungus kingdom consisting of a long series of attached cells. It is closely related to unicellular yeasts, especially Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a yeast with which it shares more than 90% of its genome. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
* Jaspersen Lab, 2007. "Sue Jasperseon, Ph.D, [http://www.stowers.org/faculty/jaspersen-lab Profile]." ''Stowers Institute for Medical Research.'' | * Jaspersen Lab, 2007. "Sue Jasperseon, Ph.D, [http://www.stowers.org/faculty/jaspersen-lab Profile]." ''Stowers Institute for Medical Research.'' | ||
* A. gossypii, March 2013. "[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ashbya_gossypii#cite_note-1 Ashbya gossypii]." | * A. gossypii, March 2013. "[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ashbya_gossypii#cite_note-1 Ashbya gossypii]." | ||
Revision as of 00:39, 8 November 2013
Classification
Higher Order Taxa:
Fungi, Ascomycota, Saccharomycetes, Saccharomycetales, Saccharomycetaceae
Species:
A. gossypii
Description and Significance
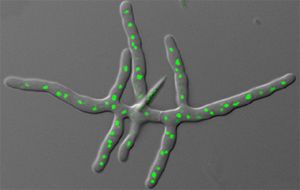
Fungus Ashbya gossypii. Nuclei are shown in green. Jaspersen Lab, 2007.
Ashbya gossypii (Eremothecium gossypii) is a filamentous fungus, meaning that it is an infectious agent of the fungus kingdom consisting of a long series of attached cells. It is closely related to unicellular yeasts, especially Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a yeast with which it shares more than 90% of its genome.
References
- Jaspersen Lab, 2007. "Sue Jasperseon, Ph.D, Profile." Stowers Institute for Medical Research.
- A. gossypii, March 2013. "Ashbya gossypii."
