Pseudomonas corrugata: Difference between revisions
Cmcole1736 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Uncurated}} | |||
=Classification= | =Classification= | ||
Kingdom: Bacteria | Kingdom: Bacteria | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
Order: Pseudomonadales | Order: Pseudomonadales | ||
Family: Pseudomonadaceae | Family: Pseudomonadaceae | ||
Genus: 'Pseudomonas' | Genus: ''Pseudomonas'' | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
==Species== | ==Species== | ||
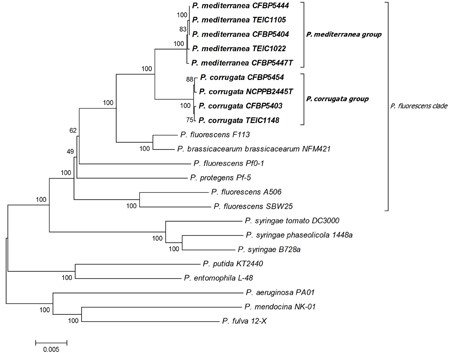
''Pseudomonas corrugata'' consists of at least 87 different strains (Catara | ''Pseudomonas corrugata'' consists of at least 87 different strains (Catara et al., 2002) and there are at least 25 more species in the ''Pseudomonas fluorescens'' group. In total there are at least 132 species within the genus. There are also a total of 7 groups within the genus. The Pcor species epithet “corrugata” refers to the typical morphology of bacterial colonies on NDA; slightly raised, with a wrinkled-rough surface and undulate margins that produce a yellow diffusible pigment (Scarlett et al., 1978). This bacterium is one of the non-fluorescent ''Pseudomonas'' species. | ||
=Description and significance= | =Description and significance= | ||
''P. corrugata'' was discovered in 1978 by Roberts and Scarlett (Scarlett | ''P. corrugata'' was discovered in 1978 by Roberts and Scarlett (Scarlett et al., 1978). This microbe is significant because uncontrolled outbreaks of it in agricultural communities can severely damage tomato crops for a season, having a huge economic impact. This bacteria attacks the pith of the tomato plant causing necrosis. Necrosis is rotting of the cell structure. ''P. corrugata'' produces wrinkled and, rarely, smooth colonies on yeast peptone glucose agar or nutrient dextrose agar; yellow to brown diffusible pigments are frequently produced. Disease symptoms include; typical symptom on tomato is necrosis and/or hollowing of the pith of the stem, the syndrome determines loss of turgidity of the plant, hydropic/necrotic areas, and long conspicuous adventitious roots on the stem. In vitro assessed against plant pathogenic fungi and bacteria, as well as the phytotoxin indicator microorganism ''Rhodotorula pilimanae'' and ''Bacillus megaterium'': in vivo used against pre- and post-harvest plant pathogens (Catara, 2007). | ||
=16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Information= | =16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Information= | ||
The closest | The closest relative of ''P. corrugate'' is ''Pseudomonas brassicacearum'' with 97% similarity, based on NCBI BLAST search. | ||
=Genome Structure= | =Genome Structure= | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Genome size is approximately 6,193,893 bp, the DNA coding region has 4,577,116 base pairs, DNA G+C content is 60.51%, total genes count is 6,211, protein coding genes are 6,165, genes with predicted function are 4,074. (Licciardello | Genome size is approximately 6,193,893 bp, the DNA coding region has 4,577,116 base pairs, DNA G+C content is 60.51%, total genes count is 6,211, protein coding genes are 6,165, genes with predicted function are 4,074. (Licciardello et al., 2014) | ||
=Cell structure and metabolism= | =Cell structure and metabolism= | ||
''P. corrugata'' is a gram-negative, oxidase-positive, non-spore forming rod, and non-fluorescent on King's B medium (Catara | ''P. corrugata'' is a gram-negative, oxidase-positive, non-spore forming rod, and non-fluorescent on King's B medium (Catara et al., 2007). ''P. corrugata'' produces wrinkled and, rarely, smooth colonies on yeast peptone glucose agar or nutrient dextrose agar; yellow to brown diffusible pigments are frequently produced. Disease symptoms include: typical symptom on tomato is necrosis and/or hollowing of the pith of the stem, the syndrome determines loss of turgidity of the plant, hydropic/necrotic areas, and long conspicuous adventitious roots on the stem. Also, there is no production of fluorescent compounds, it builds up medium sized chains of poly(hydroxyalkanoates), and is incapable of producing levan (Catara et al., 2002). | ||
=Ecology and Pathogenesis= | =Ecology and Pathogenesis= | ||
Plant-pathogenic bacterium that causes pith necrosis in tomatoes (Anzai | Plant-pathogenic bacterium that causes pith necrosis in tomatoes (Anzai et al., 2000). The first case was reported in April of 2015 in two countries simultaneously in Georgia (Kůdela et al., 2010). A range of 10 to 15% of the crops were affected (Kůdela et al., 2010). Infections are more evident when the first trusses ripen on the tomato plants. Initially, only slight wilting in the hottest part of the day and at times chlorosis of the apex can be seen. The characteristic symptom of the disease, as shown by its name, is stem pith necrosis and the pith may appear as necrotic, dry and slightly disaggregated in the core, hydropic, white or dark but presenting a hard core and necrotic in the areas near the xylom. The disease starts from the base of the stem and works up to the leaf stems and bunches. Necrosis can also affect the taproot and, occasionally, the rootlets (Catara et al., 2002). Under test conditions ''P. corrugata'' was also able to infect peppers, tobacco, and chrysanthemum (Catara et al., 2002). | ||
=Current Research= | =Current Research= | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
Anzai; Kim, H; Park, JY; Wakabayashi, H; Oyaizu, H; et al. (2000). "Phylogenetic | |||
affiliation of the pseudomonads based on 16S rRNA sequence". Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 50 (4): 1563–1589. doi:10.1099/00207713-50-4-1563. PMID 10939664. | affiliation of the pseudomonads based on 16S rRNA sequence". Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 50 (4): 1563–1589. doi:10.1099/00207713-50-4-1563. PMID 10939664. | ||
Catara V., (2007). "Pseudomonas corrugata: Plant Pathogen and/or Biological | |||
resource?" Molecular Plant Pathology 8.3: 233-244. | resource?" Molecular Plant Pathology 8.3: 233-244. | ||
Catara, V., et al. (2002). "Phenotypic and genomic evidence for the revision of | |||
''Pseudomonas | ''Pseudomonas corrugata'' and proposal of ''Pseudomonas mediterranea'' sp. nov." International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 52(5): 1749-1758. | ||
Kůdela, V., V. Krejzar, and L. Pánková (2010). " ''Pseudomonas corrugata'' and | |||
''Pseudomonas marginalis'' Associated with the collapse of tomato plants in Rockwool Slab hydroponic culture." Plant Protection Science 46(1): 1-11. | |||
Licciardello, G., Ferraro, R., Russo, M., Strozzi, F., Catara, A. F., Bella, P., & Catara, V. | |||
(2016). Transcriptome analysis of ''Pseudomonas mediterranea'' and ''P. corrugata'' plant pathogens during accumulation of medium-chain-length PHAs by glycerol bioconversion. New Biotechnology. | (2016). Transcriptome analysis of ''Pseudomonas mediterranea'' and ''P. corrugata'' plant pathogens during accumulation of medium-chain-length PHAs by glycerol bioconversion. New Biotechnology. | ||
Licciardello, G., et al. (2014) "Draft genome sequence of Pseudomonas corrugata, a | |||
phytopathogenic bacterium with potential industrial applications." Journal of Biotechnology 175: 65-66. | |||
Pandey, Anita, Lok Man S. Palni, and K.p. Hebbar (2001). "Suppression of damping-off | |||
in maize seedlings by ''Pseudomonas Corrugata''." Microbiological Research 156(2): 191-194. | |||
Trantas; Sarris, PF; Pentari, MG; Mpalantinaki, E; Ververidis, F; Goumas, DE; et al. | |||
"Diversity among Pseudomonas corrugata and Pseudomonas mediterranea isolated from tomato and pepper showing symptoms of pith necrosis in Greece". Plant Pathology. 64 (2): 307–318. doi:10.1111/ppa.12261 | "Diversity among Pseudomonas corrugata and Pseudomonas mediterranea isolated from tomato and pepper showing symptoms of pith necrosis in Greece". Plant Pathology. 64 (2): 307–318. doi:10.1111/ppa.12261 | ||
Trantas, Emmanouil A., Grazia Licciardello, Nalvo F. Almeida, Kamil Witek, Cinzia P. | |||
Strano, Zane Duxbury, Filippos Ververidis, Dimitrios E. Goumas, Jonathan D. G. Jones, David S. Guttman, Vittoria Catara, and Panagiotis F. Sarris. (2015). "Comparative Genomic Analysis of Multiple Strains of Two Unusual Plant Pathogens: ''Pseudomonas corrugata'' and ''Pseudomonas mediterranea''." Frontiers in Microbiology 6.811: 1-19. | |||
Trivedi, Pankaj, and Tongmin Sa (2007). "Pseudomonas Corrugata (NRRL B-30409) | |||
Mutants Increased Phosphate Solubilization, Organic Acid Production, and Plant Growth at Lower Temperatures." Current Microbiology 56 | Mutants Increased Phosphate Solubilization, Organic Acid Production, and Plant Growth at Lower Temperatures." Current Microbiology 56(2): 140-44. | ||
=Author= | |||
Cameron Cole, Alex Roman, and Lexi Siegle with Microbial Ecology Instructor Dr. | Cameron Cole, Alex Roman, and Lexi Siegle with Microbial Ecology Instructor Dr. Hideotoshi Urakawa | ||
Latest revision as of 13:42, 4 October 2017
Classification
Kingdom: Bacteria Phylum: Proteobacteria Class: Gammaproteobacteria Order: Pseudomonadales Family: Pseudomonadaceae Genus: Pseudomonas
Species
Pseudomonas corrugata consists of at least 87 different strains (Catara et al., 2002) and there are at least 25 more species in the Pseudomonas fluorescens group. In total there are at least 132 species within the genus. There are also a total of 7 groups within the genus. The Pcor species epithet “corrugata” refers to the typical morphology of bacterial colonies on NDA; slightly raised, with a wrinkled-rough surface and undulate margins that produce a yellow diffusible pigment (Scarlett et al., 1978). This bacterium is one of the non-fluorescent Pseudomonas species.
Description and significance
P. corrugata was discovered in 1978 by Roberts and Scarlett (Scarlett et al., 1978). This microbe is significant because uncontrolled outbreaks of it in agricultural communities can severely damage tomato crops for a season, having a huge economic impact. This bacteria attacks the pith of the tomato plant causing necrosis. Necrosis is rotting of the cell structure. P. corrugata produces wrinkled and, rarely, smooth colonies on yeast peptone glucose agar or nutrient dextrose agar; yellow to brown diffusible pigments are frequently produced. Disease symptoms include; typical symptom on tomato is necrosis and/or hollowing of the pith of the stem, the syndrome determines loss of turgidity of the plant, hydropic/necrotic areas, and long conspicuous adventitious roots on the stem. In vitro assessed against plant pathogenic fungi and bacteria, as well as the phytotoxin indicator microorganism Rhodotorula pilimanae and Bacillus megaterium: in vivo used against pre- and post-harvest plant pathogens (Catara, 2007).
16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Information
The closest relative of P. corrugate is Pseudomonas brassicacearum with 97% similarity, based on NCBI BLAST search.
Genome Structure
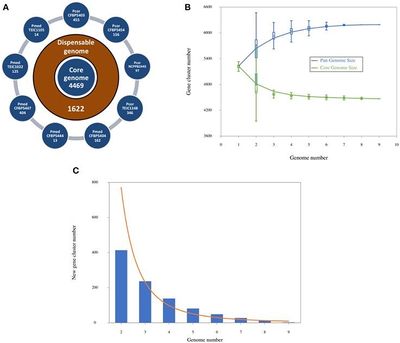
Genome size is approximately 6,193,893 bp, the DNA coding region has 4,577,116 base pairs, DNA G+C content is 60.51%, total genes count is 6,211, protein coding genes are 6,165, genes with predicted function are 4,074. (Licciardello et al., 2014)
Cell structure and metabolism
P. corrugata is a gram-negative, oxidase-positive, non-spore forming rod, and non-fluorescent on King's B medium (Catara et al., 2007). P. corrugata produces wrinkled and, rarely, smooth colonies on yeast peptone glucose agar or nutrient dextrose agar; yellow to brown diffusible pigments are frequently produced. Disease symptoms include: typical symptom on tomato is necrosis and/or hollowing of the pith of the stem, the syndrome determines loss of turgidity of the plant, hydropic/necrotic areas, and long conspicuous adventitious roots on the stem. Also, there is no production of fluorescent compounds, it builds up medium sized chains of poly(hydroxyalkanoates), and is incapable of producing levan (Catara et al., 2002).
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Plant-pathogenic bacterium that causes pith necrosis in tomatoes (Anzai et al., 2000). The first case was reported in April of 2015 in two countries simultaneously in Georgia (Kůdela et al., 2010). A range of 10 to 15% of the crops were affected (Kůdela et al., 2010). Infections are more evident when the first trusses ripen on the tomato plants. Initially, only slight wilting in the hottest part of the day and at times chlorosis of the apex can be seen. The characteristic symptom of the disease, as shown by its name, is stem pith necrosis and the pith may appear as necrotic, dry and slightly disaggregated in the core, hydropic, white or dark but presenting a hard core and necrotic in the areas near the xylom. The disease starts from the base of the stem and works up to the leaf stems and bunches. Necrosis can also affect the taproot and, occasionally, the rootlets (Catara et al., 2002). Under test conditions P. corrugata was also able to infect peppers, tobacco, and chrysanthemum (Catara et al., 2002).
Current Research
Current research involving P. corrugata includes:
● “Association with the collapse of tomato plants in rockwool slab hydroponic culture” (Kůdela et al., 2010). This study is attempting to understand how pith occurs in tomato plants that could trigger an outbreak such as the Rockwool Slab Hydroponic incident in 2008.
● Suppression of damping-off in maize seedlings by P. corrugata (Pandey et al., 2001). This is a method that may be able to improve grain yields by introducing P. corrugata to corn seedlings.
● Pseudomonas corrugata (NRRL B-30409) This is another agricultural method that researchers are hoping will improve crop yields(Trivedi et al., 2007).
References
Anzai; Kim, H; Park, JY; Wakabayashi, H; Oyaizu, H; et al. (2000). "Phylogenetic affiliation of the pseudomonads based on 16S rRNA sequence". Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 50 (4): 1563–1589. doi:10.1099/00207713-50-4-1563. PMID 10939664.
Catara V., (2007). "Pseudomonas corrugata: Plant Pathogen and/or Biological
resource?" Molecular Plant Pathology 8.3: 233-244.
Catara, V., et al. (2002). "Phenotypic and genomic evidence for the revision of
Pseudomonas corrugata and proposal of Pseudomonas mediterranea sp. nov." International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 52(5): 1749-1758.
Kůdela, V., V. Krejzar, and L. Pánková (2010). " Pseudomonas corrugata and
Pseudomonas marginalis Associated with the collapse of tomato plants in Rockwool Slab hydroponic culture." Plant Protection Science 46(1): 1-11.
Licciardello, G., Ferraro, R., Russo, M., Strozzi, F., Catara, A. F., Bella, P., & Catara, V.
(2016). Transcriptome analysis of Pseudomonas mediterranea and P. corrugata plant pathogens during accumulation of medium-chain-length PHAs by glycerol bioconversion. New Biotechnology.
Licciardello, G., et al. (2014) "Draft genome sequence of Pseudomonas corrugata, a
phytopathogenic bacterium with potential industrial applications." Journal of Biotechnology 175: 65-66.
Pandey, Anita, Lok Man S. Palni, and K.p. Hebbar (2001). "Suppression of damping-off
in maize seedlings by Pseudomonas Corrugata." Microbiological Research 156(2): 191-194.
Trantas; Sarris, PF; Pentari, MG; Mpalantinaki, E; Ververidis, F; Goumas, DE; et al.
"Diversity among Pseudomonas corrugata and Pseudomonas mediterranea isolated from tomato and pepper showing symptoms of pith necrosis in Greece". Plant Pathology. 64 (2): 307–318. doi:10.1111/ppa.12261
Trantas, Emmanouil A., Grazia Licciardello, Nalvo F. Almeida, Kamil Witek, Cinzia P.
Strano, Zane Duxbury, Filippos Ververidis, Dimitrios E. Goumas, Jonathan D. G. Jones, David S. Guttman, Vittoria Catara, and Panagiotis F. Sarris. (2015). "Comparative Genomic Analysis of Multiple Strains of Two Unusual Plant Pathogens: Pseudomonas corrugata and Pseudomonas mediterranea." Frontiers in Microbiology 6.811: 1-19.
Trivedi, Pankaj, and Tongmin Sa (2007). "Pseudomonas Corrugata (NRRL B-30409)
Mutants Increased Phosphate Solubilization, Organic Acid Production, and Plant Growth at Lower Temperatures." Current Microbiology 56(2): 140-44.
Author
Cameron Cole, Alex Roman, and Lexi Siegle with Microbial Ecology Instructor Dr. Hideotoshi Urakawa