Streptomyces Unknown Family: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{Uncurated}} ==Classification== Domain; Phylum; Class; Order; family [Others may be used. Use [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/ NCBI] link to find] ===Species=== {|...") |
|||
| (44 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Uncurated}} | {{Uncurated}} | ||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
[[File:Streptomyces_Unknown_pic.png|380px|thumb|right|]] | |||
Domain | <b>Domain:</b> Bacteria | ||
<b>Phylum:</b> Actinobacteria | |||
<b>Class:</b> Actinobacteria | |||
<b>Order:</b> Actinomycetales | |||
<b>Family:</b> Streptomycetaceae | |||
<b>Genus:</b> ''Streptomyces'' | |||
<b>Other Names:</b> | |||
*Streptomyces lavendulae | |||
*Streptomyces vinaceus | |||
*Streptomyces manipurensis | |||
*Streptomyces spororaveus | |||
*Streptomyces avidinii | |||
*Streptomyces subrutilus | |||
===Species=== | ===Species=== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 30: | ||
|} | |} | ||
<i>Genus species:</i> Streptomyces Unknown Species | |||
==Habitat Information == | ==Habitat Information == | ||
*<b>Date of Collection:</b> January 25, 2018 | |||
*<b>Location:</b> Austin, Texas | |||
*<b>Max Temperature:</b> 64 deg. F | |||
*<b>Min Temperature:</b> 29 deg. F | |||
*<b>Min Relative Humidity:</b> 20% | |||
*<b>Solar Radiation:</b> 14.13 mJ/m2 | |||
*<b>Rainfall:</b> 0% | |||
*<b>Wind Gust:</b> 4.85 mph | |||
*<b>Soil Types: </b> Speck stony clay loam (48.4%), Tarrant and Speck (24.1%), Tarrant soil (17.3%), Crawford clay (10.2%) | |||
==Description and Significance== | ==Description and Significance== | ||
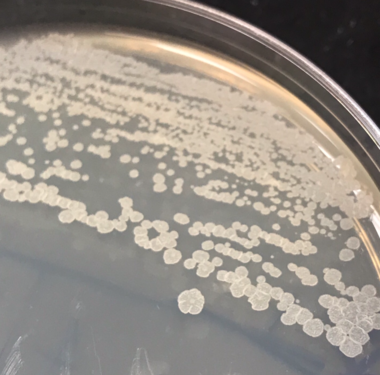
<b>Colony Description:</b> | |||
*<b>Form:</b> Irregular | |||
*<b>Elevation:</b> Flat | |||
*<b>Margin:</b> Undulate | |||
*<b>Pigmentation:</b> Colorless/Opaque | |||
*<b>Texture:</b> Dry/Rough | |||
*<b>Extracellular Pigment:</b> None | |||
*<b>Appearance:</b> Dull | |||
<b>Significance:</b> | |||
Depending on the strain, <i>Streptomyces</i> has the ability to produce bioactive secondary metabolites, such as antifungals, antivirals, immunosuppressants, and antibiotics. <i>Streptomyces</i> began with the discovery of streptothricin in 1942, and with the discovery of streptomycin two years later, scientists continued the search for antibiotics within the genus. According to one of the articles, 80% of the antibiotics are sourced from the genus <i>Streptomyces</i> today. | |||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
*<b>Size:</b> 8.7 Mbp-11.9 Mbp | |||
*<b>Content:</b> GC (Guanine & Cytosine) ranging between 66-74% | |||
*<b># of Chromosomes:</b> unknown | |||
*<b>Organization:</b> Linear | |||
*<b>Interesting Features:</b>Rolling Circle Replication Plasmids---(Unidirectional nucleic acid replication permitting rapid synthesis of multiple copies of circular molecules of DNA/RNA, such as plasmids, the genomes of bacteriophages, and the circular RNA genome of viroids.) | |||
*<b>S Ribosomal Sequence:</b> | |||
<b>>CM1_2_1-16S-rRNA-SeqF_H11.ab1:</b> | |||
GAGCTCGTAGGCGGCTTGTCACGTCGGATGTGAAAGCCCGAGGCTTAACCTCGGGTCTGCATTCGATACGGGCT | |||
AGCTAGAGTGTGGTAGGGGAGATCGGAATTCCTGGTGTAGCGGTGAAATGCGCAGATATCAGGAGGAACACCGG | |||
TGGCGAAGGCGGATCTCTGGGCCATTACTGACGCTGAGGAGCGAAAGCGTGGGGAGCGAACAGGATTAGATACC | |||
CTGGTAGTCCACGCCGTAAACGTTGGGAACTAGGTGTTGGCGCATTCCACGTCGTCGGTGCCGCAGCTAACGCA | |||
TTAAGTTCCCCGCCTGGGGAGTACGGCCGCAAGGCTAAAACTCAAAGAATTGACGGGGGCCCGCACAAGCGGCG | |||
GAGCATGTGGCTTAATTCGACGCAACGCGAAGAACCTTACCAAGGCTTGACAATACCGGAAAGCATTAGAGATA | |||
GTGCCCCCCTTGTGGTCGGTATACAGGTGGTGCATGGCTGTCGTCAGCTCGTGTCGTGAGATGTTGGGTTAAGT | |||
CCCGCAACGAGCGCAACCCTTGTCCTGTGTTGCCAGCATGCCCTTCGGGGTGATGGGGACTCAAGGAGACCGCC | |||
GGGGTCAACTCGGAGGAAGGTGGGGACGACGTCAAGTCATCATGCCCCTTATGTCTTGGGCTGCACACGTGCTA | |||
CAATGGCCGGTACAATGAGCTGCGATACCGTGAGGTGGAGCGAATCTCAAAAAGCCGGTCTCAGTTCGGATTGG | |||
GTCTGCAACTCGACCCCATGAAGTCGGAGTCGCTAGTAATCGCAGATCAGCATTGCTGCGGTGAATACGTTCCC | |||
GGGCCTGTACACACCGCCCGTCACGTCACGAAAGTCGGTAACACCCGAAGCCGGTGGCCCAACCCGTAAAGGGA | |||
GGGAGCTGTGAAGGNGGGACTGGCGATTGGGACGAAGTCGTACAGGGGT | |||
==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ||
*<b>Cell Structure:</b>Resembles fungi | |||
*<b>Metabolism:</b> Extracellular Hydrolytic Enzymes (allow metabolism of Sugars, Alcohols, Amino acids, & Aromatic compounds) | |||
*<b>Life cycles:</b> During the vegetative growth stage, replication takes place without cellular division (filamentous structure).They reproduce and disperse through the formation of spores (conidia). The spores are produced in aerial filaments called Sporophores, which rise above the colony. Because the complex life cycle of Streptomycetes resembles that of multicellular eukaryotes, it enables researchers to study the development of these more complex systems using a simpler system | |||
*<b>Energy Source:</b> Starch & Sodium Caseinate | |||
==Physiology and Pathogenesis== | |||
<b>BIOCHEMICAL TEST RESULTS</b> | |||
*<b>Gram Reaction:</b> positive | |||
*<b>Capsule Stain:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Endospore Stain:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Motility:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Phenol Red Broth Tests:</b> <i>Glucose:</i> yellowish-pink, negative; <i>Lactose:</i> red-pink, negative; <i>Sucrose:</i> red-pink, negative | |||
*<b>Starch Hydrolysis Test:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Casein Hydrolysis Test:</b> positive | |||
*<b>Gelatin Hydrolysis Test:</b> negative | |||
*<b>DNA Hydrolysis Test:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Lipid Hydrolysis Test:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Methyl Red Test:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Voges Proskauer Test:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Citrate Test:</b> positive | |||
*<b>SIM Tests:</b> negative for all | |||
*<b>Nitrate Reduction:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Urea Hydrolysis:</b> positive | |||
*<b>Triple Sugar Iron Agar:</b> negative for all | |||
*<b>Oxidase Test:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB) Test:</b> positive | |||
*<b>Hektoen Enteric Agar (HE) Test:</b> green, negative, no growth | |||
*<b>MacConkey Agar Test:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Decarboxylation Tests:</b> <i>Arginine:</i> no change; <i>Lysine:</i> negative; <i>Orinithine:</i> negative | |||
*<b> Phenylalanine Deaminase Test:</b> negative | |||
*<b> Catalase Test:</b> negative | |||
*<b> Blood Agar Test:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) Test:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Phenylethyl Alcohol Agar (PEA) Test:</b> negative | |||
*<b>Bacitracin/Optochin Susceptibility Test:</b> <i>Bacitracin:</i> resistant; <i>Optochin:</i> resistant | |||
*<b>Bile Esculin Test: </b> negative | |||
*<b>6.5% Salt Tolerance Test: </b> negative | |||
<b>PATHOGENESIS:</b> | |||
In rare cases <i>Streptomyces</i> can cause mycetoma (chronic inflammation of tissues) through inhalation of spores from soil organisms. It has also been reported to cause pneumonitis or lung abscess', bloodstream infections, and lung infections. No distinct outward symptoms, but further blood tests and microscopic tests to confirm a <i>Streptomyces</i> infection. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[ | |||
[Z. (May 02). 6-3 Streptomyces. Retrieved May 2, 2018, from https://instruction.bact.wisc.edu/instr/book/displayarticle/93] | |||
[de Lima Procópio, R., da Silva, I., Martins, M., de Azevedo, J., & de Araújo, J. (2018). Antibiotics produced by Streptomyces. Retrieved 2 May 2018, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1413867012001341] | |||
<http://aem.asm.org/content/75/9/2920.full> Manteca, Angel, Sanchez, Jesus. "Streptomyces Development in Colonies and Soils". "Applied and Environmental Microbiology". 2009. Volume 75 no. 9. p. 2920-2924. | |||
<https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1413867012001341> Emerson de Lima Procopio, Rudi, and Reis da Silva, Ingrid. "Antibiotics produced by Streptomyces". "The Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases". September to October 2012. Volume 16, Issue 5. p. 466-471. | |||
<https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17369139> Kapadia, M, Rolston, KV, and Han, XY. "Invasive Streptomyces infections: six cases and literature review". "American Journal of Clinical Pathology". April 2007. Volume 127. p. 619-624. | |||
==Author== | ==Author== | ||
Page authored by | Page authored by Caylinda Miller and Maya Robinson, students of Prof. Kristine Hollingsworth at Austin Community College. | ||
<!-- Do not remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Kristine Hollingsworth at Austin Community College]] | <!-- Do not remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Kristine Hollingsworth at Austin Community College]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:04, 4 May 2018
Classification
Domain: Bacteria
Phylum: Actinobacteria
Class: Actinobacteria
Order: Actinomycetales
Family: Streptomycetaceae
Genus: Streptomyces
Other Names:
- Streptomyces lavendulae
- Streptomyces vinaceus
- Streptomyces manipurensis
- Streptomyces spororaveus
- Streptomyces avidinii
- Streptomyces subrutilus
Species
|
NCBI: Taxonomy |
Genus species: Streptomyces Unknown Species
Habitat Information
- Date of Collection: January 25, 2018
- Location: Austin, Texas
- Max Temperature: 64 deg. F
- Min Temperature: 29 deg. F
- Min Relative Humidity: 20%
- Solar Radiation: 14.13 mJ/m2
- Rainfall: 0%
- Wind Gust: 4.85 mph
- Soil Types: Speck stony clay loam (48.4%), Tarrant and Speck (24.1%), Tarrant soil (17.3%), Crawford clay (10.2%)
Description and Significance
Colony Description:
- Form: Irregular
- Elevation: Flat
- Margin: Undulate
- Pigmentation: Colorless/Opaque
- Texture: Dry/Rough
- Extracellular Pigment: None
- Appearance: Dull
Significance:
Depending on the strain, Streptomyces has the ability to produce bioactive secondary metabolites, such as antifungals, antivirals, immunosuppressants, and antibiotics. Streptomyces began with the discovery of streptothricin in 1942, and with the discovery of streptomycin two years later, scientists continued the search for antibiotics within the genus. According to one of the articles, 80% of the antibiotics are sourced from the genus Streptomyces today.
Genome Structure
- Size: 8.7 Mbp-11.9 Mbp
- Content: GC (Guanine & Cytosine) ranging between 66-74%
- # of Chromosomes: unknown
- Organization: Linear
- Interesting Features:Rolling Circle Replication Plasmids---(Unidirectional nucleic acid replication permitting rapid synthesis of multiple copies of circular molecules of DNA/RNA, such as plasmids, the genomes of bacteriophages, and the circular RNA genome of viroids.)
- S Ribosomal Sequence:
>CM1_2_1-16S-rRNA-SeqF_H11.ab1:
GAGCTCGTAGGCGGCTTGTCACGTCGGATGTGAAAGCCCGAGGCTTAACCTCGGGTCTGCATTCGATACGGGCT AGCTAGAGTGTGGTAGGGGAGATCGGAATTCCTGGTGTAGCGGTGAAATGCGCAGATATCAGGAGGAACACCGG TGGCGAAGGCGGATCTCTGGGCCATTACTGACGCTGAGGAGCGAAAGCGTGGGGAGCGAACAGGATTAGATACC CTGGTAGTCCACGCCGTAAACGTTGGGAACTAGGTGTTGGCGCATTCCACGTCGTCGGTGCCGCAGCTAACGCA TTAAGTTCCCCGCCTGGGGAGTACGGCCGCAAGGCTAAAACTCAAAGAATTGACGGGGGCCCGCACAAGCGGCG GAGCATGTGGCTTAATTCGACGCAACGCGAAGAACCTTACCAAGGCTTGACAATACCGGAAAGCATTAGAGATA GTGCCCCCCTTGTGGTCGGTATACAGGTGGTGCATGGCTGTCGTCAGCTCGTGTCGTGAGATGTTGGGTTAAGT CCCGCAACGAGCGCAACCCTTGTCCTGTGTTGCCAGCATGCCCTTCGGGGTGATGGGGACTCAAGGAGACCGCC GGGGTCAACTCGGAGGAAGGTGGGGACGACGTCAAGTCATCATGCCCCTTATGTCTTGGGCTGCACACGTGCTA CAATGGCCGGTACAATGAGCTGCGATACCGTGAGGTGGAGCGAATCTCAAAAAGCCGGTCTCAGTTCGGATTGG GTCTGCAACTCGACCCCATGAAGTCGGAGTCGCTAGTAATCGCAGATCAGCATTGCTGCGGTGAATACGTTCCC GGGCCTGTACACACCGCCCGTCACGTCACGAAAGTCGGTAACACCCGAAGCCGGTGGCCCAACCCGTAAAGGGA GGGAGCTGTGAAGGNGGGACTGGCGATTGGGACGAAGTCGTACAGGGGT
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
- Cell Structure:Resembles fungi
- Metabolism: Extracellular Hydrolytic Enzymes (allow metabolism of Sugars, Alcohols, Amino acids, & Aromatic compounds)
- Life cycles: During the vegetative growth stage, replication takes place without cellular division (filamentous structure).They reproduce and disperse through the formation of spores (conidia). The spores are produced in aerial filaments called Sporophores, which rise above the colony. Because the complex life cycle of Streptomycetes resembles that of multicellular eukaryotes, it enables researchers to study the development of these more complex systems using a simpler system
- Energy Source: Starch & Sodium Caseinate
Physiology and Pathogenesis
BIOCHEMICAL TEST RESULTS
- Gram Reaction: positive
- Capsule Stain: negative
- Endospore Stain: negative
- Motility: negative
- Phenol Red Broth Tests: Glucose: yellowish-pink, negative; Lactose: red-pink, negative; Sucrose: red-pink, negative
- Starch Hydrolysis Test: negative
- Casein Hydrolysis Test: positive
- Gelatin Hydrolysis Test: negative
- DNA Hydrolysis Test: negative
- Lipid Hydrolysis Test: negative
- Methyl Red Test: negative
- Voges Proskauer Test: negative
- Citrate Test: positive
- SIM Tests: negative for all
- Nitrate Reduction: negative
- Urea Hydrolysis: positive
- Triple Sugar Iron Agar: negative for all
- Oxidase Test: negative
- Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB) Test: positive
- Hektoen Enteric Agar (HE) Test: green, negative, no growth
- MacConkey Agar Test: negative
- Decarboxylation Tests: Arginine: no change; Lysine: negative; Orinithine: negative
- Phenylalanine Deaminase Test: negative
- Catalase Test: negative
- Blood Agar Test: negative
- Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) Test: negative
- Phenylethyl Alcohol Agar (PEA) Test: negative
- Bacitracin/Optochin Susceptibility Test: Bacitracin: resistant; Optochin: resistant
- Bile Esculin Test: negative
- 6.5% Salt Tolerance Test: negative
PATHOGENESIS:
In rare cases Streptomyces can cause mycetoma (chronic inflammation of tissues) through inhalation of spores from soil organisms. It has also been reported to cause pneumonitis or lung abscess', bloodstream infections, and lung infections. No distinct outward symptoms, but further blood tests and microscopic tests to confirm a Streptomyces infection.
References
[Z. (May 02). 6-3 Streptomyces. Retrieved May 2, 2018, from https://instruction.bact.wisc.edu/instr/book/displayarticle/93] [de Lima Procópio, R., da Silva, I., Martins, M., de Azevedo, J., & de Araújo, J. (2018). Antibiotics produced by Streptomyces. Retrieved 2 May 2018, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1413867012001341]
<http://aem.asm.org/content/75/9/2920.full> Manteca, Angel, Sanchez, Jesus. "Streptomyces Development in Colonies and Soils". "Applied and Environmental Microbiology". 2009. Volume 75 no. 9. p. 2920-2924.
<https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1413867012001341> Emerson de Lima Procopio, Rudi, and Reis da Silva, Ingrid. "Antibiotics produced by Streptomyces". "The Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases". September to October 2012. Volume 16, Issue 5. p. 466-471.
<https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17369139> Kapadia, M, Rolston, KV, and Han, XY. "Invasive Streptomyces infections: six cases and literature review". "American Journal of Clinical Pathology". April 2007. Volume 127. p. 619-624.
Author
Page authored by Caylinda Miller and Maya Robinson, students of Prof. Kristine Hollingsworth at Austin Community College.