Acinetobacter calcoaceticus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Very short pages]] | |||
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus | Acinetobacter calcoaceticus | ||
{{Uncurated}} | {{Uncurated}} | ||
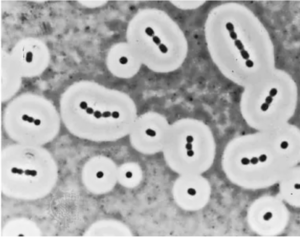
[[Image: | [[Image:Acinetobactercalcoaceticus.png|thumb|300px|right|Legend. Image credit: Name or Publication.]] | ||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
Bacteria; Pseudomonadota; Gammaproteobacteria; Pseudomonadales; Moraxellaceae | |||
===Species=== | ===Species=== | ||
{| | {| | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
|} | |} | ||
'' | '' Acinetobacter A. calcoaceticus'' | ||
==Description and Significance== | ==Description and Significance== | ||
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus is a soil bacterium. It is located in sewage and soil and is capable of causing nosocomial infections. | |||
Despite being regarded nonpathogenic in most cases, Acinetobacters are causal agents of nosocomial infections, particularly in the elderly. | |||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus has a size of 0.9 - 1.6 micrometers by 1.5 - 2.5 micrometers. It has a chromosome of 4,110,074 base pairs and a plasmid of 5,920 base pairs. It has a rod shape. | |||
==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ||
The Acinetobacter calcoaceticus may use a broad variety of organic substances as its only source of carbon and energy. It is a Gram-negative nonpathogenic bacteria, holds considerable potential in bioremediation. It was initially isolated due to its capacity to use diesel as its only carbon source. | |||
==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ||
The Acinetobacter calcoaceticus can be found in soil and sewage. While it is usually found in dirt, it may also be detected in and collected from human specimens, interstitial regions, axillae, toe webs, pharynx, and various healthy people's secretions. They form 25% of the skin flora in normal people. Colonization of the digestive system has been observed in both newborns and adults. Rectal Acinetobacter colonization carries the danger of translocation. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
E. Bergogne-Bérézin, P. Kämpfer. (2014). Acinetobacter. Acinetobacter - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. Retrieved November 17, 2022, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/acinetobacter | |||
Acinetobacter. Description of the Genus - Acinetobacter. (n.d.). Retrieved November 17, 2022, from https://catalog.hardydiagnostics.com/cp_prod/Content/hugo/Acinetobacter.htm | |||
==Author== | ==Author== | ||
Page authored by | Page authored by Israel Haro, student of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington. | ||
<!-- Do not remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Bradley Tolar at UNC | <!-- Do not remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington]] | ||
Wilmington]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:32, 21 May 2024
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus
Classification
Bacteria; Pseudomonadota; Gammaproteobacteria; Pseudomonadales; Moraxellaceae
Species
|
NCBI: [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=1007084&lvl= 3&lin=f&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock] |
Acinetobacter A. calcoaceticus
Description and Significance
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus is a soil bacterium. It is located in sewage and soil and is capable of causing nosocomial infections.
Despite being regarded nonpathogenic in most cases, Acinetobacters are causal agents of nosocomial infections, particularly in the elderly.
Genome Structure
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus has a size of 0.9 - 1.6 micrometers by 1.5 - 2.5 micrometers. It has a chromosome of 4,110,074 base pairs and a plasmid of 5,920 base pairs. It has a rod shape.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
The Acinetobacter calcoaceticus may use a broad variety of organic substances as its only source of carbon and energy. It is a Gram-negative nonpathogenic bacteria, holds considerable potential in bioremediation. It was initially isolated due to its capacity to use diesel as its only carbon source.
Ecology and Pathogenesis
The Acinetobacter calcoaceticus can be found in soil and sewage. While it is usually found in dirt, it may also be detected in and collected from human specimens, interstitial regions, axillae, toe webs, pharynx, and various healthy people's secretions. They form 25% of the skin flora in normal people. Colonization of the digestive system has been observed in both newborns and adults. Rectal Acinetobacter colonization carries the danger of translocation.
References
E. Bergogne-Bérézin, P. Kämpfer. (2014). Acinetobacter. Acinetobacter - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. Retrieved November 17, 2022, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/acinetobacter
Acinetobacter. Description of the Genus - Acinetobacter. (n.d.). Retrieved November 17, 2022, from https://catalog.hardydiagnostics.com/cp_prod/Content/hugo/Acinetobacter.htm
Author
Page authored by Israel Haro, student of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington.