Pendulispora rubella: Difference between revisions
| (30 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Uncurated}} | {{Uncurated}} | ||
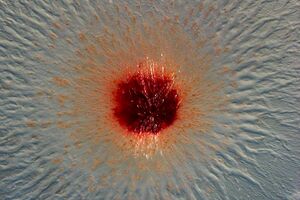
[[File:csm_Aufnahme-213902-0010_d2b8388e24.jpg|thumb|300px|right|Diagram of microscopic imaging of <i>Pendiluspora rubella</i> colony. Image credit: Garcia, R. et al., (2024).]] | |||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
Pendiluspora rubella | <i>Pendiluspora rubella</i> (MSr11367) | ||
==Description and Significance== | ==Description and Significance== | ||
<i>P. rubella</i> has a wide range of acid tolerance as it can grow in a pH range of 4-12. This mesophilic organism can thrive in conditions where the temperature range is 18°C-37°C. Unlike other myxobacteria, <i>P. rubella</i> forms a unicellular fruiting body producing powdery round spores and does not form a sporangial coat nor a slime envelope around the spores. | |||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
Pendulispora rubella (MSr11367) has a circular genome with 10,733 total genes. Named GCF_037157805.1-RS_2024_10_26 and fully mapped on 10/26/2024 12:40:18. | |||
==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ||
"Pendulus" meaning 'hanging so as to swing freely or hanging downward' [2] is the prefix for Pendulispora. This is to illustrate the way that <i>P. rubella</i> bears its spores. An advancing swarm colony pattern with flare-like edges, slender rod-shaped vegetative cells, and dormant spores can characterize its growth. <i>P. rubella</i> MSr11367T produces a family of N-terminally acetylated and C-terminally reduced tetrapeptides with an all L-configured amino acid sequence. <i>P. rubella</i> has a unique set of cellular machinery contributing to its metabolism and function. The genes that encode their synthesis mechanics display unparalleled enzymatics. The first ever discovered non-ribosomal peptide synthetase acetylation domain was found within their genome [2]. <i>P. rubella</i> releases rounded spores during spore dispersal that appear powdery. | |||
==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ||
| Line 51: | Line 45: | ||
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.<br><br> | If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.<br><br> | ||
Pendulispora rubella is a soil-living organism | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[ | [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NZ_CP089983.1 Garcia, R., Popoff, A., Bader, C.D., Loehr, J., Walesch, S., Walt, C., Boldt, J., Bunk, B., Haeckl, F.J.F.P.J., Gunesch, A.P., Birkelbach, J., Nuebel, U., Pietschmann, T., Bach, T. and Mueller, R. "Discovery of the Pendulisporaceae a myxobacterial family with distinct sporulation behavior and unique specialized metabolism". ''Unpublished''. 2024.] | ||
[https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0059:entry=pendulus] | |||
==Author== | ==Author== | ||
Page authored by Colleen Bolmanski, Dakota Lowery & Beckham LaBarbera, students of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington. | Page authored by Colleen Bolmanski, Dakota Lowery, & Beckham LaBarbera, students of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington. | ||
<!-- Do not remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington]] | <!-- Do not remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:09, 21 November 2024
Classification
Bacteria; Myxococcota; Myxococcia; Myxococcales; Sorangiineae; Pendulisporaceae
Species
|
NCBI: [1] |
Pendiluspora rubella (MSr11367)
Description and Significance
P. rubella has a wide range of acid tolerance as it can grow in a pH range of 4-12. This mesophilic organism can thrive in conditions where the temperature range is 18°C-37°C. Unlike other myxobacteria, P. rubella forms a unicellular fruiting body producing powdery round spores and does not form a sporangial coat nor a slime envelope around the spores.
Genome Structure
Pendulispora rubella (MSr11367) has a circular genome with 10,733 total genes. Named GCF_037157805.1-RS_2024_10_26 and fully mapped on 10/26/2024 12:40:18.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
"Pendulus" meaning 'hanging so as to swing freely or hanging downward' [2] is the prefix for Pendulispora. This is to illustrate the way that P. rubella bears its spores. An advancing swarm colony pattern with flare-like edges, slender rod-shaped vegetative cells, and dormant spores can characterize its growth. P. rubella MSr11367T produces a family of N-terminally acetylated and C-terminally reduced tetrapeptides with an all L-configured amino acid sequence. P. rubella has a unique set of cellular machinery contributing to its metabolism and function. The genes that encode their synthesis mechanics display unparalleled enzymatics. The first ever discovered non-ribosomal peptide synthetase acetylation domain was found within their genome [2]. P. rubella releases rounded spores during spore dispersal that appear powdery.
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Habitat; symbiosis; biogeochemical significance; contributions to environment.
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
Pendulispora rubella is a soil-living organism
References
Author
Page authored by Colleen Bolmanski, Dakota Lowery, & Beckham LaBarbera, students of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington.