Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
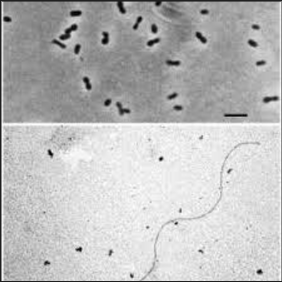
[[Image: | [[Image:Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum.png|thumb|300px|right|Fig. 1) Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum has only a singular flagellum and takes a curved or vibrio shape.]] | ||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
| Line 20: | Line 18: | ||
==Description and Significance== | ==Description and Significance== | ||
Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum is a gram-negative thermophile that is highly involved in the process of hydrogen oxidation in extreme environments (hydrogen-dependent biogeochemical processes). It also has a very large sulfate reduction contribution which helps out the in sulfate cycling, a key process in its native habitat. Without this process many of the organisms in the area would be without a primary food source as nutrients are so scarce at such great depth and pressure. | Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum is a gram-negative thermophile that is highly involved in the process of hydrogen oxidation in extreme environments (hydrogen-dependent biogeochemical processes).(1) It also has a very large sulfate reduction contribution which helps out the in sulfate cycling, a key process in its native habitat. Without this process many of the organisms in the area would be without a primary food source as nutrients are so scarce at such great depth and pressure. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 25: | ||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum only has a singular circular chromosome. It typically doesn't get larger than that in this species. However other closely related species can vary significantly. | Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum only has a singular circular chromosome. It typically doesn't get larger than that in this species. However other closely related species can vary significantly. It does contain 32 nucelotides and 1658 proteins all of which are identical protein groups.(2) | ||
| Line 33: | Line 31: | ||
==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ||
Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum is a typically curved or vibrio shape. It is gram-negative and possesses a single polar flagellum. The cells themselves are relatively small, only occurring singly or in pairs. It typical growth range occurs between 50 and 70 degrees Celsius. It is non-spore forming. | Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum is a typically curved or vibrio shape. It is gram-negative and possesses a single polar flagellum. The cells themselves are relatively small, only occurring singly or in pairs. It typical growth range occurs between 50 and 70 degrees Celsius. It is non-spore forming.(1) | ||
==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ||
Although Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum is typically observed to be an aquatic species, there has not been any major research dedicated to possibly locate it elsewhere. These current known habitats typically include volcanic hot springs, deep-sea hydrothermal sulfides, and other marine environments. | Although Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum is typically observed to be an aquatic species, there has not been any major research dedicated to possibly locate it elsewhere. These current known habitats typically include volcanic hot springs, deep-sea hydrothermal sulfides, and other marine environments.(1) | ||
| Line 43: | Line 41: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
(1)Jeanthon, C., L’Haridon, S., Cueff, V., Banta, A., Reysenbach, A., & Prieur, D. (2002). Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum sp. nov., a thermophilic, chemolithoautotrophic, sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent at Guaymas Basin, and emendation of the genus Thermodesulfobacterium. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SYSTEMATIC AND EVOLUTIONARY MICROBIOLOGY, 52(3), 765–772. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-52-3-765 | |||
(2)Moussard, H., et al. “Thermodesulfatator Indicus Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., a Novel Thermophilic Chemolithoautotrophic Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium Isolated from the Central Indian Ridge.” International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, vol. 54, no. 1, 1 Jan. 2004, pp. 227–233, https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02669-0. | |||
Latest revision as of 18:48, 1 December 2024
Classification
Bacteria, Thermodesulfobacteria, Thermodesulfobacteria, Thermodesulfobacteriales, Thermodesulfobacteriaceae, Thermodesulfobacterium, T. Hydrogeniphilium
Species
Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum
Description and Significance
Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum is a gram-negative thermophile that is highly involved in the process of hydrogen oxidation in extreme environments (hydrogen-dependent biogeochemical processes).(1) It also has a very large sulfate reduction contribution which helps out the in sulfate cycling, a key process in its native habitat. Without this process many of the organisms in the area would be without a primary food source as nutrients are so scarce at such great depth and pressure.
Genome Structure
Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum only has a singular circular chromosome. It typically doesn't get larger than that in this species. However other closely related species can vary significantly. It does contain 32 nucelotides and 1658 proteins all of which are identical protein groups.(2)
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum is a typically curved or vibrio shape. It is gram-negative and possesses a single polar flagellum. The cells themselves are relatively small, only occurring singly or in pairs. It typical growth range occurs between 50 and 70 degrees Celsius. It is non-spore forming.(1)
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Although Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum is typically observed to be an aquatic species, there has not been any major research dedicated to possibly locate it elsewhere. These current known habitats typically include volcanic hot springs, deep-sea hydrothermal sulfides, and other marine environments.(1)
References
(1)Jeanthon, C., L’Haridon, S., Cueff, V., Banta, A., Reysenbach, A., & Prieur, D. (2002). Thermodesulfobacterium hydrogeniphilum sp. nov., a thermophilic, chemolithoautotrophic, sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent at Guaymas Basin, and emendation of the genus Thermodesulfobacterium. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SYSTEMATIC AND EVOLUTIONARY MICROBIOLOGY, 52(3), 765–772. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-52-3-765
(2)Moussard, H., et al. “Thermodesulfatator Indicus Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., a Novel Thermophilic Chemolithoautotrophic Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium Isolated from the Central Indian Ridge.” International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, vol. 54, no. 1, 1 Jan. 2004, pp. 227–233, https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02669-0.
Author
Page authored by Sara Dominguez-Tapia, Ty Goller, Christian Nicholson, & Juliana Paris, students of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington.