Leishmania: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{ | {{Curated}} | ||
'''A [[Microbial Biorealm]] page on the subgenus ''Leishmania''''' | |||
''' | |||
[[Image:leishmania.jpg|thumb|300px|right|''Leishmania major'' by E. Draberova. Image from [http://www.img.cas.cz/mci/ Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic.]]] | [[Image:leishmania.jpg|thumb|300px|right|''Leishmania major'' by E. Draberova. Image from [http://www.img.cas.cz/mci/ Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic.]]] | ||
| Line 14: | Line 13: | ||
''Leishmania major, L. donovani, L. braziliensis'' | ''Leishmania major, L. donovani, L. braziliensis'' | ||
{| | |||
| height="10" bgcolor="#FFDF95" | | |||
'''NCBI: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?id=38568 Taxonomy] [http://www.sanger.ac.uk/Projects/L_major/ Genome] ''' | |||
|} | |||
==Description and Significance== | ==Description and Significance== | ||
''Leishmania'' is a parasite which causes human leishmaniasis. The genus ''Leishmania'' is unique among parasites in that its species are divided based not on the form and structure of the cells, but rather on the pathology and symptoms of the disease they cause. ''Leishmania ''may infect many vertebrates, but in human hosts the infection most frequently stems from the bites of sand fly vectors or, in the case of ''Leishmania major'', from gerbils and other small rodent vectors. Leishmaniasis can take three forms: dermal cutaneous leishmaniasis, visceral leishmaniasis, and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. Dermal cutaneous leishmaniasis, generated by ''Leishmania major'', causes sores on the human host's skin, which range in appearance and degree of discomfort. The sores are treatable with antibiotics and | ''Leishmania'' is a parasite which causes human leishmaniasis. The genus ''Leishmania'' is unique among parasites in that its species are divided based not on the form and structure of the cells, but rather on the pathology and symptoms of the disease they cause. ''Leishmania ''may infect many vertebrates, but in human hosts the infection most frequently stems from the bites of sand fly vectors or, in the case of ''Leishmania major'', from gerbils and other small rodent vectors. Leishmaniasis can take three forms: dermal cutaneous leishmaniasis, visceral leishmaniasis, and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. Dermal cutaneous leishmaniasis, generated by ''Leishmania major'', causes sores on the human host's skin, which range in appearance and degree of discomfort. The sores are [http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/leishmaniasis/health_professionals/index.html#tx treatable with antibiotics], and treatment may prevent spread of systemic infection. At present there is no vaccine. Visceral leishmaniasis, produced by ''Leishmania donovani'', is identified by an enlargement of the liver and spleen; symptoms include breathing difficulties, edema, diarrhea, and bleeding mucus membranes. If untreated for an extended period of time, visceral leishmaniasis may result in death. Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, caused by ''Leishmania braziliensis'', initially yields topical sores at the time of the vector bite; however, secondary infections may lead to permanently disfiguring ulcerations in the mucus cavities of the mouth and nose. | ||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
| Line 25: | Line 29: | ||
==Cell Structure and Metabolism== | ==Cell Structure and Metabolism== | ||
[[Image:1475-9292-2-14-1-l.jpg|thumb| | [[Image:1475-9292-2-14-1-l.jpg|thumb|200px|left| Life cycle. When ''Leishmania'' invades the sand fly vector, the promastigote form settles in the midgut and reproduces asexually. The promastigotes are transmitted to the vertebrate host when the sand fly vector bites. Once inside the vertebrate host, ''Leishmania'' invades the host's cells, where it morphs into its amastigote form after losing its flagella to the macrophages of the host's immune system. In the cells of the host the amastigote multiplies and eventually kill the cell, upon which the amastigotes are released to other cells. Human leishmaniasis' symptoms are the effects of these amastigotes destruction of cells. Image from [http://www.kinetoplastids.com/content/2/1/14#IDASA3YC Kinetoplastid Biology and Disease.]]] | ||
''Leishmania'' 's promastigote form (found in the vector) is similar to the amastigote, but possesses a prominent flagella. The surface membrane has binding site molecules such as glycoproteins, and manose receptors have also been detected. These are important in the uptake of the promastigotes by macrophages in the host cell. Antibodies in the host serum bind to the promastigotes and facilitate uptake and entry into the macrophage. The macrophages have Fc receptors on their surface. Upon losing the flagella (see life cycle, below) ''Leishmania'''s amastigote form (found in the cells of the vertebrate host) is spherical and is contained within a parasitophorus vacuole within a macrophage. There is a prominent nucleus and kinetoplast, and the vacuolated cytoplasm contains lysosomes. The outer membrane has a polysaccharide component but there is no surface coat.Once inside the host cell, ''Leishmania ''is able to protect itself from powerful host immunities by using several unique defense mechanisms, including its rapid cell division. ''Leishmania'' is a heterotophic organism whose prominent flagella may allow it to puncture host cells, allowing the promastigote to consume nutrients and obtain energy from the cell sap. | ''Leishmania'' 's promastigote form (found in the vector) is similar to the amastigote, but possesses a prominent flagella. The surface membrane has binding site molecules such as glycoproteins, and manose receptors have also been detected. These are important in the uptake of the promastigotes by macrophages in the host cell. Antibodies in the host serum bind to the promastigotes and facilitate uptake and entry into the macrophage. The macrophages have Fc receptors on their surface. Upon losing the flagella (see life cycle, below) ''Leishmania'''s amastigote form (found in the cells of the vertebrate host) is spherical and is contained within a parasitophorus vacuole within a macrophage. There is a prominent nucleus and kinetoplast, and the vacuolated cytoplasm contains lysosomes. The outer membrane has a polysaccharide component but there is no surface coat.Once inside the host cell, ''Leishmania ''is able to protect itself from powerful host immunities by using several unique defense mechanisms, including its rapid cell division. ''Leishmania'' is a heterotophic organism whose prominent flagella may allow it to puncture host cells, allowing the promastigote to consume nutrients and obtain energy from the cell sap. A newly discovered hybrid of Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis and Leishmania (Viannia) peruviana was recently identified in Peru. Transmission of the hybrid parasite was attributed to Phlebotomine Sand Fly species, Lutzomyia tejadai and Lu fischeri. | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Latest revision as of 14:05, 13 May 2016
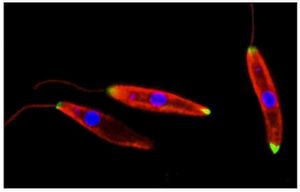
A Microbial Biorealm page on the subgenus Leishmania
Classification
Higher order taxa:
Eukaryota; Euglenozoa; Kinetoplastida; Trypanosomatidae; Leishmania
Species:
Leishmania major, L. donovani, L. braziliensis
Description and Significance
Leishmania is a parasite which causes human leishmaniasis. The genus Leishmania is unique among parasites in that its species are divided based not on the form and structure of the cells, but rather on the pathology and symptoms of the disease they cause. Leishmania may infect many vertebrates, but in human hosts the infection most frequently stems from the bites of sand fly vectors or, in the case of Leishmania major, from gerbils and other small rodent vectors. Leishmaniasis can take three forms: dermal cutaneous leishmaniasis, visceral leishmaniasis, and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. Dermal cutaneous leishmaniasis, generated by Leishmania major, causes sores on the human host's skin, which range in appearance and degree of discomfort. The sores are treatable with antibiotics, and treatment may prevent spread of systemic infection. At present there is no vaccine. Visceral leishmaniasis, produced by Leishmania donovani, is identified by an enlargement of the liver and spleen; symptoms include breathing difficulties, edema, diarrhea, and bleeding mucus membranes. If untreated for an extended period of time, visceral leishmaniasis may result in death. Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, caused by Leishmania braziliensis, initially yields topical sores at the time of the vector bite; however, secondary infections may lead to permanently disfiguring ulcerations in the mucus cavities of the mouth and nose.
Genome Structure
Leishmania major's genome Friedlin has been sequenced, and is found to have a 32.8mb genome with 36 chromosomes and a G+C content of approx. 63%. For a complete table of sequenced data of the Leishmania major genome Friedlin, click here.
Cell Structure and Metabolism
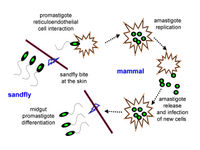
Leishmania 's promastigote form (found in the vector) is similar to the amastigote, but possesses a prominent flagella. The surface membrane has binding site molecules such as glycoproteins, and manose receptors have also been detected. These are important in the uptake of the promastigotes by macrophages in the host cell. Antibodies in the host serum bind to the promastigotes and facilitate uptake and entry into the macrophage. The macrophages have Fc receptors on their surface. Upon losing the flagella (see life cycle, below) Leishmania's amastigote form (found in the cells of the vertebrate host) is spherical and is contained within a parasitophorus vacuole within a macrophage. There is a prominent nucleus and kinetoplast, and the vacuolated cytoplasm contains lysosomes. The outer membrane has a polysaccharide component but there is no surface coat.Once inside the host cell, Leishmania is able to protect itself from powerful host immunities by using several unique defense mechanisms, including its rapid cell division. Leishmania is a heterotophic organism whose prominent flagella may allow it to puncture host cells, allowing the promastigote to consume nutrients and obtain energy from the cell sap. A newly discovered hybrid of Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis and Leishmania (Viannia) peruviana was recently identified in Peru. Transmission of the hybrid parasite was attributed to Phlebotomine Sand Fly species, Lutzomyia tejadai and Lu fischeri.
Ecology
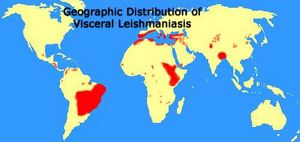
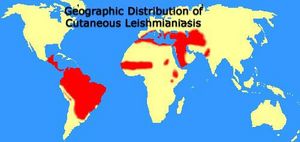
The Leishmania parasite is found in 88 countries, in Central and South America, Mexico, southern Europe (very rarely), the Middle East, parts of Asia, and primarily eastern and northern Africa. Its habitat ranges from tropical rainforests to arid regions, depending on the type of vector (predominantly insect or rodent) each particular species inhabits. Leishmania is transported between vertebrate hosts through vector bites and causes cell disruption and subsequent illness in its host.
References
Drâberova, E.. Leishmania major. Molecular and Cellular Immunology.
"Geographic Distribution of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis." Map.
"Geographic Distribution of Visceral Leishmaniasis." Map.
Graphic Images of Parasites . Ohio State University College of Biological Sciences.
Parasitic Disease Information . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Smith, James. Parasitism and Symbiosis - 177-345A. McGill University.
Totals for genome sequencing of Leishmania major Friedlin . The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute.
For more information on parasites similar to Leishmania, see Trypanosoma.