Ashbya gossypii: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Short pages]] | |||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
==='''Higher Order Taxa:'''=== | ==='''Higher Order Taxa:'''=== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
==Description and Significance== | ==Description and Significance== | ||
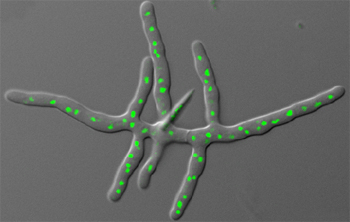
[[File:Ashbya_Gossypii.jpeg|right|Fungus ''Ashbya gossypii.'' Nuclei are shown in green. [http://www.stowers.org/faculty/jaspersen-lab Jaspersen Lab], 2007.]] | [[File:Ashbya_Gossypii.jpeg|right|Fungus ''Ashbya gossypii.'' Nuclei are shown in green. [http://www.stowers.org/faculty/jaspersen-lab Jaspersen Lab], 2007. (''see references for more information.'')]] | ||
'''''Ashbya gossypii''' | '''''Ashbya gossypii''' | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
In addition, because this fungal species is so closely related to yeasts (especially ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae,'') it acts as a model for studying regulatory networks. Explorations of these networks reveal the functional differences between filamentous growth and yeast growth. This is important to understanding diseases that affect the environment and humans, such as ''Candida albicans.'' [http://www.nature.com/nrmicro/journal/v3/n5/abs/nrmicro1148.html]. ''Candida albicans'', a human fungal pathogen, switches in morphology from yeast to filamentous form in response to specific environmental stimuli, which is important in studying pathology. | In addition, because this fungal species is so closely related to yeasts (especially ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae,'') it acts as a model for studying regulatory networks. Explorations of these networks reveal the functional differences between filamentous growth and yeast growth. This is important to understanding diseases that affect the environment and humans, such as ''Candida albicans.'' [http://www.nature.com/nrmicro/journal/v3/n5/abs/nrmicro1148.html]. ''Candida albicans'', a human fungal pathogen, switches in morphology from yeast to filamentous form in response to specific environmental stimuli, which is important in studying pathology. | ||
<br><br> | <br> | ||
(''scroll over photograph to view copyright.'') | |||
<br> | |||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
| Line 38: | Line 43: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Professor Peter Philippsen, Ordinarius of Microbiology at the Biozentrum Basel, was the first scientist to fully examine ''Ashbya Gossypii'' (a few years they completed the sequencing of the ''Saccahromyces cerevisiae'' genome in 1996.)[http://www.biozentrum.unibas.ch/news-events/news-details/article/election-of-peter-philippsen-to-the-rank-of-aaas-fellow/] In these explorations of the two species, these scientists discovered these extensive similarities. | Professor Peter Philippsen, Ordinarius of Microbiology at the Biozentrum Basel, was the first scientist to fully examine ''Ashbya Gossypii'' (a few years they completed the sequencing of the ''Saccahromyces cerevisiae'' genome in 1996.)[http://www.biozentrum.unibas.ch/news-events/news-details/article/election-of-peter-philippsen-to-the-rank-of-aaas-fellow/] In these explorations of the two species, these scientists discovered these extensive similarities. | ||
<br> | |||
==Growth== | ==Growth== | ||
| Line 51: | Line 56: | ||
Sporulation occurs at the end of the ''A. gossypii'' growth phase. The hyphae develop sporangia, enclosures in which the spores are formed, that originate from the '''septate''' compartments. (''see '''Cell Structure''' section''.) To release the spores, the sporangia begin to separate from each other. The hyphae break into fragments at the septal sites (the discs), the sporangia lyse, and the spores are set free. The individual spores can then begin a new life cycle. | Sporulation occurs at the end of the ''A. gossypii'' growth phase. The hyphae develop sporangia, enclosures in which the spores are formed, that originate from the '''septate''' compartments. (''see '''Cell Structure''' section''.) To release the spores, the sporangia begin to separate from each other. The hyphae break into fragments at the septal sites (the discs), the sporangia lyse, and the spores are set free. The individual spores can then begin a new life cycle. | ||
<br> | |||
Scientists also speculate that sporulation in ''A. gossypii'' is a result of nutrient deprivation. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
In contrast with ''S. cerevisiae'' which has mating pheromes, ''A. gossypii'' does not require mating for sporulation. This data was discovered in an experiment studying mutant strains of the species, which had mutant strains of pherome receptor genes but could still sporulate. [http://www.genetics.org/content/early/2013/07/03/genetics.113.151019.full.pdf]. | In contrast with ''S. cerevisiae'' which has mating pheromes, ''A. gossypii'' does not require mating for sporulation. This data was discovered in an experiment studying mutant strains of the species, which had mutant strains of pherome receptor genes but could still sporulate. [http://www.genetics.org/content/early/2013/07/03/genetics.113.151019.full.pdf]. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 65: | ||
''Ashbya gossypii'' is made up of hyphae, or long, thin, branch-like filamentous structures. The nuclei lined up inside the hyphae act independently though they are contained in one cytoplasm. As the nuclei flow through the hyphae, they undergo mitosis at sites of branch formation (where a hyphae will branch off into two, etc.) The two daughter cells will then flow through the new hypha. According to MATLAB-based tracking methods, diffusions of proteins allow communication between nuclei. There are ongoing studies addressing the question of whether the nuclei are competing for resources or if they are functionally independent of one another. [http://www.dartmouth.edu/~gladfelterlab/projects/]. | ''Ashbya gossypii'' is made up of hyphae, or long, thin, branch-like filamentous structures. The nuclei lined up inside the hyphae act independently though they are contained in one cytoplasm. As the nuclei flow through the hyphae, they undergo mitosis at sites of branch formation (where a hyphae will branch off into two, etc.) The two daughter cells will then flow through the new hypha. According to MATLAB-based tracking methods, diffusions of proteins allow communication between nuclei. There are ongoing studies addressing the question of whether the nuclei are competing for resources or if they are functionally independent of one another. [http://www.dartmouth.edu/~gladfelterlab/projects/]. | ||
==Cell Structure== | |||
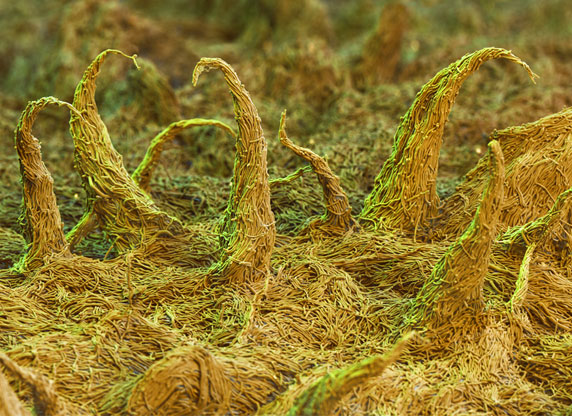
[[File:AshbyaGossypiiMicroscope.jpeg||right| ''Ashbya gossypii''. [http://www.biotechnologie.de/BIO/Navigation/DE/Aktuelles/menschen,did=119486.html Photography by Nicole Ottawa.] ''Gelber Farbstoffpilz; Biotechnologie.de, 2013.'' (''see references for more information'')]] | |||
To the naked eye, ''Ashbya gossypii'' colonies are flat and similar in size and appearance to hair. Under a microscope, they range in color from pale-yellow to vibrant yellow. Their asci, or sexual spore-bearing cells, are long and thin, like thread, and translucent. The ascospores are long and thin as well and also have hooked appendages. [http://www.atcc.org/products/all/10895.aspx#generalinformation]. In addition, ''A. gossypii'' consists of mycelia and hyphae. The hyphae, like branches of a tree, extend into the substrate surrounding it. They each consist of a single cell membrane and nuclei. Each hypha has "compartments" separated by septa, which can be seen at a very young stage as rings, or discs. The septa allow the transfer of nuclei from the older parts of the mycelia to the younger parts. The compartments in the hyphae contain about eight nuclei each. | |||
<br> | |||
(''scroll over photograph to view copyright.'') | |||
==Ecology and | ==Ecology, Pathology and Evolution== | ||
===Ecology=== | ===Ecology=== | ||
As briefly mentioned under '''Growth''', | As briefly mentioned under '''Growth''', | ||
''Ashbya gossypii'' and fungi in general involve apical growth. This form of growth allows it to extend into fresh zones of substrate, | ''Ashbya gossypii'' and fungi in general involve apical growth. This form of growth allows it to extend into its environment and interact with it. The hypha elongate toward fresh zones of substrate and from the tips of hyphae, enzymes are released in order to obtain nutrients. Enzymes released from the tips of the hypha will break down the food into simpler molecules, which can then be transported into the mycelium. Enzyme secretion is especially important for growth when the fungi cells encounter an insoluble polymer such as cellulose, which decreases the organism's rate of enzyme diffusion. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22143993]. | ||
===Pathology=== | ===Pathology=== | ||
| Line 82: | Line 86: | ||
''Ashbya gossypii'' is a pathogen in certain crops that causes stigmatomycosis. (Ashby and Novell, 1926.) This fungal disease is transmitted by sucking insects and was first discovered in cotton, where it affects the development of hair cells in cotton balls. It can then transfer to citrus fruits, causing dry rot disease in which the fruits dry out and collapse. [http://genome.jgi.doe.gov/Ashgo1/Ashgo1.home.html] In the early 1900s, the pathogen, along with two other fungi, caused stigmatomycosis in cotton crops, making it nearly impossible to grow cotton in certain regions and causing huge economical damage. (Frederic P. Miller, Agnes F. Vandome, John McBrewster 2010.) | ''Ashbya gossypii'' is a pathogen in certain crops that causes stigmatomycosis. (Ashby and Novell, 1926.) This fungal disease is transmitted by sucking insects and was first discovered in cotton, where it affects the development of hair cells in cotton balls. It can then transfer to citrus fruits, causing dry rot disease in which the fruits dry out and collapse. [http://genome.jgi.doe.gov/Ashgo1/Ashgo1.home.html] In the early 1900s, the pathogen, along with two other fungi, caused stigmatomycosis in cotton crops, making it nearly impossible to grow cotton in certain regions and causing huge economical damage. (Frederic P. Miller, Agnes F. Vandome, John McBrewster 2010.) | ||
===Evolution=== | |||
''Ashbya gossypii'' is a successful pathogen because of the way in which it evolves. In a recent study, experiments demonstrated that mutant strains of the fungi produced more spores than the wild type. This implies that mutant spores ultimately have a greater chance of survival than wild type spores. While mutant spores are more likely to have fatal changes in their genetics, they are more varied than wild type spores, which could make them more evolutionarily fit if their environment were to change. [http://www.genetics.org/content/early/2013/07/03/genetics.113.151019.full.pdf]. | |||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| Line 88: | Line 95: | ||
* Jaspersen Lab, 2007. "Sue Jaspersen, Ph.D, [http://www.stowers.org/faculty/jaspersen-lab Profile]." ''Stowers Institute for Medical Research.'' | * Jaspersen Lab, 2007. "Sue Jaspersen, Ph.D, [http://www.stowers.org/faculty/jaspersen-lab Profile]." ''Stowers Institute for Medical Research.'' | ||
* Biozentrum: The Center for Molecular Life Sciences, 2013. "Election of Peter Philippsen to the Rank of AAAS Fellow, [http://www.biozentrum.unibas.ch/news-events/news-details/article/election-of-peter-philippsen-to-the-rank-of-aaas-fellow/]." ''University of Basel.'' | * Biozentrum: The Center for Molecular Life Sciences, 2013. "Election of Peter Philippsen to the Rank of AAAS Fellow, [http://www.biozentrum.unibas.ch/news-events/news-details/article/election-of-peter-philippsen-to-the-rank-of-aaas-fellow/]." ''University of Basel.'' | ||
* Nature Reviews Microbiology, May 2005 "[http://www.nature.com/nrmicro/journal/v3/n5/abs/nrmicro1148.html ''Ashbya gossypii'': A Model for Fungal Developmental Biology]." ''Nature Publishing Group, 2013''. | * Nature Reviews Microbiology, May 2005. "[http://www.nature.com/nrmicro/journal/v3/n5/abs/nrmicro1148.html ''Ashbya gossypii'': A Model for Fungal Developmental Biology]." ''Nature Publishing Group, 2013''. | ||
* The Essentials of Life Science Research, 2012. "[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/10895.aspx#generalinformation ''Eremothecium gossypii'' (Ashby et Nowell) Kurtzman (ATCC 10895)]. ''ATCC copyright''. | * The Essentials of Life Science Research, 2012. "[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/10895.aspx#generalinformation ''Eremothecium gossypii'' (Ashby et Nowell) Kurtzman (ATCC 10895)]. ''ATCC copyright''. | ||
* Lisa Wasserstrom, Klaus B. Lengeler, Andrea Walther, and Jurgen Wendland, 2013. [http://www.genetics.org/content/early/2013/07/03/genetics.113.151019.full.pdf "Molecular Determinants of Sporulation in ''Ashbya gossypii'']. ''Carlsberg Laboratory; Yeast Genetics. | * Lisa Wasserstrom, Klaus B. Lengeler, Andrea Walther, and Jurgen Wendland, 2013. [http://www.genetics.org/content/early/2013/07/03/genetics.113.151019.full.pdf "Molecular Determinants of Sporulation in ''Ashbya gossypii'']. ''Carlsberg Laboratory; Yeast Genetics. | ||
| Line 96: | Line 103: | ||
* Jim Deacon, Institute of Cell and Molecular Biology, 2008. [http://archive.bio.ed.ac.uk/jdeacon/microbes/apical.htm The Microbial World: Fungal tip growth and hyphal tropisms]. ''University of Edinbergh.'' | * Jim Deacon, Institute of Cell and Molecular Biology, 2008. [http://archive.bio.ed.ac.uk/jdeacon/microbes/apical.htm The Microbial World: Fungal tip growth and hyphal tropisms]. ''University of Edinbergh.'' | ||
* The Joint Genome Institute, 2013. [http://genome.jgi.doe.gov/Ashgo1/Ashgo1.home.html ''Ashbya gossypii'']. ''The Regents of the University of California''. | * The Joint Genome Institute, 2013. [http://genome.jgi.doe.gov/Ashgo1/Ashgo1.home.html ''Ashbya gossypii'']. ''The Regents of the University of California''. | ||
*Frederic P. Miller, Agnes F. Vandome, John McBrewster (Ed.), 2010. "Ashbya gossypii" book. '' | *Frederic P. Miller, Agnes F. Vandome, John McBrewster (Ed.), 2010. "Ashbya gossypii" book. ''Alphascript Publishing and VDM Publishing House Ltd.'' | ||
* | *Nicole Ottawa. [http://www.biotechnologie.de/BIO/Navigation/DE/Aktuelles/menschen,did=119486.html ''Ashbya gossypii'' Photograph]. ''Article by Gelber Farbstoffpilz, Biotechnologie.de, 2013''. | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
Edited by Jenna Cartusciello, student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 116 Information in Living Systems, 2013, Kenyon College. | Edited by Jenna Cartusciello, student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 116 Information in Living Systems, 2013, Kenyon College. | ||
Latest revision as of 17:56, 29 September 2015
Classification
Higher Order Taxa:
Fungi, Ascomycota, Saccharomycetes, Saccharomycetales, Saccharomycetaceae
Species:
A. gossypii
Description and Significance
Ashbya gossypii (Eremothecium gossypii) is a filamentous fungus, meaning that it is an infectious agent of the fungus kingdom consisting of a long series of attached cells. It is closely related to unicellular yeasts, especially Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a yeast with which it shares more than 90% of its genome.
Ashbya gossypii is an effective fungus in which to study the growth of long and multinucleate (more than one nucleus) fungal cells. It has a small genome, haploid nuclei, and efficient gene targeting methods, characteristics that make it favorable in studies. Through the work of Professor Peter Philippsen and research team, basic yet essential knowledge was gained on the species which is now applied to problems in medicine and agriculture [1].
In addition, because this fungal species is so closely related to yeasts (especially Saccharomyces cerevisiae,) it acts as a model for studying regulatory networks. Explorations of these networks reveal the functional differences between filamentous growth and yeast growth. This is important to understanding diseases that affect the environment and humans, such as Candida albicans. [2]. Candida albicans, a human fungal pathogen, switches in morphology from yeast to filamentous form in response to specific environmental stimuli, which is important in studying pathology.
(scroll over photograph to view copyright.)
Genome Structure
click to see full picture.
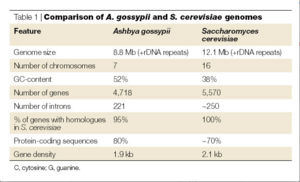
The genome for Ashbya gossypii, fully sequenced in 2004 by the Biozentrum lab, is the smallest genome of a free-living eukaryote thus far, coming up to only 9.2 megabases. It contains a total of 4718 protein-coding genes. As mentioned above, more than 90% of its genes are similar to that of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Thus scientists were able to reconstruct the evolutionary history of both organisms, finding that most of the genome was conserved. A. gossypii and S. cerevisiae diverged from a common ancestor that had approximately 5,000 genes. In the divergence, genetic duplication occurred in S. cerevisiae, which resulted in this species having approximately 1,000 more genes and 16 chromosomes. Genes were lost in A. gossypii, giving it 7 chromosomes and thus fewer genes than either S. cerevisiae or its ancestor species. This divergence, over 100 million years ago, resulted in a main difference between the two species, which is the way in which the two species grow. S. cerevisiae grows through the expansion of buds: a bubble forms on the tip of the yeast cell which continues to grow into a new cell. In constrast, A. gossypii grows as the polar surface of the cell simply lengthens, resulting in one cell membrane with strings of nuclei inside. [3]
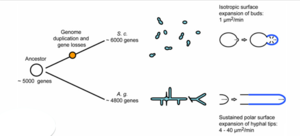
The comparison of these genes reveals shared homology and synteny (the condition of two or more genes being located on the same chromosome) between the two species.
Professor Peter Philippsen, Ordinarius of Microbiology at the Biozentrum Basel, was the first scientist to fully examine Ashbya Gossypii (a few years they completed the sequencing of the Saccahromyces cerevisiae genome in 1996.)[4] In these explorations of the two species, these scientists discovered these extensive similarities.
Growth
Life Cycle
Ashbya gossypii begins its life cycle as a single spore. It's isotropic growth involves the haploid spore's germination and the formation of a germ bubble. Once the germ bubble is formed, two germ tubes grow from opposite sites of the bubble, creating the mycelium. From here the young mycelium continues to form and the hyphae diverge and lengthen.
Sporulation occurs at the end of the A. gossypii growth phase. The hyphae develop sporangia, enclosures in which the spores are formed, that originate from the septate compartments. (see Cell Structure section.) To release the spores, the sporangia begin to separate from each other. The hyphae break into fragments at the septal sites (the discs), the sporangia lyse, and the spores are set free. The individual spores can then begin a new life cycle.
Scientists also speculate that sporulation in A. gossypii is a result of nutrient deprivation.
In contrast with S. cerevisiae which has mating pheromes, A. gossypii does not require mating for sporulation. This data was discovered in an experiment studying mutant strains of the species, which had mutant strains of pherome receptor genes but could still sporulate. [5].
A Closer Look at Hyphae
Ashbya gossypii is made up of hyphae, or long, thin, branch-like filamentous structures. The nuclei lined up inside the hyphae act independently though they are contained in one cytoplasm. As the nuclei flow through the hyphae, they undergo mitosis at sites of branch formation (where a hyphae will branch off into two, etc.) The two daughter cells will then flow through the new hypha. According to MATLAB-based tracking methods, diffusions of proteins allow communication between nuclei. There are ongoing studies addressing the question of whether the nuclei are competing for resources or if they are functionally independent of one another. [6].
Cell Structure
To the naked eye, Ashbya gossypii colonies are flat and similar in size and appearance to hair. Under a microscope, they range in color from pale-yellow to vibrant yellow. Their asci, or sexual spore-bearing cells, are long and thin, like thread, and translucent. The ascospores are long and thin as well and also have hooked appendages. [7]. In addition, A. gossypii consists of mycelia and hyphae. The hyphae, like branches of a tree, extend into the substrate surrounding it. They each consist of a single cell membrane and nuclei. Each hypha has "compartments" separated by septa, which can be seen at a very young stage as rings, or discs. The septa allow the transfer of nuclei from the older parts of the mycelia to the younger parts. The compartments in the hyphae contain about eight nuclei each.
(scroll over photograph to view copyright.)
Ecology, Pathology and Evolution
Ecology
As briefly mentioned under Growth, Ashbya gossypii and fungi in general involve apical growth. This form of growth allows it to extend into its environment and interact with it. The hypha elongate toward fresh zones of substrate and from the tips of hyphae, enzymes are released in order to obtain nutrients. Enzymes released from the tips of the hypha will break down the food into simpler molecules, which can then be transported into the mycelium. Enzyme secretion is especially important for growth when the fungi cells encounter an insoluble polymer such as cellulose, which decreases the organism's rate of enzyme diffusion. [8].
Pathology
Ashbya gossypii is a pathogen in certain crops that causes stigmatomycosis. (Ashby and Novell, 1926.) This fungal disease is transmitted by sucking insects and was first discovered in cotton, where it affects the development of hair cells in cotton balls. It can then transfer to citrus fruits, causing dry rot disease in which the fruits dry out and collapse. [9] In the early 1900s, the pathogen, along with two other fungi, caused stigmatomycosis in cotton crops, making it nearly impossible to grow cotton in certain regions and causing huge economical damage. (Frederic P. Miller, Agnes F. Vandome, John McBrewster 2010.)
Evolution
Ashbya gossypii is a successful pathogen because of the way in which it evolves. In a recent study, experiments demonstrated that mutant strains of the fungi produced more spores than the wild type. This implies that mutant spores ultimately have a greater chance of survival than wild type spores. While mutant spores are more likely to have fatal changes in their genetics, they are more varied than wild type spores, which could make them more evolutionarily fit if their environment were to change. [10].
References
- Jaspersen Lab, 2007. "Sue Jaspersen, Ph.D, Profile." Stowers Institute for Medical Research.
- Biozentrum: The Center for Molecular Life Sciences, 2013. "Election of Peter Philippsen to the Rank of AAAS Fellow, [11]." University of Basel.
- Nature Reviews Microbiology, May 2005. "Ashbya gossypii: A Model for Fungal Developmental Biology." Nature Publishing Group, 2013.
- The Essentials of Life Science Research, 2012. "Eremothecium gossypii (Ashby et Nowell) Kurtzman (ATCC 10895). ATCC copyright.
- Lisa Wasserstrom, Klaus B. Lengeler, Andrea Walther, and Jurgen Wendland, 2013. "Molecular Determinants of Sporulation in Ashbya gossypii. Carlsberg Laboratory; Yeast Genetics.
- Gladfelter Lab, 2013. "Nuclear Anarchy: Timing Variability in the Cell Division Cycle." Trustees of Dartmouth College.
- "Ashbya gossypii Ashbya Genome Database," September 2013. EnsemblFungi.
- Ribeiro O, Domingues L, Penttilä M, Wiebe MG., 2011 "Nutritional requirements and strain heterogeneity in Ashbya gossypii". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Jim Deacon, Institute of Cell and Molecular Biology, 2008. The Microbial World: Fungal tip growth and hyphal tropisms. University of Edinbergh.
- The Joint Genome Institute, 2013. Ashbya gossypii. The Regents of the University of California.
- Frederic P. Miller, Agnes F. Vandome, John McBrewster (Ed.), 2010. "Ashbya gossypii" book. Alphascript Publishing and VDM Publishing House Ltd.
- Nicole Ottawa. Ashbya gossypii Photograph. Article by Gelber Farbstoffpilz, Biotechnologie.de, 2013.
Edited by Jenna Cartusciello, student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 116 Information in Living Systems, 2013, Kenyon College.