Geomicrobiology: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
====Life Support and Waste Management==== | ====Life Support and Waste Management==== | ||
[[Image:Melissaloop.jpeg|thumb|300px|right|General concept of the MELISSA loop for advanced life support[http://ecls.esa.int/ecls/?p=newmelissaloop Image Source]]] | |||
The biggest use of microbes in space exploration and settlement would be the use of photosynthetic organisms to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and food in what is known as a biological life support system. Additionally the waste from these processes could be used to make more carbon dioxide, recycling the nutrients, water and carbon. The Micro Ecological Life Support System, designed by European Space Agency, is a model system of an advance biological life support system that would be based on different species of microbes and plants. Consisting of many bioreactors and plant chambers, MELiSSA would break down the organic waste from the crew and non-edible parts of the higher plants (Gòdia et al 2002). We can learn a lot about how MELiSSA works by looking at soil systems and processes here on Earth. The MELiSSA loop is the basis of the life support system created by the ESA and uses processes we see all the time on earth. For example, the transformations of nitrogen (mineralization, nitrification, immobilization and denitrification) show the different ways nitrogen is transformed in soil and in the atmosphere. From studying how microbes interact in soil has helped us create MELiSSA, which combines multiple systems to produce food, water and oxygen for space explorers. | |||
====Energy Production==== | ====Energy Production==== | ||
One example of the use of microbes in in the production of energy and additional waste management is the use of a MFC, or microbial fuel cell. MFCs can be used to generate electricity and process waste, but they currently produce low amounts of energy and depend on microbes processing organic matter in an anaerobic anode chamber (Cockell 2010). On earth MFCs can be made using the soil found all around us because soil contains a diverse population of microbes, along with the nutrients needed by those microbes to generate energy. | |||
Revision as of 19:33, 14 March 2016
Geomicrobiology is the interdisciplinary study of the interactions of microorganisms with earth materials. It concerns the role of microbes in geological and geochemical processes. The field of geomicrobiology has revealed new insights into the intersection of life with the physical and chemical composition of Earth’s surface. Soil microbes play a large role in the transformations of elements and minerals. The interactions between microbes and elements and minerals is especially important in the near surface environment known as Earth’s Critical Zone, where biotic and abiotic factors regulate the conditions for life-sustaining resources. Virtually all elements can be transformed by microbes and many elemental cycles depend on soil microbes (Gadd 2010). The relationships between microorganisms and these inorganic compounds have important implications for both the surrounding natural environment and human use. Soil microbes can be used by humans in mineral resource extraction and bioremediation.
Key processes of geomicrobiology
Examples of Geomicrobiology Interactions in nature
Examples of microbial metabolism of metals and inorganic substances
Examples of Applied Geomicrobiology
Geomicrobiology has many useful applications for humans. Many microbes are involved with breaking down toxic compounds (see bioremediation in soil wiki), mineral extraction, and the manufacturing of valuable minerals and compounds.
Space exploration
Life Support and Waste Management
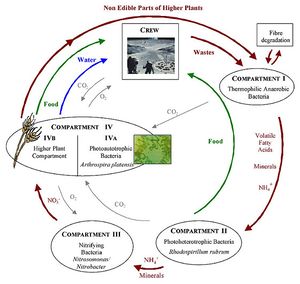
The biggest use of microbes in space exploration and settlement would be the use of photosynthetic organisms to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and food in what is known as a biological life support system. Additionally the waste from these processes could be used to make more carbon dioxide, recycling the nutrients, water and carbon. The Micro Ecological Life Support System, designed by European Space Agency, is a model system of an advance biological life support system that would be based on different species of microbes and plants. Consisting of many bioreactors and plant chambers, MELiSSA would break down the organic waste from the crew and non-edible parts of the higher plants (Gòdia et al 2002). We can learn a lot about how MELiSSA works by looking at soil systems and processes here on Earth. The MELiSSA loop is the basis of the life support system created by the ESA and uses processes we see all the time on earth. For example, the transformations of nitrogen (mineralization, nitrification, immobilization and denitrification) show the different ways nitrogen is transformed in soil and in the atmosphere. From studying how microbes interact in soil has helped us create MELiSSA, which combines multiple systems to produce food, water and oxygen for space explorers.
Energy Production
One example of the use of microbes in in the production of energy and additional waste management is the use of a MFC, or microbial fuel cell. MFCs can be used to generate electricity and process waste, but they currently produce low amounts of energy and depend on microbes processing organic matter in an anaerobic anode chamber (Cockell 2010). On earth MFCs can be made using the soil found all around us because soil contains a diverse population of microbes, along with the nutrients needed by those microbes to generate energy.
Key Microorganisms within Geomicrobiology
Geomicrobiology included organisms that are concidered extremophiles. Extremophiles are microorganisms that live in areas considered too hostile for most. An example of an extremophile is anerobic sulfate reducing bacteria, which are know to live in hyper-saline lagoons in Brazil and Australia. It is believed these bacteria may be responsible for the formation of dolmitea. A good example of an geomicrobe is Pseudomonas putidia a description of which can be found at [2].
Process - key points
Geomicrobiological processes are relevant in many natural environments including aquifers, geological and geochemical processes, extreme environments (acidic, extreme temperatures and saline conditions) and metal ion reduction. Some of the most important processes include: 1- Weathering 2- Precipitation of carbonates and phosphates 3- Ocean crust support 4- Nuclear waste disposal 5- Hot springs
Weathering
Weathering plays an important role on Earth ecosystems and is important for the release of nutrients into the biosphere as a result of rock dissolution or the regulation of long-term climate by the consumption of atmospheric carbon dioxide from silicate alterations. Weathering has been considered a strictly physical and chemical process. Nonetheless, many weathering processes can be affected by the presence of microbial communities. All types of rocks are susceptible to microbial weathering, including siliceous and calcareous rocks. In general microbial weathering is due to the formation of organic acids or the production of metal-chelating siderophores on the surface of rock or minerals. Other processes include oxidative or reductive conditions of metals on rocks or minerals (Herrera et al., 2008). Additional information can be found in the following link: [3]
Precipitation of carbonates and phosphates
The influence of Bacteria in mineral precipitation has been described in different natural habitats including aquatic environments and geological systems. Carbonate precipitation is controlled by bacteria processes and one of the mechanisms proposed is the production of ammonium by metabolizing nitrogen base organic compounds which increases environment pH. Other authors report that the matrix of extracellular polymeric secretions (EPS) affects mineral precipitation Simultaneous precipitation of struvite (MgNH4PO4•6H2O) associated with bacterial activity has been described in vitro carbonate precipitation experiments as well as carbonate and phosphate precipitation by bacteria from saline soils (Delgado et al., 2008). Additional information can be found in the following link: [4]
Ocean crust support
Microbiological studies on sediment cores collected by the Deep Sea Drilling Program (DSDP) and the Ocean Drilling Program (ODP) have demonstrated the presence of microbial communities in deeply buried marine sediments. Prokaryotes in the marine sub-seafloor biosphere have been estimated to comprise one-tenth to one-third of the world’s living biomass and therefore probably play an important role in global biogeochemical processes. Microbial populations in these regions vary considerably as a result of sediment type and age, organic matter availability, temperature and sedimentation rate. An example of the processes involved in this type of ecosystems was proposed for the Juan de Fuca Ridge in the northeast pacific and can be found below (Engelen et al., 2008). Additional information can be found in the following link: [5]
Nuclear waste disposal
Fungi can be very radiation-resistant and can survive and colonize concrete barriers under severe radioactive contamination. After ten years of the catastrophe of Chernobyl in 1986 extensive fungal growth was observed on the walls and other building structures constructed in the inner part of the “Shelter” built over the fourth Unit of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant. Safe long-term storage of both existing and future nuclear wastes is of vital importance in protecting the environment, therefore the study of these fungi has been key for future construction of nuclear waste repositories. The deterioration of concrete by fungi is performed by common mechanisms used by fungi for rock and mineral weathering. Some of the microorganisms isolated from these extreme environments include modified strains from the genera Alternaria, Cladosporium, and Aureobasidium (Fomina et al., 2007). Additional information can be found in the following link:[6]
Microbial Energetics
The Big Picture: a nice summary of microbial metabolism can be found at:
An important part of microbial metabolism is microbial energenetics. Microbial energenetics are driven by Gibbs free-energy yield derived from ATP. ATP is heterotrophically generated by fermentation or respiration. The latter requires terminal electron acceptors (e.g. molecular oxygen, nitrate, sulphate, ferric iron, carbon dioxide, or molecular hydrogen), and produces greater amounts of ATP per unit substrate. Fermentation is less feasible in the presence of either highly oxidised or highly reduced substrate, and may rise toxic products (simple organic acids) that can eventually impede the process. The energy in soil is preserved in both organic and inorganic components enabling the microbial communities to sustain catabolic and anabolic processes.
Examples of Geomicrobes as Related to the elements they metabolize
Sulfur
Sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) comprise of several groups of bacteria that use sulfate as an oxidizing agent, reducing it to sulfide. Most sulfate-reducing bacteria can also use other oxidized sulfur compounds such as sulfite and thiosulfate, or elemental sulfur. This type of metabolism is called dissimilatory, since sulfur is not incorporated - assimilated - into any organic compounds. Sulfate-reducing bacteria have been considered as a possible way to deal with acid mine waters that are produced by other bacteria.
Another interested description of SRB is found at: [7].
'Acidithiobacillus' is a genus of Proteobacteria. The members of this genus used to belong to Thiobacillus, before they were reclassified in the year 2000. Members of this genus can be fined in pyrite deposits, metabolizing iron and sulfur and producing sulfuric acid.
Iron
Example: 'Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans' consumes sulfur and produces sulfuric acid. This bacterium in conjunction with others of the same genus is currently used in a mining technique called bioleaching whereby metals are extracted from their ores through oxidation. The bacteria are used as catalysts.
Manganese
Bacillus sp. strain SG-1 and 'Pseudomonas putida' are common soil and freshwater Mn(II)-oxidizing bacterium. Mn(II)-oxidizing bacteria are a diverse group found in almost all environments. These bacteria are up to 5 orders of magnitude faster than abiotic reactions in the production of Mn oxides which have an amorphous structure with a high surface area. Mn(II) oxides are the only known oxidants of Cr(III) in the environment. The mechanism of Mn(II) oxidation by these bacteria is not clear, although recent outcomes from studies with Bacillus sp. strain SG-1 have shown that a Mn(III) is an intermediate in the final oxidation of Mn(II) through enzymatic activity. For more information on this group of bacterium look at the reference from Karen et al., 2007
Uranium-Nitrate relationship
Contamination of aquifers by Uranium produced from nuclear weapons and fuel is becoming a real problem in different parts of the world. These aquifers are generally oxidized, therefore uranium predominantly exists as U(VI) usually coupled with carbonate making the compound quite soluble.
Uranium reduction occurs under anaerobic conditions with Fe(III) and/or sulfate reduction. The biogeochemical processes that occur after uranium reduction are poorly understood. Resent research has shown that the addition of nitrate (a common co-contaminant with uranium) to U(IV)-containing sediments leads to the oxidation and remobilization of U(IV). Microorganisms responsible in this process are believed to be associated with nitrate dependent Fe(II)-oxidizing microorganisms (Senko et al., 2005).
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is an important nutrient for all living organisms. Most P found in living systems is in the form of inorganic phosphate and its esters. There are a number of studies showing biochemical reactions of P compounds that do not involve the formation of phosphate esters and these reactions involve compounds in which the P is at a lower valence state. On earth virtually all known phosphorus exists in the +5 oxidation state. Nonetheless, there are also two additional known forms phosphonates (+3) and phosphinates (+1). Studies have demonstrated the reduction of phosphate in anaerobic soil and during corrosion of metals under anaerobic conditions. A number of bacteria have been shown to be capable of oxidizing reduced P compounds when this is the sole source of P. Inorganic phosphite (+3) was oxidized to phosphate by numerous laboratory strains of microorganisms, including prokaryotes such as Escherichia coli, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and several species of Pseudomonas and Rhizobium, as well as one eukaryote, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Hypophosphite (+1) can also be oxidized to phosphate by Pseudomonas fluorescens, Bacillus caldolyticus and Pseudomonas stutzeri WM88. Apatite is the primary inorganic source of phosphorus in the biosphere. Soil fungi are known to increase plant-available phosphorus by promoting dissolution of various phosphate minerals. Some of the fungi involved are Zygomycetes in the order of Mucorales and Ascomycetes (Metcalf et al., 1998 and Rosling et al., 2007)
Others
The Epsilon-proteobacteria have recently been recognized as globally ubiquitous in marine and terrestrial ecosystems. They play a major role in biogeochemical and geological processes and have been isolated from sulfur rich terrestrial and marine environments, some of which are considered extreme habitats. Most representatives are only known through the 16S rRNA gene sequence despite current effort to develop culture techniques (Campbell et al., 2006).
'Hydrogenophilaceae' also belongs to the Proteobacteria, and it is believed to be made of two genera. They are thermophilic bacterium growing in temperatures close to 50 °C. They obtain their energy from hydrogen oxidation. Example: Thiobacillus genus; includes only species from beta proteobacteria. This bacterium is used as a pest control in potato fields to control scabs.
Examples of Applied Geomicrobiology
Geomicrobiology has many useful applications for humans. Many microbes are involved with breaking down toxic compounds (see bioremediation in soil wiki), mineral extraction, and the manufacturing of valuable minerals and compounds.
Space exploration
Life Support and Waste Management
Current Research and Links
There is a very interesting site hosted by the Geomicrobiology & Environmental Microbiology Studies at Louisiana State University [8] This site is filled with current research photos and informative discussions concerning the topic.
Geomicrobiology of the Tinto River, a model of interest for biohydrometallurgy Researchers have been using molecular and non molecular techniques to study the microbial ecology in the Tinto river (Southwestern Spain). The acidic conditions of the river (average pH 2.3) make it an example of an extreme environment. Researchers have found while sulfur does play a role in the rivers acidity Iron is the key element. Within the river Iron acts both as an substrate for oxidizing bacteria and as an electron acceptor in the anoxic areas of the river. Isotopic dating has concluded the rivers conditions have evolved from natural phenomena and are not the results of manmade pollutants. [9]
Key Laboratory of Marine Geology and Environment, Institute of Oceanology, China; has published on current research showing Rhodobaterales are primary surface colonizers in temperate costal marine waters. [10] In there study used nonnutritive inert materials such as plexi glass and glass to test for microorgansis in seawater off the Qingdao coast. The understanding is bacteria are know to be surface colonizers but which bacteria was relativly unknown untill now.
References
Campbell, B.J., Engel, A.S., Porter, M.L., and Takai, K. (2006) The versatile Epsilonproteobacteria: Key players in sulphidic habitats. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 4: 458-468. [11]
Dang, H., Li, T., Chen, M., Hunng, G. 2007.ross-Ocean Distribution of Rhodobacterales Bacteria as Primary Surface Colonizers in Temperate Coastal Marine Waters. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 70:1 52-60.
Delgado, G. Delgado, R., Parraga, J., Rivadeneyra, M. A., Aranda, V. 2008. Precipitation of Carbonates and Phosphates by Bacteria in Extract Solutions from a Semi-arid Saline Soil. Influence of Ca2+ and Mg2+ Concentrat ions and Mg2+/Ca2+ Molar Ratio in Biomineralization. Geomicro. J. 25:1–13.
Engelen, B., Ziegelmuller, K., Wolf, L., Kopke, B., Gittel, A., Cypionka, H., Treude, T., Nakagawa, S., Inahaki, F., Lever, M. A., Steinsbu, B. O. 2008. Fluids from the Oceanic Crust Support Microbial Activities within the Deep Biosphere. Geomicro. J. 25:56-66.
Fomina, M., Podgorsky, V. S., Olishevska, V., Kadoshnikov, V. M., Pisanska, I. R., Hillier, S., Gadd, G. M. 2007. Fungal Deterioration of Barrier Concrete used in Nuclear Waste Disposal. Geomicro. J. 24:643-653.
Gonzalez-Toril, E., Gomez, F.,Rodriquez, N., Fernandez, D., Zuluaga, J., Marin, I., and Amils, R. "Geomicrobiology of the Tinto River, a model of interest for biohydrometallurgy". Hydrometalluragy. 71:301-309.
Herrera, A., Cockell, C. S., Self, S., Blaxter, M., Reitner, J., Arp, G., Drose, W., Thorsteinsson, T. , Tindle, A. G.2008. Bacterial Colonization and Weathering of Terrestrial Obsidian in Iceland. Geomicro. J. 25: 25-37.
Metcalf, W. W., Wolfe, R. S. 1998. Molecular Genetic Analysis of Phosphite and Hypophosphite Oxidation by Pseudomonas stutzeri WM88. J. Bacter. 21: 5547-5558
Murray, K. J., Tebo, B. M. 2007. Cr(III) Is Indirectly Oxidized by the Mn(II)-Oxidizing Bacterium Bacillus sp. Strain SG-1 Environ. Science Technology. 41: 528-533.
Rosling, A., Suttle, K B., Johansson, E., Van Hees, P. A. W., Banfield, J. F. 2007. Phosphorous availability influences the dissolution of apatite by soil fungi. Geobiology 5 (3): 265–280.
Senko, J. M., Suflita, J. M., Krumholz, L. R. 2005. Geochemical Controls on Microbial Nitrate-Dependent U(IV) Oxidation. Geomicro. J. 22:371-378
Sylvia, D. M., Hartel, P. G., Fuhrmann, J. J., Zuberer, D. A. Principles of Applications of Soil Microbiology. 2nd edition. 2005. Pearson Prentice Hall.
Edited by student of Kate Scow
![[1]](/images/9/92/DCP_7175.JPG)
