Demodex folliculorum: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
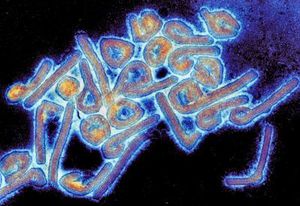
Demodex folliculorum is a species of mite that lives in human hair follicles. | Demodex folliculorum is a species of mite that lives in human hair follicles. The Demodex genus of parasitic mites contains sixty-five species found on sebaceous oil glands or hair follicles of mammals. D. folliculorum is most commonly localized on the human face particularly in the eyelashes and eyebrows. Infants will immediately acquire D. folliculorum from contact with other human hosts and the presence of mites increases throughout the human lifespan. | ||
Select a topic about genetics or evolution in a specific organism or ecosystem.<br> | Select a topic about genetics or evolution in a specific organism or ecosystem.<br> | ||
The topic must include one section about microbes (bacteria, viruses, fungi, or protists). This is easy because all organisms and ecosystems have microbes. | The topic must include one section about microbes (bacteria, viruses, fungi, or protists). This is easy because all organisms and ecosystems have microbes. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 32: | ||
Include some current research, with at least one image.<br><br> | Include some current research, with at least one image.<br><br> | ||
Sample citations: <ref>[http://www.plosbiology.org/article/fetchObject.action?uri=info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pbio.1000005&representation=PDF Hodgkin, J. and Partridge, F.A. "<i>Caenorhabditis elegans</i> meets microsporidia: the nematode killers from Paris." 2008. PLoS Biology 6:2634-2637.]</ref> | Sample citations: </ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Demodex_folliculorum</ref> | ||
</ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3884930/</ref> | |||
<ref>[http://www.plosbiology.org/article/fetchObject.action?uri=info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pbio.1000005&representation=PDF Hodgkin, J. and Partridge, F.A. "<i>Caenorhabditis elegans</i> meets microsporidia: the nematode killers from Paris." 2008. PLoS Biology 6:2634-2637.]</ref> | |||
<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3847443/ Bartlett et al.: Oncolytic viruses as therapeutic cancer vaccines. Molecular Cancer 2013 12:103.]</ref> | <ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3847443/ Bartlett et al.: Oncolytic viruses as therapeutic cancer vaccines. Molecular Cancer 2013 12:103.]</ref> | ||
<br><br>A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes. | <br><br>A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 49: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
<br>Edited by | <br>Edited by Scarlett Jones, student of [mailto:slonczewski@kenyon.edu Joan Slonczewski] for [http://biology.kenyon.edu/courses/biol116/biol116_Fall_2013.html BIOL 116 Information in Living Systems], 2019, [http://www.kenyon.edu/index.xml Kenyon College]. | ||
<!--Do not edit or remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Joan Slonczewski at Kenyon College]] | <!--Do not edit or remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Joan Slonczewski at Kenyon College]] | ||
Revision as of 01:54, 28 October 2019
Introduction
Demodex folliculorum is a species of mite that lives in human hair follicles. The Demodex genus of parasitic mites contains sixty-five species found on sebaceous oil glands or hair follicles of mammals. D. folliculorum is most commonly localized on the human face particularly in the eyelashes and eyebrows. Infants will immediately acquire D. folliculorum from contact with other human hosts and the presence of mites increases throughout the human lifespan.
Select a topic about genetics or evolution in a specific organism or ecosystem.
The topic must include one section about microbes (bacteria, viruses, fungi, or protists). This is easy because all organisms and ecosystems have microbes.
Compose a title for your page.
Type your exact title in the Search window, then press Go. The MicrobeWiki will invite you to create a new page with this title.
Open the BIOL 116 Class 2019 template page in "edit."
Copy ALL the text from the edit window.
Then go to YOUR OWN page; edit tab. PASTE into your own page, and edit.
At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki. The insertion code consists of:
Double brackets: [[
Filename: PHIL_1181_lores.jpg
Thumbnail status: |thumb|
Pixel size: |300px|
Placement on page: |right|
Legend/credit: Electron micrograph of the Ebola Zaire virus. This was the first photo ever taken of the virus, on 10/13/1976. By Dr. F.A. Murphy, now at U.C. Davis, then at the CDC.
Closed double brackets: ]]
Other examples:
Bold
Italic
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
Section 1 Genetics
Include some current research, with at least one image.
Sample citations: </ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Demodex_folliculorum</ref>
</ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3884930/</ref>
[1]
[2]
A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes.
Section 2 Microbiome
Include some current research, with a second image.
Conclusion
Overall text length should be at least 1,000 words (before counting references), with at least 2 images. Include at least 5 references under Reference section.
References
Edited by Scarlett Jones, student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 116 Information in Living Systems, 2019, Kenyon College.