Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
[Sample reference] [http://ijs.sgmjournals.org/cgi/reprint/50/2/489 Takai, K., Sugai, A., Itoh, T., and Horikoshi, K. "''Palaeococcus ferrophilus'' gen. nov., sp. nov., a barophilic, hyperthermophilic archaeon from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent chimney". ''International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology''. 2000. Volume 50. p. 489-500.] | [Sample reference] [http://ijs.sgmjournals.org/cgi/reprint/50/2/489 Takai, K., Sugai, A., Itoh, T., and Horikoshi, K. "''Palaeococcus ferrophilus'' gen. nov., sp. nov., a barophilic, hyperthermophilic archaeon from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent chimney". ''International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology''. 2000. Volume 50. p. 489-500.] | ||
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC358129/#:~:text=Erysipelothrix%20rhusiopathiae%20is%20a%20nonsporulating,of%20mammals%20and%20other%20animals. Reboli,A.,Farrar, W., "Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: an occupational pathogen." National Library of Medicine | [https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC358129/#:~:text=Erysipelothrix%20rhusiopathiae%20is%20a%20nonsporulating,of%20mammals%20and%20other%20animals. Reboli,A.,Farrar, W., "Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: an occupational pathogen." National Library of Medicine.] | ||
https://microbe-canvas.com/Bacteria/gram-positive-rods/cells-irregular/catalase-negative-8/vancomycin-resistent/erysipelothrix-rhusiopathiae.html. Microbe Canvas. "Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae." Dept. Medical Microbiology and Infectious diseases | [https://microbe-canvas.com/Bacteria/gram-positive-rods/cells-irregular/catalase-negative-8/vancomycin-resistent/erysipelothrix-rhusiopathiae.html. Microbe Canvas. "Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae." Dept. Medical Microbiology and Infectious diseases.] | ||
==Author== | ==Author== | ||
Revision as of 01:44, 27 November 2024
Classification
Bacteria; Bacillota; Erysipelotrichia; Erysipelotrichales; Erysipelotrichaceae; Erysipelothrix.
Species
|
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: [1] |
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Description and Significance
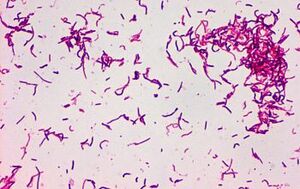
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae is a gram-positive bacteria, and is also in the shape of a rod. It is found predominantly in soil and water that has been infected by an animal containing the bacteria. One of the primary animals susceptible to it are pigs. This bacteria has a longer lifespan and can live for weeks in soil or animal matter. This is all important to not only protect animals from it, but humans as well. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae is zootonic which means it can jump from animals to humans. Being able to safely manage this bacteria is important for the health of humans.
Genome Structure
Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence?
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Habitat; symbiosis; biogeochemical significance; contributions to environment.
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
References
Microbe Canvas. "Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae." Dept. Medical Microbiology and Infectious diseases.
Author
Page authored by Isabelle Oberdorf, Makayla Watson, Keanna Teodoro, & Jacqui Olsen, students of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington.