Desulfococcus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Desulfococcus groups are one of the most active population in coastal sediments. | ''Desulfococcus'' groups are one of the most active population in coastal sediments. | ||
In general, | In general, sulfate-reducing bacteria group are considered as obligate anaerobes, but some SRB can survive in the presence of oxygen. For example, ''Duslfobulbus'', ''Desulfobacter'' and ''Desulfotomaculum'' species are predominant in the lower part of sediments, while the ''Desulfococcus'' and ''Deuslfovibrio'' groups predominantly occupy in the upper part of the photo-oxic zone (Risatti et al, 1994). However, in oxic condition ''Desulfococcus use energy only for maintenance. They can grow only at anoxic condition so that they are considered as anaerobic bacteria. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Edited by student of Kate Scow | Edited by student of Kate Scow | ||
Revision as of 02:51, 17 March 2008
A Microbial Biorealm page on the genus Desulfococcus
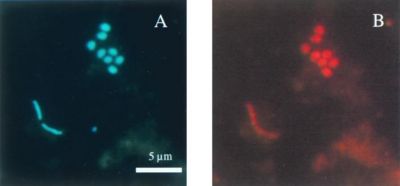
Classification
Higher order taxa:
Bacteria; Proteobacteria; delta/epsilon subdivisions; Deltaproteobacteria; Desulfobacterales; Desulfobacteraceae
Species:
|
NCBI: Taxonomy Genome: Desulfococcus oleovorans Hxd3 ' |
Desulfococcus biacutus, Desulfococcus multivorans, Desulfococcus oleovorans, Desulfococcus sp. DSM 8541
Description and Significance
Desulfococcus group is cultivated bacteria as well as Desulfosarcina. They can completely oxidize acetate by using sulfate as electron acceptor under anoxic condition. They are involved in Chemoautotrophs, anaerobic, thermophilic and mesophilic bacteria. In coastal marine sediments, over 50% of carbon is decomposed by sulfate-reducing bacteria including Desulfococcus. Also, they play an important role in the cycling of sulfur compounds of in sea water(Das et al 2006).
Genome Structure
The genome of Desulfococcus oleovorans is completely sequenced. Desulfococcus oleovorans is a sulfate-reducing δ-proteobacterium. Strain Hxd3 of Desulfococcus oleoborans was isolated from an oil tank. Desulfococcus oleoborans can use alkanes from C12 to C20 due to strain Hxd3, they have best growth rate in the range form C15 to C18.
Cell Structure and Metabolism
Desulfococcus are sphere shape bacteria. Desulfococcus oleovorans can use alkanes from C12 to C20, 1-hexadecene, 1-hexadecanol, 2-hexadecanol, palmitate and stearate as electron donors and sulfate as terminal electron acceptor for the growth(Aeckersberg et al., 1991). This indicates that Desulfococcus oleovorans play an crucial role in the accumulation of sulfide(Rueter et al., 1994). Also, Desulfococcus have the capability of detoxifying mercury compounds. Desulfococcus can methylate mercury(Macalady et al 2000)
Ecology
Desulfococcus groups are one of the most active population in coastal sediments. In general, sulfate-reducing bacteria group are considered as obligate anaerobes, but some SRB can survive in the presence of oxygen. For example, Duslfobulbus, Desulfobacter and Desulfotomaculum species are predominant in the lower part of sediments, while the Desulfococcus and Deuslfovibrio groups predominantly occupy in the upper part of the photo-oxic zone (Risatti et al, 1994). However, in oxic condition Desulfococcus use energy only for maintenance. They can grow only at anoxic condition so that they are considered as anaerobic bacteria.
References
Edited by student of Kate Scow
