Methylothermus thermalis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ||
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces. | Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces. | ||
| Line 54: | Line 57: | ||
[[Image:TableI II X.jpg|frame| Characteristics of type I, type II, and type X methanotrophs; phylogenetic signature probes 1041 and 1035 will not hyidize with 16S rRNAs from members of the genus Methylomonas. Probes MM650 and MM850 have been employed to detect some species in this genus. From https://www.ocean.udel.edu/cms/thanson/TH-MicroRev.pdf Hanson R and Hanson T, 1996.].]] | [[Image:TableI II X.jpg|frame| Characteristics of type I, type II, and type X methanotrophs; phylogenetic signature probes 1041 and 1035 will not hyidize with 16S rRNAs from members of the genus Methylomonas. Probes MM650 and MM850 have been employed to detect some species in this genus. From https://www.ocean.udel.edu/cms/thanson/TH-MicroRev.pdf Hanson R and Hanson T, 1996.].]] | ||
Revision as of 03:38, 21 April 2008
Classification
Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Methylococcales; Methylococcaceae
Species
|
Methylothermus thermalis |
|
NCBI: Taxonomy |
Description and Significance
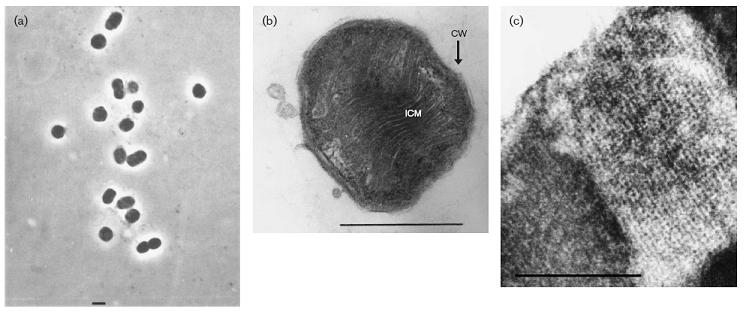
Gram-negative, non-motile coccoids 0.6-0.8 micrometers in diameter. Describe the appearance, habitat, etc. of the organism, and why you think it is important.
Genome Structure
the nifH gene was not detected with PCR analysis. Also, the mmoX gene was not detected by PCR using the respective primer set that is universal for the known mmoX genes of methanotrophs. Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence?
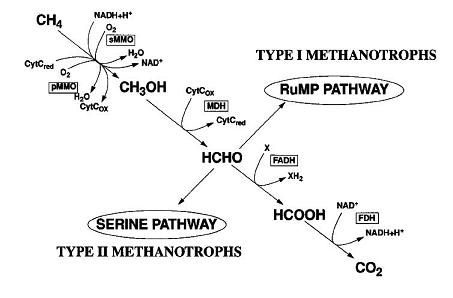
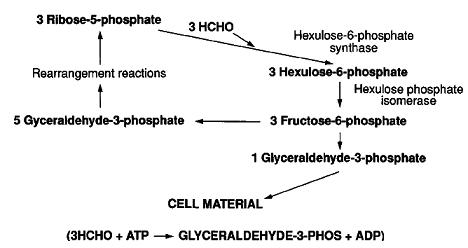
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Ecology
Japanese Hot Spring; Require methane or methanol as a carbon source to growth. Can use nitrate, ammonia, urea, tryptophan,
lysine, glutamate, formamide and Triss as nitrogen sources, but no growth was obsevered without one of these sources. symbiosis; biogeochemical significance; contributions to environment.

References
Author
Page authored by Anthony Heidt and James Goodrow Jr., student of Prof. Jay Lennon at Michigan State University.