Ear: Difference between revisions
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
Ear infections usually start with a viral infection, such as a cold. The middle ear becomes inflamed from the infection, and fluid builds up behind the eardrum. | Ear infections usually start with a viral infection, such as a cold. The middle ear becomes inflamed from the infection, and fluid builds up behind the eardrum. | ||
Ear infections also can be associated with dysfunction or swelling within the Eustachian tubes - the narrow passageways that connect the middle ear to the nose. Normally these tubes equalize pressure inside and outside the ear. But a child's Eustachian tubes are narrower and shorter than those of an adult. This makes it easier for fluid to get trapped in the middle ear when the Eustachian tubes dysfunction or become blocked during a cold. | Ear infections also can be associated with dysfunction or swelling within the Eustachian tubes - the narrow passageways that connect the middle ear to the nose. Normally these tubes equalize pressure inside and outside the ear. But a child's Eustachian tubes are narrower and shorter than those of an adult. This makes it easier for fluid to get trapped in the middle ear when the Eustachian tubes dysfunction or become blocked during a cold. | ||
Another factor in ear infections is swelling of the adenoids. These are tissues located in the upper throat near the Eustachian tubes. Adenoids contain lymphocytes - cells that normally fight infection. But sometimes the adenoids themselves get infected or enlarged, blocking the Eustachian tubes. Infection in the adenoids can also spread to the Eustachian tubes. | Another factor in ear infections is swelling of the adenoids. These are tissues located in the upper throat near the Eustachian tubes. Adenoids contain lymphocytes - cells that normally fight infection. But sometimes the adenoids themselves get infected or enlarged, blocking the Eustachian tubes. Infection in the adenoids can also spread to the Eustachian tubes. | ||
The most common bacteria that grows in the middle ear and causes Otitis media is Haemophilus Influenzae. It is Gram negative bacteria where it has a thin cell walls. “It | The most common bacteria that grows in the middle ear and causes Otitis media is Haemophilus Influenzae. It is Gram negative bacteria where it has a thin cell walls. “It | ||
is generally aerobic but can grow as a facultative anaerobe” (4). According to a current research there is some environment in the middle ear that helps the bacteria grow and survive like histidine “Our results suggest that the ability to make histidine is an important factor in bacterial growth and survival in the middle ear, where nutrients such as histidine may be found in limiamounts”(5). | is generally aerobic but can grow as a facultative anaerobe” (4). According to a current research there is some environment in the middle ear that helps the bacteria grow and survive like histidine “Our results suggest that the ability to make histidine is an important factor in bacterial growth and survival in the middle ear, where nutrients such as histidine may be found in limiamounts”(5). | ||
This infection or the microbe mostly effect children under 6 years old. Children at young age can not fight the microbe or a bacterium that enters their body like adults do. For many reasons, children at a young age their bodies start growing and by time they get stronger. Children’s immune system develops and gets stronger when they grow completely. That is one reason why at a young age their body can not fight any microbe they detect as they do when they’re older. | This infection or the microbe mostly effect children under 6 years old. Children at young age can not fight the microbe or a bacterium that enters their body like adults do. For many reasons, children at a young age their bodies start growing and by time they get stronger. Children’s immune system develops and gets stronger when they grow completely. That is one reason why at a young age their body can not fight any microbe they detect as they do when they’re older. | ||
Otitis media happens when a child gets a virus that infects the Eustachian tube, “this tube connects between the nose and the middle ear” (2). Children start feeling pain and fluid start draining from ears. “The lack of ventilation may allow fluid from the tissue that lines the middle ear to accumulate. If the eustachian tube remains plugged, the fluid cannot drain and begins to collect in the normally air-filled middle ear” (3). | Otitis media happens when a child gets a virus that infects the Eustachian tube, “this tube connects between the nose and the middle ear” (2). Children start feeling pain and fluid start draining from ears. “The lack of ventilation may allow fluid from the tissue that lines the middle ear to accumulate. If the eustachian tube remains plugged, the fluid cannot drain and begins to collect in the normally air-filled middle ear” (3). | ||
The second common bacteria that causes the Otitis media infection is Moraxella catarrhalis(aka also known as Branhamella catarrhalis.) It is a bacterium belonging to the Neisseriaceae family. It is considered to cause of middle ear infections and sinusitis in children, and lower respiratory infections in adults. It has also been attributed to pneumonia, bronchitis, meningitis, neonatal ophthalmia, and urinary tract infections. This bacterium is an aerobic, gram negative diplococcus. It is kidney bean shaped and is 0.6 - 1.0 um in diameter and often appears in pairs or tetrads. | The second common bacteria that causes the Otitis media infection is Moraxella catarrhalis(aka also known as Branhamella catarrhalis.) It is a bacterium belonging to the Neisseriaceae family. It is considered to cause of middle ear infections and sinusitis in children, and lower respiratory infections in adults. It has also been attributed to pneumonia, bronchitis, meningitis, neonatal ophthalmia, and urinary tract infections. This bacterium is an aerobic, gram negative diplococcus. It is kidney bean shaped and is 0.6 - 1.0 um in diameter and often appears in pairs or tetrads. | ||
Revision as of 04:50, 27 August 2008
Intro to the Ear
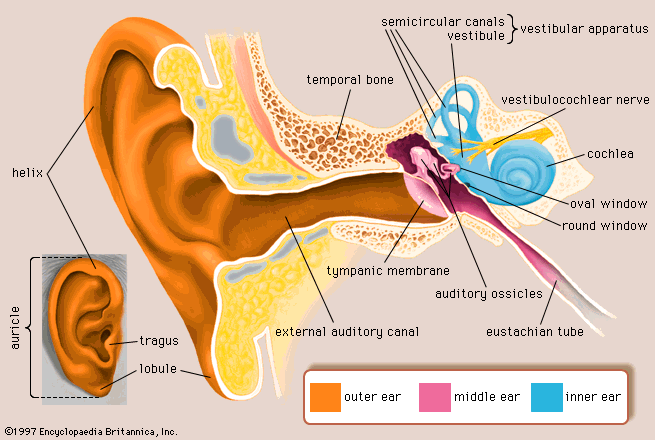
The Human Ear: The human ear is comprised of 3 main parts: outer, middle, and inner. The outer ear consists of the pinna, which is the visible part of the ear, and the auditory ear canal to the tympanic membrane(ear drum). The membrane separates the outer ear from the middle ear which is an air-filled space that is connected to the nasopharynx via the eustachian tube. The middle ear consists of the malleus, incus, and stapes. These three tiny bones carry sound from the ear drum to the inner ear. The inner ear (aka the bony labyrinth) is comprised of the membraneous labyrinth which encloses both cochlea and the vestibular apparatus.(1)
Physical Conditions of the Normal Healthy Ear
The conditions of the pinna are similar to that of the skin. Closer to the ear canal the skin develops a thin lining of ear wax. Ear wax is composed mostly of dead skin cells and keratin with a small mixture of cerumen, sweat, and oil. Cerumen is secreted from the ceruminous glands located in the first third outer part of the ear canal and is thought to be composed mainly of cholesterol, squalene, wax esters, ceramides, and triglycerides. The cerumen also has antibacterial/fungal properties which can be attributed to its slight acidic pH of 6.1 and the presence of lysozyme. In normal individuals, the ear wax is continuously pushed out of the ear canal by the slow migration of the top layer of skin cells from the tympanic membrane towards the outer ear. The ear wax traps any foreign particles/organisms on its way out. The ear canal is a dark, moist, close to body temperature(~37C), and abundant with nutrients from dead skin cells.(2)(3) If not for the cerumen, the ear canal would be a very hospital place for microbes.
The middle ear, or tympanic cavity, is an air filled space that is connected to the outer ear via the tympanic membrane and the inner ear via the fenestra vestibuli. A mucous membrane lines the middle ear that is continuous with the nasal passageways and nasopharynx via the eustachian tube. This continuity allows the person to equalize the air pressure inside the cavity with that of the outside environment. The mucus serves to trap any particles and microbes that are inside and slowly move it towards the throat to be swallowed or coughed out. This migration of mucus is important to prevent microbes from colonizing as the tympanic cavity would otherwise present a very favorable environment for microbes. It is abundant in nutrients, moist, dark, protected from the external environment, and at body temperature. (4)
The inner ear consists of two labyrinth structures. The bony labyrinth and the membraneous labyrinth. The bony labyrinth is filled with a fluid called perilymph and encloses the membraneous labyrinth. The membraneous labyrinth comprises the vestibular apparatus and the cochlea. It is filled with a seperate fluid that does not mix with the perilymph called endolymph. The both fluids are derived from blood plasma implying a high concentration of nutrients and a similar pH (~7.4). A characteristic of perilymph is that its concentration of sodium is high (about 150 milliequivalents per litre) and its concentration of potassium is low (about 5 milliequivalents per litre), similar to other extracellular fluids. Conversely endolymph has a low concentration of sodium (about 15 milliequivalents per litre) and a high concentration of potassium (about 140 milliequivalents per litre).(5) Since the inner ear is completely membrane enclosed, it should be virtually imperveous to bacterial colonization under normal circumstances.
Microbes in the Healthy Ear
Because it is exposed to the outside environment, despite the best efforts of the ceruminous glands, the normal healthy outer ear still houses a variety of microbes. The some of the most common bacteria are Staphylococcus epidermis, Turicellaotitidis, Alloiococousotitis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Corynebacterium, Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus saprophyticum. The most common fungal microbe known to reside in the ear is Candida albicans. (7)(8)
Microbes that are known to inhabit the middle ear are Streptococci, Haemophilus pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and less commonly mycobacterium.
The healthy inner ear should be virtually microbe free.
Interactions Between microbes
In the middle ear, research shows that alpha hemolytic streptococci from healthy children inhibit pneumococci and H. influenzae, two pathogens that cause Otitis media. (9)
Normal Changes to the Environment of the Ear
Do any of the physical conditions change? How do those changes affect the microbes?
In regards to the ear, the environment of the outer ear is subject to the most variation as it is exposed to the outside environment. One of the biggest effects on the environment of the ear would be those that remove the ear wax. This can occur through excessive showering or swimming as water/soap can wash away the thin protective lining of ear wax. Loss of the cerumen encourages the growth of microbes that are normally kept under control by its antimicrobial properties. Use of cotton swaps or hair pins is also common practice as a means to remove ear wax. In addition to the removal of the ear wax, they can also scratch the surface of the skin which can allow microbes to get in to the unprotected tissue. Use of cotton swabs also can push the ear wax further into the canal, which if allowed to build up can become impacted and damage the inner ear canal and the tympanic membrane. These too provide opportunities for microbes to infect the underlying tissue.
The infectous opportunity of the ear also grows smaller as the person grows older. Young children with immature immune systems are more susceptible to infection by microbes than are adults with developed immune systems.
Blockage of the Eustachian tube can also increase the likelihood of ear infections. This occurs when the mucus in the tube gets too thick or becomes blocked as can occur during a cold or allergies. Blockage of the tube prevents a healthy flow of mucus out of the middle ear.
Infections of the Ear
When do microbes infect the ear, what conditions? Why do those conditions allow the microbes do infect the ear? How do other infections cause a change in the conditions of the ear? How do those change in conditions allow other microbes to infect the ear?
Middle Ear: The middle ear is the small part of eardrum. It can get infected when microbes from the nose and throat are trapped there. A cold could cause Eustachian tube that connects pharynx to the middle ear swell. When the tube swells enough to become blocked, it can trap fluid inside the ear. This makes it a perfect place for germs to grow and cause an infection. The medical term for middle ear infections is otitis media. Otitis refers to inflammation of the ear, and media means middle. Ear infections usually start with a viral infection, such as a cold. The middle ear becomes inflamed from the infection, and fluid builds up behind the eardrum. Ear infections also can be associated with dysfunction or swelling within the Eustachian tubes - the narrow passageways that connect the middle ear to the nose. Normally these tubes equalize pressure inside and outside the ear. But a child's Eustachian tubes are narrower and shorter than those of an adult. This makes it easier for fluid to get trapped in the middle ear when the Eustachian tubes dysfunction or become blocked during a cold.
Another factor in ear infections is swelling of the adenoids. These are tissues located in the upper throat near the Eustachian tubes. Adenoids contain lymphocytes - cells that normally fight infection. But sometimes the adenoids themselves get infected or enlarged, blocking the Eustachian tubes. Infection in the adenoids can also spread to the Eustachian tubes.
The most common bacteria that grows in the middle ear and causes Otitis media is Haemophilus Influenzae. It is Gram negative bacteria where it has a thin cell walls. “It is generally aerobic but can grow as a facultative anaerobe” (4). According to a current research there is some environment in the middle ear that helps the bacteria grow and survive like histidine “Our results suggest that the ability to make histidine is an important factor in bacterial growth and survival in the middle ear, where nutrients such as histidine may be found in limiamounts”(5). This infection or the microbe mostly effect children under 6 years old. Children at young age can not fight the microbe or a bacterium that enters their body like adults do. For many reasons, children at a young age their bodies start growing and by time they get stronger. Children’s immune system develops and gets stronger when they grow completely. That is one reason why at a young age their body can not fight any microbe they detect as they do when they’re older. Otitis media happens when a child gets a virus that infects the Eustachian tube, “this tube connects between the nose and the middle ear” (2). Children start feeling pain and fluid start draining from ears. “The lack of ventilation may allow fluid from the tissue that lines the middle ear to accumulate. If the eustachian tube remains plugged, the fluid cannot drain and begins to collect in the normally air-filled middle ear” (3).
The second common bacteria that causes the Otitis media infection is Moraxella catarrhalis(aka also known as Branhamella catarrhalis.) It is a bacterium belonging to the Neisseriaceae family. It is considered to cause of middle ear infections and sinusitis in children, and lower respiratory infections in adults. It has also been attributed to pneumonia, bronchitis, meningitis, neonatal ophthalmia, and urinary tract infections. This bacterium is an aerobic, gram negative diplococcus. It is kidney bean shaped and is 0.6 - 1.0 um in diameter and often appears in pairs or tetrads.
Resources
1)
2)
3)^Bortz JT, Wertz PW, Downing DT. "Composition of cerumen lipids." J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990 Nov;23(5 Pt 1):845-9.
4)^James E. Crouch. "Functional Human Anatomy" Lea and Febiger 1978
5)^Encyclopedia Britannica. "Anatomy of the Human Ear" http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/175622/ear/65043/Endolymph-and-perilymph#tab=active~checked%2Citems~checked&title=human%20ear%20%3A%3A%20Endolymph%20and%20perilymph%20--%20Britannica%20Online%20Encyclopedia
7)^Stroman DW, Roland PS, Dohar J, Burt W. "Microbiology of normal external auditory canal." Laryngoscope. 2001 Nov;111(11 Pt 1):2054-9
8)^Campos A, Arias A, Betancor L, Rodríguez C, Hernández AM, López Aguado D, Sierra A. "Study of common aerobic flora of human cerumen." J Laryngol Otol. 1998 Jul;112(7):613-6
9)^Tano K, Grahn-Håkansson E, Holm SE, Hellström S. "Inhibition of OM pathogens by alpha-hemolytic streptococci from healthy children, children with SOM and children with rAOM." Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2000 Dec 22;56(3):185-90.
http://www.meddean.luc.edu/depts/otolaryn/patient_ed/pdf/ENT%20INNER%20EAR%20FLUID%20IMBALANCE.pdf
http://jama.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/abstract/291/8/981 ( Outbreak of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections Caused by Piercing of Upper Ear Cartilage)
a. Ronna Staley, MD, James J. Fitzgibbon, MD, Catherine Anderson, and LSM, MSN. "Auricular Infections Caused by High Ear Piercing in Adolescents." PEDIATRICS. Vol. 99 No. 4 April 1997, pp. 610-611