Wigglesworthia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Biorealm}} | |||
{| | {| | ||
| height="69" bgcolor="#FFDF95" | | | height="69" bgcolor="#FFDF95" | | ||
Revision as of 14:33, 14 August 2006
A Microbial Biorealm page on the Wigglesworthia

Classification
Higher order taxa:
Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Enterobacteriales; Enterobacteriaceae
Species:
Wigglesworthia glossinidia, W. pallidipes
Description and Significance
Wigglesworthia, discovered by British entomologist Sir Vincent Brian Wigglesworth, are Gram-negative bacteria. Although much is known about its symbiotic relationship with the tsetse fly (Glossina spp.), few other characteristics of Wigglesworthia are understood because attempts to cultivate it in a laboratory setting have not yet been successful.
Genome Structure
The Wigglesworthia glossinidia genome was first sequenced in 2002, by Leyla Akman and Serap Aksoy. However, more research on the genome sequence is being completed on a regular basis. Because the organism cannot be cultivated in a laboratory, Akman and Aksoy took the bacterial DNA directly from tsetse fly guts. The Wigglesworthia genome is one of the smallest genomes sequenced, since the genome shrunk over the years. Since it co-evolved with the tsetse fly, it was able to eliminate genes already contained by its host. Although a symbiotic organism, the Wigglesworthia glossinidia genome contains many genes of free-living organisms, such as genes for motility.
Cell Structure and Metabolism
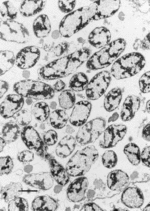
Wiggleworthia are rod-shaped. Although they are nonmotile, these organisms do contain genes that synthesize for flagella.
Wigglesworthia is an obligate organism. It recieves nutrients from the tsetse fly. However, little is known about this organism's metabolic processes because it is so difficult to study.
The Wigglesworthia life cycle is typical of other bacteria; it includes reproduction by division.
Ecology
Wigglesworthia is best known for the symbiotic relationship between Wigglesworthia glossinidia and the tsetse fly. In fact, W. glossinidia is unable to survive outside of its host. Research suggests that the bacteria infected its host 50 to 80 million years ago. Bacteria are vertically transmitted, passed from mother to offspring during reproduction. Wigglesworthia glossinidia is housed in specialized cells called mycetocytes (bacteriocytes). The mycetocytes form a specialized organelle called the mycetome. The tsetse fly transmits African trypanosomes, parasites that cause African sleeping sickness. Wigglesworthia glossinidia is acquired through reproduction; mother flies pass it on to their young. The tsetse fly requires this bacterium to provide it with vitamins not naturally found in its diet. These vitamins are required for the fly's fertitliy. Without the bacteria, the tsetse fly is sterile.
Within the tsetse fly, the trypanosomes aggregate around the mycetocytes, suggesting that they obtain nutrients from W. glossinidia as well. Currently, researchers are studying ways to remove Wigglesworthia glossinidia from the gut of the fly, thus controlling African sleeping sickness. Research performed by Dale and Welburn (2001) indicates that broad-spectrum antibiotics such as ampicillin an tetracycline destroy Wigglesworthia glossinidia, preventing growth and reproduction in its host.
