Tea Tree Oil Treatment of MRSA: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
TTO composition is internationally regulated and may be available in various chemotypes, including the terpinen-4-ol chemotype and terpinolene chemotype.<sup>2</sup> Terpinen-4-ol comprises between 30 to 40% of TTO's commercial composition.<sup>2</sup> International regulation of TTO composition calls for this relatively high composition of terpinen-4-ol in commercial production due to its historical medicinal properties. | TTO composition is internationally regulated and may be available in various chemotypes, including the terpinen-4-ol chemotype and terpinolene chemotype.<sup>2</sup> Terpinen-4-ol comprises between 30 to 40% of TTO's commercial composition.<sup>2</sup> International regulation of TTO composition calls for this relatively high composition of terpinen-4-ol in commercial production due to its historical medicinal properties. | ||
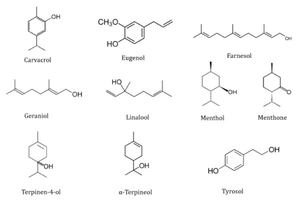
[[Image:terpene_deriv.png|thumb|300px|right|text-top|Figure 1: Formulae of the eight terpenic derivatives (carvacrol, farnesol, geraniol, linalool, menthol, menthone, terpinen-4-ol, and α-terpineol),the phenylpropanoid (eugenol) and the phenethyl alcohol (tyrosol) studied by Marcos-Arias, C et al. Reference: Marcos-Arias, C., Eraso, E., Madariaga, L., Quindós, G. <i>Complement Altern Med</i> (2011). Figure obtained from NIH's Open Access Database.]<br> | [[Image:terpene_deriv.png|thumb|300px|right|text-top|Figure 1: Formulae of the eight terpenic derivatives (carvacrol, farnesol, geraniol, linalool, menthol, menthone, terpinen-4-ol, and α-terpineol),the phenylpropanoid (eugenol) and the phenethyl alcohol (tyrosol) studied by Marcos-Arias, C et al. Reference: Marcos-Arias, C., Eraso, E., Madariaga, L., Quindós, G. <i>Complement Altern Med</i> (2011). Figure obtained from NIH's Open Access Database.]]<br> | ||
==Antimicrobial Activity== | ==Antimicrobial Activity== | ||
Revision as of 04:56, 25 March 2013
Introduction
Antibiotic resistance is a growing problem. As more pathogens become resistant to commonly used antibiotics, they become more difficult for medical practitioners to treat. The impotence of common antibiotics underscores the importance of determining alternative anti-microbial treatments. Studies indicate the effectiveness of tea tree oil as treatment for infections of drug-resistant bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, or MRSA.
Staphyloccocus aureus, also known as staph bacteria or MRSA, is a Gram-positive coccus-shaped anaerobic bacterium. MRSA often colonizes on the skin or nostrils of healthy individuals, and is relatively harmless at these sites. If S. aureus enters the body (e.g., wounds, cuts), it may cause infections. In such instances, the MRSA infection may range from mild (e.g., pimples)to life-threatening (e.g., infection of bloodstream, joints, or bones). MRSA is spread through contact and most commonly contracted in public settings.
Tea tree oil is the essential oil derived from the Australian native plant Melaleuca alternifolia. Tea tree oil has been topically applied for centuries as a folk remedy for acne, lice, athlete's foot, and a number of other conditions. Clinical studies indicate that tea tree oil can also treat skin infection caused by MRSA. MRSA is a type of staph bacteria that is resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics, such as penicillin, amoxicillin, oxacillin, and methicillin. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), MRSA is a public health problem as it is commonly contracted in healthcare and community settings. Tea tree oil's bacteriocidal and bacteriostatic effects make this plant extract a plausible addition or supplement to a MRSA treatment plan. Tea tree oil's anti-microbial properties are attributed to its composition of a chemical class known as terpenes, specifically terpinene-4-ol.
Tea Tree Oil Composition and Chemistry
Commercially available tea tree oil (TTO) is a composition of nearly 100 chemical compounds determined by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.1 TTO is primarily composed of a class of chemicals called terpenes. Specifically, monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, and other terpene alcohols dominate this composition. Terpenes are volatile, aromatic hydrocarbons and are typically soluble with nonpolar solvents. 2 Terpinen-4-ol is the specific compound believed responsible for TTO's anti-microbial activity.2 It is a monoterpene alcohol with the chemical formula C10H18O. It is believed to be the primary antimicrobial component of TTO.
TTO composition is internationally regulated and may be available in various chemotypes, including the terpinen-4-ol chemotype and terpinolene chemotype.2 Terpinen-4-ol comprises between 30 to 40% of TTO's commercial composition.2 International regulation of TTO composition calls for this relatively high composition of terpinen-4-ol in commercial production due to its historical medicinal properties.
Antimicrobial Activity
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Side Effects
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Conclusion
Overall paper length should be 3,000 words, with at least 3 figures.
References
http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/MRSA/Pages/Introduction.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0004520/
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/natural/113.html
http://epubs.scu.edu.au/cpcg_pubs/482/
http://openi.nlm.nih.gov/detailedresult.php?img=3258290_1472-6882-11-119-1&req=4
1. Brophy, J. J., N. W. Davies, I. A. Southwell, I. A. Stiff, and L. R. Williams. 1989. Gas chromatographic quality control for oil of Melaleuca terpinen-4-ol type (Australian tea tree). J. Agric. Food Chem. 37:1330-1335.
2. Carson, C. F., Hammer, K. A., Riley, T. V. Malalueca alternifolia (tea tree) oil: a review of antimicrobial and other medicinal properties. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 19, 50-62 (2008)
3. Griffin, S. G., S. G. Wyllie, J. L. Markham, and D. N. Leach. 1999. The role of structure and molecular properties of terpenoids in determining their antimicrobial activity. Flav. Fragr. J. 14:322-332.
Edited by Karen Leung, a student of Nora Sullivan in BIOL187S (Microbial Life) in The Keck Science Department of the Claremont Colleges Spring 2013.