Spiroplasma melliferum: Difference between revisions
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
==Metabolism== | ==Metabolism== | ||
<I>Spiroplasma melliferum</I> ferments glucose and hydrolyzes arginine (1). It also possesses all the genes required for glycolysis to convert glucose-6-phophate into pyruvate which is used for the production of cysteine (1). | |||
Revision as of 17:01, 11 January 2014
A Microbial Biorealm page on Spiroplasma melliferum
Classification
Higher Order Taxa:
Class: Mollicutes
Order: Mycoplasmatales
Family: Spiroplasmataceae
Genus: Spiroplasma
Species: melliferum
NCBI Accession #: JQ347516
Description and Significance
Genome Structure
The whole-genome shotgun sequencing of S. Melliferum IPMB4A produced a draft assembly that was ~1.1 Mb in size and covered ~80% of the chromosome (1).
Cell and Colony Structure
Spiroplasma melliferum is a helical, motile bacteria without cell walls (1). Spiroplasma melliferum has a classic fried-egg shaped colony morphology.
Metabolism
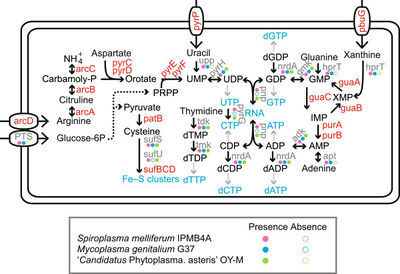
Spiroplasma melliferum ferments glucose and hydrolyzes arginine (1). It also possesses all the genes required for glycolysis to convert glucose-6-phophate into pyruvate which is used for the production of cysteine (1).
Ecology
Endosymbiotic inhabitants.
Pathology
While most of the Spiroplasma species appeared to be harmless commensals of insects, a small number of species have evolved pathogenicity toward various arthropods and plants (1).
Host: infects the honeybee.