Candidatus Solibacter usitatus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
This species was initially isolated from rotationally grazed pasture of perennial ryegrass and white clover in Victoria, Australia (1). | This species was initially isolated from rotationally grazed pasture of perennial ryegrass and white clover in Victoria, Australia (1). | ||
It has an exceptionally large genome and is theorized to engage in horizontal gene transfer which contributes to its ability to persist in an environment. This species produces enzymes capable of breaking down organic carbon for metabolism and also participates in reducing nitrates. These forms of metabolism lend to this species ability to create heterogeneous nutrient concentrations throughout the soil it inhabits ( | It has an exceptionally large genome and is theorized to engage in horizontal gene transfer which contributes to its ability to persist in an environment. This species produces enzymes capable of breaking down organic carbon for metabolism and also participates in reducing nitrates. These forms of metabolism lend to this species ability to create heterogeneous nutrient concentrations throughout the soil it inhabits (2). | ||
This species growth has been observed microscopically in soils as filamentous, but it forms clusters when grown in liquid culture (3). In nature, this species produces a biofilm which acts as an ecosystem engineer in soil. It does this by producing a medium that resides between soil particles. As the species engages in ion transfer with the environment it produces the biofilm to protect itself. This slowly expanding biofilm reduces moisture and nutrient fluxuations in the soil environment. This contributes to a species ability to survive under stressful environmental conditions ( | This species growth has been observed microscopically in soils as filamentous, but it forms clusters when grown in liquid culture (3). In nature, this species produces a biofilm which acts as an ecosystem engineer in soil. It does this by producing a medium that resides between soil particles. As the species engages in ion transfer with the environment it produces the biofilm to protect itself. This slowly expanding biofilm reduces moisture and nutrient fluxuations in the soil environment. This contributes to a species ability to survive under stressful environmental conditions (2). | ||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
[[Image:Whole_genome_Structure.jpg|thumbnail|295px|Figure 2. Whole genome sequence for ''Candidatus Solibacter usitatus''. Image from the IMG system [http://img.doe.gov]]] | [[Image:Whole_genome_Structure.jpg|thumbnail|295px|Figure 2. Whole genome sequence for ''Candidatus Solibacter usitatus''. Image from the IMG system [http://img.doe.gov]]] | ||
Based on whole genome sequencing, this species was found to have a 9.9 Mb long genome ( | Based on whole genome sequencing, this species was found to have a 9.9 Mb long genome (4), which is about twice the size of other closely related Acidiobacteria found to inhabit soil (2). Horizontal gene transfer is hypothesized to account for how this species acquired its unusual genome size (2), and also implies biological and ecological strains upon the living organism (4). It is theorized that the amount of mobile elements encoded in a genome correlate with the historical frequency of horizontal gene transfer events. This is significant because mobile elements are theorized to contribute toward genome plasticity and evolution over time, which could provide a competitive advantage to this species and enable it to exploit various environmental resources (5). | ||
A large number of genes encoding for carbohydrate transport and metabolism were found. This species has more genes encoding these functions than “the human genome and about three times as many as Saccharomyces cerevisiae” ( | A large number of genes encoding for carbohydrate transport and metabolism were found. This species has more genes encoding these functions than “the human genome and about three times as many as Saccharomyces cerevisiae” (6). These genes were also found to have high sequence similarity with fungal homologs which further suggests an ancestral horizontal gene transfer (2). | ||
Genes encoding for candidate cellulases of glycoside hydrolases were found, which suggests this species is capable of degrading cellulose substrates and implies the genome is also encoded with other enzymes capable of degrading plant compounds ( | Genes encoding for candidate cellulases of glycoside hydrolases were found, which suggests this species is capable of degrading cellulose substrates and implies the genome is also encoded with other enzymes capable of degrading plant compounds (2). Further analysis also suggests this species has the flexibility to metabolize carbon as a mixotroph because it contains genes encoding for carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (7). Since oxidation of carbon monoxide has been prevalently documented among other major groups of soil organisms (7), it is hypothesized that this along with the ability to degrade complex polymers associated with vegetation, occur as a survival mechanism in environments with low carbon concentration (2). | ||
The genetic potential for nitrate reductase was observed. This potential is significant because nitrogen reduction is a multi-step process yielding in molecular nitrogen, which is a limiting nutrient in ecosystems. This species ability to reduce nitrates leads to heterogeneous deposition and subsequent spatial variability in nutrient concentrations across a landscape. No evidence for nitrogen fixation or denitrification has been demonstrated ( | The genetic potential for nitrate reductase was observed. This potential is significant because nitrogen reduction is a multi-step process yielding in molecular nitrogen, which is a limiting nutrient in ecosystems. This species ability to reduce nitrates leads to heterogeneous deposition and subsequent spatial variability in nutrient concentrations across a landscape. No evidence for nitrogen fixation or denitrification has been demonstrated (2). | ||
While this species is not thought to contain genes for iron permease, which is involved in iron uptake ( | While this species is not thought to contain genes for iron permease, which is involved in iron uptake (8), it has sequences with domain structures similar to those used in other species. Gene sequence libraries document the 16S rRNA from iron-rich mine environments to be frequently dominated by Acidobacteria (9, 10, 11). This suggests possible involvement with iron (II) uptake and is hypothesized to be a valuable role in iron redox reactions (2). | ||
==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ||
This species is a small ( | This species is a small (2) rod shaped bacterium (1). It is non-motile and free living in aerobic habitats within mesophilic temperatures (1) at a pH in the range of 3.5-6.5 (2). It is chemoorganotrophic; utilizing organic carbon for growth and energy (1). It persists in environments with high substrate affinity and low nutrient concentration (2), by engaging in biofilm production. It has a slow metabolism and is only culturable in oligotrophic media (2). | ||
This species is equipped with a large number of anion:cation symporters (4), which is thought to be advantageous to organisms living in low nutrient environments ( | This species is equipped with a large number of anion:cation symporters (4), which is thought to be advantageous to organisms living in low nutrient environments (12). When compared to other closely related Acidiobacteria, this species has a 2-4 times as many transporters. It also had a large number of secondary porters to transport various other substrates such as amino acids, metals, fatty acids, proteins, in a carrier-mediated process (2). | ||
==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ||
[[Image:soil_components.jpg|thumbnail|365px|Figure 4. Soil matrix influenced by nutrient and water availability. Image from FAO [http://www.extension.org/pages/54401/basic-soil-components#.U2BwVKIklNI]]]. | [[Image:soil_components.jpg|thumbnail|365px|Figure 4. Soil matrix influenced by nutrient and water availability. Image from FAO [http://www.extension.org/pages/54401/basic-soil-components#.U2BwVKIklNI]]]. | ||
This species has been observed to engage in environmentally dependent functions. This functional diversity is hypothesized to aid in dealing with extreme variation in moisture, temperature, and nutrient cycles ( | This species has been observed to engage in environmentally dependent functions. This functional diversity is hypothesized to aid in dealing with extreme variation in moisture, temperature, and nutrient cycles (5). | ||
Cellulose production exhibited by this species contributes toward biofilm production, which increases its survivability under conditions of environmental stress by aiding in moisture retention and providing soil with aeration (14 | Cellulose production exhibited by this species contributes toward biofilm production, which increases its survivability under conditions of environmental stress by aiding in moisture retention and providing soil with aeration (13, 14). The biofilm production exhibited by this species also functions to reduce nutrient fluxuations by acting as a medium between the soil particles (15). This is significant because water and nutrients are valuable commodities to understand in light of global environmental change. | ||
Cellulase synthesis by acidobacteria has been suggested to promote the ability of a biofilm to adhere to ferric iron-rich substrates and produce “bioshrouds” to be used remedially in sulfide mine tailing environments (16). This suggests the future of characterizing cellulose production should include testing formation ability of the microfibrils to demonstrate the network formation ( | Cellulase synthesis by acidobacteria has been suggested to promote the ability of a biofilm to adhere to ferric iron-rich substrates and produce “bioshrouds” to be used remedially in sulfide mine tailing environments (16). This suggests the future of characterizing cellulose production should include testing formation ability of the microfibrils to demonstrate the network formation (2). | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 15:04, 30 April 2014
Classification
Bacteria; Phylum: Acidobacteria; Class: Solibacteres; Order: Solibacterales; Family: Solibacteraceae
Species
|
NCBI: Taxonomy |
- Candidatus Solibacter usitatus
Description and Significance
This species was initially isolated from rotationally grazed pasture of perennial ryegrass and white clover in Victoria, Australia (1).
It has an exceptionally large genome and is theorized to engage in horizontal gene transfer which contributes to its ability to persist in an environment. This species produces enzymes capable of breaking down organic carbon for metabolism and also participates in reducing nitrates. These forms of metabolism lend to this species ability to create heterogeneous nutrient concentrations throughout the soil it inhabits (2).
This species growth has been observed microscopically in soils as filamentous, but it forms clusters when grown in liquid culture (3). In nature, this species produces a biofilm which acts as an ecosystem engineer in soil. It does this by producing a medium that resides between soil particles. As the species engages in ion transfer with the environment it produces the biofilm to protect itself. This slowly expanding biofilm reduces moisture and nutrient fluxuations in the soil environment. This contributes to a species ability to survive under stressful environmental conditions (2).
Genome Structure
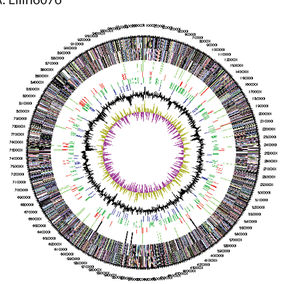
Based on whole genome sequencing, this species was found to have a 9.9 Mb long genome (4), which is about twice the size of other closely related Acidiobacteria found to inhabit soil (2). Horizontal gene transfer is hypothesized to account for how this species acquired its unusual genome size (2), and also implies biological and ecological strains upon the living organism (4). It is theorized that the amount of mobile elements encoded in a genome correlate with the historical frequency of horizontal gene transfer events. This is significant because mobile elements are theorized to contribute toward genome plasticity and evolution over time, which could provide a competitive advantage to this species and enable it to exploit various environmental resources (5).
A large number of genes encoding for carbohydrate transport and metabolism were found. This species has more genes encoding these functions than “the human genome and about three times as many as Saccharomyces cerevisiae” (6). These genes were also found to have high sequence similarity with fungal homologs which further suggests an ancestral horizontal gene transfer (2).
Genes encoding for candidate cellulases of glycoside hydrolases were found, which suggests this species is capable of degrading cellulose substrates and implies the genome is also encoded with other enzymes capable of degrading plant compounds (2). Further analysis also suggests this species has the flexibility to metabolize carbon as a mixotroph because it contains genes encoding for carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (7). Since oxidation of carbon monoxide has been prevalently documented among other major groups of soil organisms (7), it is hypothesized that this along with the ability to degrade complex polymers associated with vegetation, occur as a survival mechanism in environments with low carbon concentration (2).
The genetic potential for nitrate reductase was observed. This potential is significant because nitrogen reduction is a multi-step process yielding in molecular nitrogen, which is a limiting nutrient in ecosystems. This species ability to reduce nitrates leads to heterogeneous deposition and subsequent spatial variability in nutrient concentrations across a landscape. No evidence for nitrogen fixation or denitrification has been demonstrated (2).
While this species is not thought to contain genes for iron permease, which is involved in iron uptake (8), it has sequences with domain structures similar to those used in other species. Gene sequence libraries document the 16S rRNA from iron-rich mine environments to be frequently dominated by Acidobacteria (9, 10, 11). This suggests possible involvement with iron (II) uptake and is hypothesized to be a valuable role in iron redox reactions (2).
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
This species is a small (2) rod shaped bacterium (1). It is non-motile and free living in aerobic habitats within mesophilic temperatures (1) at a pH in the range of 3.5-6.5 (2). It is chemoorganotrophic; utilizing organic carbon for growth and energy (1). It persists in environments with high substrate affinity and low nutrient concentration (2), by engaging in biofilm production. It has a slow metabolism and is only culturable in oligotrophic media (2).
This species is equipped with a large number of anion:cation symporters (4), which is thought to be advantageous to organisms living in low nutrient environments (12). When compared to other closely related Acidiobacteria, this species has a 2-4 times as many transporters. It also had a large number of secondary porters to transport various other substrates such as amino acids, metals, fatty acids, proteins, in a carrier-mediated process (2).
Ecology and Pathogenesis
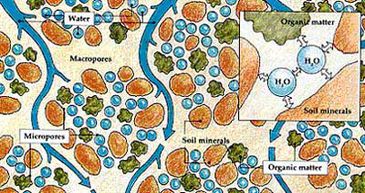
.
This species has been observed to engage in environmentally dependent functions. This functional diversity is hypothesized to aid in dealing with extreme variation in moisture, temperature, and nutrient cycles (5).
Cellulose production exhibited by this species contributes toward biofilm production, which increases its survivability under conditions of environmental stress by aiding in moisture retention and providing soil with aeration (13, 14). The biofilm production exhibited by this species also functions to reduce nutrient fluxuations by acting as a medium between the soil particles (15). This is significant because water and nutrients are valuable commodities to understand in light of global environmental change.
Cellulase synthesis by acidobacteria has been suggested to promote the ability of a biofilm to adhere to ferric iron-rich substrates and produce “bioshrouds” to be used remedially in sulfide mine tailing environments (16). This suggests the future of characterizing cellulose production should include testing formation ability of the microfibrils to demonstrate the network formation (2).
References
Author
Page authored by Kristine Ader, student of Prof. Jay Lennon at IndianaUniversity.
