Y. enterocolitica: Difference between revisions
From MicrobeWiki, the student-edited microbiology resource
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
| species = <i>Y. enterocolitica</i> | | species = <i>Y. enterocolitica</i> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
{|| height="10" bgcolor="#FFDF95" |'''NCBI: [ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=630&lvl=3&lin=f&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock Taxonomy] Genome: <font size="2">[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/1041 Genome]</font>'''|} | {|| height="10" bgcolor="#FFDF95" |'''NCBI: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=630&lvl=3&lin=f&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock Taxonomy] Genome: <font size="2">[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/1041 Genome]</font>'''|} | ||
===Description=== | ===Description=== | ||
==Pathogenesis== | ==Pathogenesis== | ||
Revision as of 21:08, 16 July 2014
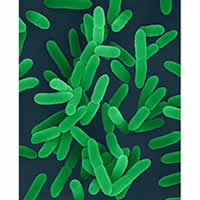
Scanning electron microscope image of Yersinia enterocolitica. From:http://www.nbbcfood.info/foodmatters/foodsafetyatoz/images/30fsmyersinia.jpg
Etiology/Bacteriology
Taxonomy
| Domain = Bacteria
| Phylum = Proteobacteria
| Class = Gammaproteobacteria
| Order = Enterobacteriales
| Family = Enterobacteriaceae
| Genus = Yersinia
| species = Y. enterocolitica
Description
Pathogenesis
Transmission
Infectious dose, incubation, and colonization
Epidemiology
Virulence Factors
Clinical Features
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention
Prevention of Yersinia enterocolitica infection is easy if one is aware of what to avoid. The most common mode of transmission is via poultry and livestock. Thus, avoid raw or undercooked meats. Make sure that milk products are pasteurized before consumption. If raw meat must be handled, clean hands thoroughly to avoid cross-contamination. Beware of cross-contamination in the kitchen by cleaning all surfaces and appliances with soap and hot water. Animal feces may also be contaminated so dispose of all animal waste properly.

