Bacteroide composition in the gut: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Uncurated}} | {{Uncurated}} | ||
The Bacterial kingdom has played a significant role in Homo sapien evolution. Only ten percent of the cells existing in the body are human. Genetically, we are about 1% human, and 99% bacterial [10]. | The Bacterial kingdom has played a significant role in Homo sapien evolution. Only ten percent of the cells existing in the body are human. Genetically, we are about 1% human, and 99% bacterial [[#References|[10]]]. | ||
[[Image:1369260_bild1_b--ckhed.jpg|thumb|300px|right|<br><b>Figure 1. </b><i>Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron</i> in relation to food particles in the mouse intestine, provided by [http://gut.bmj.com/content/early/2011/11/23/gutjnl-2011-301104.full Larsson et al., 2012]]] | [[Image:1369260_bild1_b--ckhed.jpg|thumb|300px|right|<br><b>Figure 1. </b><i>Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron</i> in relation to food particles in the mouse intestine, provided by [http://gut.bmj.com/content/early/2011/11/23/gutjnl-2011-301104.full Larsson et al., 2012]]] | ||
The human colon contains the majority of microorganisms in the body, and 25% of these are species of Bacteroides. Bacteroides species are anaerobic, non-spore forming, gram-negative rods that have adapted to, and now thrive in, the human gut [7]. The relationship between Bacteroides and the host has recently been considered mutual, given that the relationship increases the fitness of both species. Given the long history of coevolution between microbiota and the intestine, it has now been shown that bacteroides function as a multifunctional organ that provides metabolic components we do not contain in our own genome [10]. Some of these metabolic traits include carbohydrate fermentation, freeing simplified carbohydrates to be reabsorbed by the large intestine and to be used for energy by the host. Through various metabolic mechanisms, Bacteroides provide simplified amino acids and vitamins, while simultaneously utilizing a wide range of dietary polysaccharides for growth (Hooper, Midtvedt, and Gordon. 2002). | The human colon contains the majority of microorganisms in the body, and 25% of these are species of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bacteroides Bacteroides]. Bacteroides species are anaerobic, non-spore forming, gram-negative rods that have adapted to, and now thrive in, the human gut [[[#References|[7]]]. The relationship between Bacteroides and the host has recently been considered mutual, given that the relationship increases the fitness of both species. Given the long history of coevolution between microbiota and the intestine, it has now been shown that bacteroides function as a multifunctional organ that provides metabolic components we do not contain in our own genome [[#References|[10]]]. Some of these metabolic traits include carbohydrate fermentation, freeing simplified carbohydrates to be reabsorbed by the large intestine and to be used for energy by the host. Through various metabolic mechanisms, Bacteroides provide simplified amino acids and vitamins, while simultaneously utilizing a wide range of dietary polysaccharides for growth (Hooper, Midtvedt, and Gordon. 2002). | ||
Due to the metabolic role of Bacteroides in carbohydrate fermentation, there has been some evidence showing a correlation between diet, gut flora, and obesity. Given the significant role Bacteroides play in the gut, the effect of diet on their mechanisms of action and composition overall is a relevant topic of analysis (Turnbaugh, 2009). How body flora composition might affect adiposity is particularly crucial in light of the drastic shift in food source in the United States and its consequent growing obesity epidemic. | Due to the metabolic role of Bacteroides in carbohydrate fermentation, there has been some evidence showing a correlation between diet, gut flora, and obesity. Given the significant role Bacteroides play in the gut, the effect of diet on their mechanisms of action and composition overall is a relevant topic of analysis (Turnbaugh, 2009). How body flora composition might affect adiposity is particularly crucial in light of the drastic shift in food source in the United States and its consequent growing obesity epidemic. | ||
Revision as of 17:05, 22 March 2015
The Bacterial kingdom has played a significant role in Homo sapien evolution. Only ten percent of the cells existing in the body are human. Genetically, we are about 1% human, and 99% bacterial [10].
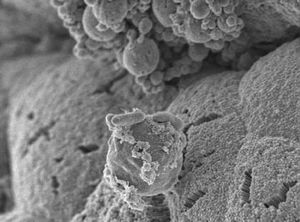
Figure 1. Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron in relation to food particles in the mouse intestine, provided by Larsson et al., 2012
The human colon contains the majority of microorganisms in the body, and 25% of these are species of Bacteroides. Bacteroides species are anaerobic, non-spore forming, gram-negative rods that have adapted to, and now thrive in, the human gut [[[#References|[7]]]. The relationship between Bacteroides and the host has recently been considered mutual, given that the relationship increases the fitness of both species. Given the long history of coevolution between microbiota and the intestine, it has now been shown that bacteroides function as a multifunctional organ that provides metabolic components we do not contain in our own genome [10]. Some of these metabolic traits include carbohydrate fermentation, freeing simplified carbohydrates to be reabsorbed by the large intestine and to be used for energy by the host. Through various metabolic mechanisms, Bacteroides provide simplified amino acids and vitamins, while simultaneously utilizing a wide range of dietary polysaccharides for growth (Hooper, Midtvedt, and Gordon. 2002).
Due to the metabolic role of Bacteroides in carbohydrate fermentation, there has been some evidence showing a correlation between diet, gut flora, and obesity. Given the significant role Bacteroides play in the gut, the effect of diet on their mechanisms of action and composition overall is a relevant topic of analysis (Turnbaugh, 2009). How body flora composition might affect adiposity is particularly crucial in light of the drastic shift in food source in the United States and its consequent growing obesity epidemic.
Genomic and Proteomic Advances
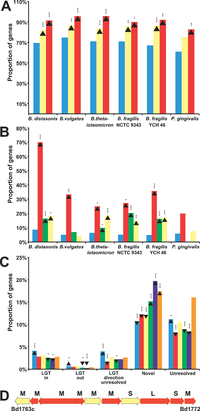
Figure 2. Lateral Gene Transfer in Bacteroidetes Promotes Niche Specialization(A) Proportions of genes found in each genome. Non-laterally transferred genes (blue) are proportionally more often involved in metabolism. Genes assigned “Primary metabolism” (yellow) and “Protein biosynthesis” (red), are compared. Upward-pointing arrowhead indicate gene enrichment and downward-pointing arrowhead show gene depletion . Asterisks indicate statistical significance, single asterisk (*) indicates p < 0.05; double asterisks (**) indicate p < 0.01; and triple asterisks (***) indicate p < 0.001. For B,C, and D see original publication by Xu et al., 2007
Recently, genomic and proteomic analyses have provided insight into the mechanisms in which microbiota adapt and thrive within varying microenvironments. Sequencing B. thetaiotaomicron and B. fragilis show notable genomic commonalities. These Bacteroides, like eukaryotes, show low gene content for the size of their genome (Xu and Gordon, 2003). A large portion of the their genetic make-up consists of proteins containing over 1,000 amino acids, which, it seems, allow for a vast selection of relevant proteins for gene expression. Putative relevant proteins have been determined by homology to other known proteins. Of the 4779 proteins identified in the B. thetaiotaomicron proteome, 58% were ascribed a supposed function based on other known proteins, 18% were homologous to proteins without a known function, and 24% were not homologous to any protein identified in the public domain [10]. The variety of functions is presumed to aid Bacteroides species in multiple ways: the proteome induces the mechanism by which some Bacteroides acquire and hydrolyze otherwise indigestible dietary polysaccharides, and includes an environment-sensing apparatus with extracytoplasmic function sigma factors and one- and two-component signal transduction systems [#References|[10]]]
B. thetaiotaomicron contains the capacity to utilize glycans derived from the colon. The majority (61%) of the necessary enzymes (glycohyrolases) potentially exist in the periplasm, and are necessary to the polysaccharide fermentation process that increases energy availability to the host. Other extracellular proteins have been shown to facilitate the binding of starches to the cell surface to be digested by other extracellular enzymes [#References|[10]]]
Additionally, B. thetaiotaomicron was shown to contain a significant population of ECF-sigma factors, which according to other identified homologous genes, are cotranscribed with regulatory proteins that respond to external environmental stimulus and act on gene expression accordingly.
The majority of one-component signal transduction systems were shown to be similar to other genes responsible for nutrient utilization, providing further evidence of Bacteroides’ genetically evolved fitness advantage in nutrient acquisition.
Through genomic and proteomic sequencing, some of the mechanism underlying the adaptive capabilities of the Bacteroide species in the human gut have been identified. The expansive array of proteins available to them mediates their ability to respond to their environment, thrive within the rapidly changing microenvironment of the colon, and acquire and ferment complex carbohydrates for their own energy source as well as for the host.
To study the genetically adaptive characteristics of Bacteroides to the gut habitat further, Xu and associated sequenced the genomes of two gut-dwelling Bacteroide species Bacteroides vulgatus and Bacteroides distasonis and compared their common orthologs to non-gut Bacteroides Porphyromonas gingivalis W83 (found in human mouth) and Cytophaga hutchinsonii ATCC 33406 (found in soil). It was shown that Factors such as lateral gene transfer, mobile elements, and gene amplification allow Bacteroides to vary the surface of their cells, sense the environment, and gain access to nutrients in the intestine. The authors concluded that these processes have allowed the symbiotic relationship between Bacteroidetes and the human gut environment to thrive. In studying how various factors (i.e. diet, stress, or antibiotic consumption) affect the microbiome, the adaptational activity of Bacteroidetes can contribute to the understanding of what cellular processes are specifically affected by external factors affecting the composition of gut flora [#References|[11]]].
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
Overall paper length should be 3,000 words, with at least 3 figures with data.
Enterotype and Diet
In 2011, Peer Bork and colleagues identified three clusters of microbiota species, termed enterotypes, and defined as “densely populated areas in a multi-dimensional space of community composition” (p. 177).[1] Type 1 is characterized by high levels of Bacteroides, type two is dominated by Prevotella, and Ruminococcus is prevalent in type 3. In accordance with other genomic and proteomic analysis, the Bacteroides and Parabacteroides found in the type 1 enterotype fermented carbohydrates and proteins by the use of galactosidases, hexosaminidases, proteases enzymes for degradation as well as through glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathways. It was shown that enterotype composition is species driven, however, identification of molecular functioning of each species is necessary to determine health differences between hosts with varying enterotypes. Age, body mass index, gender, or nationality showed no clear causation to enterotype composition.
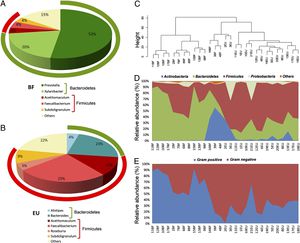
16S rRNA gene surveys show differences in microbiota composition between children populations. (A and B) Pie charts of median values of bacterial taxa identified in fecal samples of Burkina Faso and European children. Bacteroides (green) and Firmicutes (red) For (C), (D), and (E) see source: De Filippo et al., 2010.
However, long-term dietary changes have been shown to alter the microbiota of the gut. A study by Wu and colleagues (2011) analyzed fecal samples, using diet inventories and 16S rDNA sequencing, from 98 individuals in order to determine the effect of diet on enterotype identity and microbiome composition. The authors concluded that while microbiome composition changed within 24 hours, enterotype identity shifts are associated with long-term dietary changes. Composition of enterotypes, particularly protein and animal fat (Bacteroides) versus carbohydrates (Prevotella), were most affected in long-term analysis. Their findings provide evidence that diet affects the amount of bacteroides living in the gut, and that the change is time-dependent.
Another study also showed a possible correlation between long-term diet and enterotype composition. De Filippo et al., in 2010, used high-throughput 16S rDNA sequencing and biochemical analyses to assess microbiota differences between children eating a fiber-rich, high-carbohydrate diet in Burkina Faso and European children fed diets high in fat and protein. The European children showed high levels of Bacteroides, while the Burkina Faso children contained microbiomes enriched by the Prevotella enterotype, known to contain genes that allow for xylan and cellulose hydrolysis. This genetic advantage may be completely lacking in children fed western diets. While there are many distinguishing factors between the two populations that might account for enterotype differences, diet is an obvious possible causative factor given what is known about the metabolic properties of bacterial species in the gut.
The authors of the Africa/Europe comparison hypothesize that diseases associated with enterotype composition may be treated by long-term dietary changes. It is also suggested that preservation of human communities in isolated areas is important, in that they may contain contain fitness advantages due to ancient coevolutionary symbioses between themselves and their microbiomes.
Bacteroides and Obesity
Several studies have shown relationships between diet, obesity, and microbiome composition. One study analyzed via genetic sequencing of the bacterial contents of fecal samples from 12 “obese” and 5 “lean” (according to the BMI scale) individuals. Obese individuals were found to have 20% more Firmicutes species and almost 90% less Bacteroidetes compared to the lean group. Furthermore, after one year of spent on a low-carbohydrate or low-fat diet, obese individuals showed a significant change in microbiota composition after shedding 25% of their body weight. Proportions of Bacteriodetes increased while the Firmicutes population decreased after the year-long diet and weight loss (Fig. 4). The results by Ley and associates provide evidence toward an inverse relationship between adiposity and Bacteroides proportions in the gut. Their evidence also suggests dietary therapeutic techniques toward treating or preventing obesity-associated disease. However, the small sample size of the study lens itself to critical debate in its applicability to the larger population.
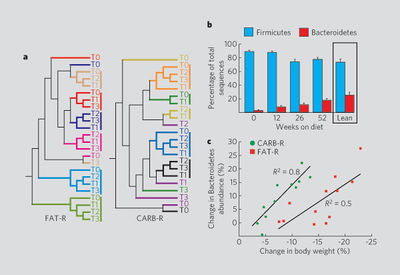
A study by Turnbaugh (2009) [#References|[6]]]showed parallel results to those of Ley, Turnbaugh, and Gordon (2006)[5]The authors successfully mimicked human gut environments in mice by transplanting fecal matter into germ-free C57BL/6J (“humanized”) mice by metagenomic analysis of their bacterial colonization. Transitioning from a low-fat, plant-rich diet to a high-sugar “western” diet significantly changed the contents of the host’s microbiota in a single day, and these changes altered metabolic pathways and gene expression of the microbiome, and eventually increased adiposity. Adiposity fluctuated depending on microbiota transplantation. Humanized mice fed the western diet showed higher levels of Firmicute species and Erysipelotrichi and Bacilli species and less representation of Bacteroides (Fig 4). The pathways identified in the microbiome of the lean mice included glycan degradation and fatty acid metabolism, the same pathways previously assigned to Bacteroides. These findings support the hypothesis that Bacteroides may contribute to lower body mass, and that microbiota composition in the colon is responsive to changes in diet.
A correlation between decreased proportions of Bacteroides in the microbiota and obesity has not been found in every investigation on the topic. Arumugam and colleagues showed no correlation between type 1 enterotype and leanness.[#References|[5]]] SImilarly, Duncan and colleagues found no evidence of differences in Bacteroide proportions in fecal samples between obese and non-obese subjects, and weight loss dieting did not alter their original observations.[#References|[3]]]
Further Reading
Genomic analysis of Bacteroides fragilis reveals extensive DNA inversions regulating cell surface adaptation--Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
References
Edited by Maggie Schein, a student of Suzanne Kern in BIOL168L S2 (Microbiology) in The Keck Science Department of the Claremont Colleges Spring 2014.
