Desulfurobacterium: Difference between revisions
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Uncurated}} | {{Uncurated}} | ||
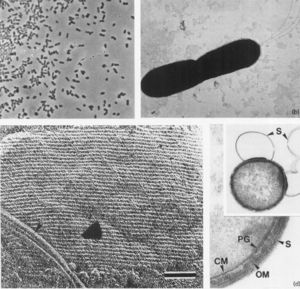
[[File:Desulfurobacterium thermolithotrophum Structure.jpg|thumb|left| Phase-contrast (a) and electron micrographs of isolate BSA (b-d) , negatively stained dividing cell showing polar flagella (b), Freeze-etched cells and metal-shadowed intact cells of isolate BSA (c) showing the S-layer lattice, and typical cell envelope of a Gram-negative bacterium becoming visible by ultrathin selection (d).]] | |||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
Bacteria, Aquificae, Aquificae, Desulfurobacteriales, Desulfurobacteriaceae, <var>Desulfurobacterium, Desulfurobacterium thermolithotrophum</var> | Bacteria, Aquificae, Aquificae, Desulfurobacteriales, Desulfurobacteriaceae, <var>Desulfurobacterium, Desulfurobacterium thermolithotrophum</var> | ||
===Species=== | ===Species=== | ||
Revision as of 18:43, 27 April 2015
Classification
Bacteria, Aquificae, Aquificae, Desulfurobacteriales, Desulfurobacteriaceae, Desulfurobacterium, Desulfurobacterium thermolithotrophum
Species
Desulfurobacterium thermolithotrophum
Related Species:
Desulfurobacterium atlanticum, Desulfurobacterium crinifex, Desulfurobacterium pacificum
|
NCBI: Taxonomy |
Description and Significance
Describe the appearance, habitat, etc. of the organism, and why you think it is important.
Genome Structure
Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence?
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Habitat; symbiosis; biogeochemical significance; contributions to environment.
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
References
Author
Page authored by William Van Cleef III & Meghan Von Holt, student of Prof. Jay Lennon at IndianaUniversity.
