Soil Health: Difference between revisions
From MicrobeWiki, the student-edited microbiology resource
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
===Soil Quality vs. Soil Health=== | ===Soil Quality vs. Soil Health=== | ||
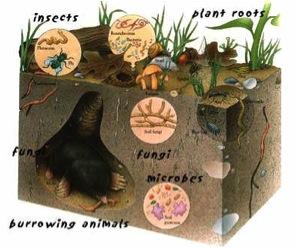
[[File:11 living soil.jpg|frame|border|right|top|upright|alt=Alt|The physical, chemical, and biological interactions driven by soil microorganisms in a healthy soil support a complex food web, including human beings.]] | [[File:11 living soil.jpg|frame|border|right|top|upright|alt=Alt|The physical, chemical, and biological interactions driven by soil microorganisms in a healthy soil support a complex food web, including human beings.]] | ||
Much like the success of the human body is measured by its health, soil health is a measure of a complex set of biological, chemical and physical interactions which are driven by microbial processes. The soil supports and sustains most life forms on earth, but it is the work of microorganisms that give soil its unique life giving properties. | Much like the success of the human body is measured by its health, soil health is a measure of a complex set of biological, chemical and physical interactions which are driven by microbial processes. The soil supports and sustains most life forms on earth, but it is the work of microorganisms that give soil its unique life giving properties. | ||
==Definitions and Indicators== | ==Definitions and Indicators== | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
===FAO=== | ===FAO=== | ||
===NRCS=== | ===NRCS=== | ||
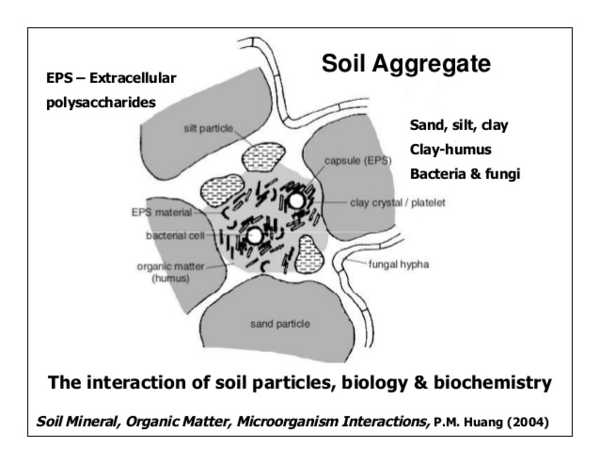
[[File:22 aggregate.png|thumb|border|right|top|upright=2.0|alt=Alt|An example distribution of extracellular polysaccharides, humus, fungal hyphae, and bacterial cells in a soil aggregate.]] | [[File:22 aggregate.png|thumb|border|right|top|upright=2.0|alt=Alt|An example distribution of extracellular polysaccharides, humus, fungal hyphae, and bacterial cells in a soil aggregate.]] | ||
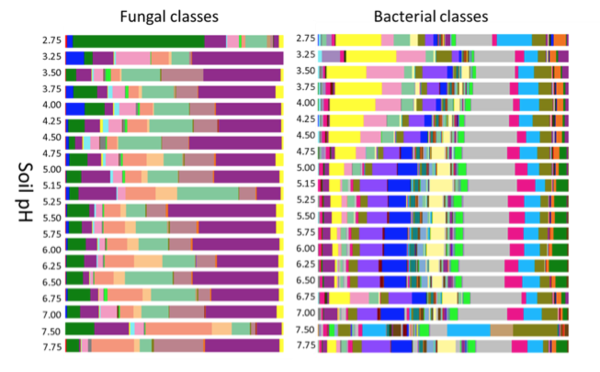
[[File:22 pH distribution.png|thumb|border|left|top|upright=2.0|alt=Alt|The effect of soil pH on the composition of fungal and bacterial communities. Each band color represents a different taxonomic class.]] | |||
===Beyond Existing Indicators: Incorporating Soil Biology=== | ===Beyond Existing Indicators: Incorporating Soil Biology=== | ||
Revision as of 23:55, 14 March 2016
Introduction
The Living Soil
Soil Quality vs. Soil Health
Much like the success of the human body is measured by its health, soil health is a measure of a complex set of biological, chemical and physical interactions which are driven by microbial processes. The soil supports and sustains most life forms on earth, but it is the work of microorganisms that give soil its unique life giving properties.