Pseudomonas syringae: Bioprecipitation Mechanisms and Implications: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- Do not edit this line-->{{Curated}} | <!-- Do not edit this line-->{{Curated}} | ||
==Section== | ==Section== | ||
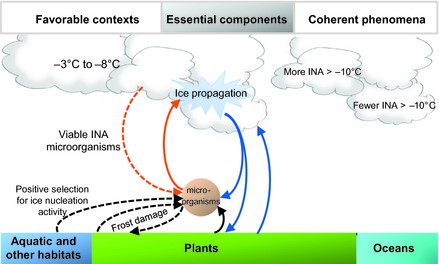
[[Image:Project Pic.jpg|thumb| | [[Image:Project Pic.jpg|thumb|500px|right|The bioprecipitation cycle diagram with two key factors that highlight the system. First, micro-organisms such as P.syringae that conduct the ice nucleation process. Second, the water vapor from plants, oceans, and aquatic environments that these micro-organism use in the atmosphere http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/gcb.12447/epdf.]] | ||
<br>By []<br> | <br>By []<br> | ||
<br>At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki.<br><br>The insertion code consists of: | <br>At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki.<br><br>The insertion code consists of: | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
<br>Introduce the topic of your paper. What is your research question? What experiments have addressed your question? Applications for medicine and/or environment?<br> | <br>Introduce the topic of your paper. What is your research question? What experiments have addressed your question? Applications for medicine and/or environment?<br> | ||
Sample citations: <ref>[http:// | Sample citations: <ref>[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/gcb.12447/epdf Morris, C.E. et al. “Bioprecipitation: a feedback cycle linking Earth history, ecosystem dynamics and land use through biological ice nucleators in the atmosphere.” 2014. Global Change Biology 20: 341–351.]</ref> | ||
<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3847443/ Bartlett et al.: Oncolytic viruses as therapeutic cancer vaccines. Molecular Cancer 2013 12:103.]</ref> | <ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3847443/ Bartlett et al.: Oncolytic viruses as therapeutic cancer vaccines. Molecular Cancer 2013 12:103.]</ref> | ||
<br><br>A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes. | <br><br>A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes. | ||
Revision as of 01:00, 22 April 2016
Section
By []
At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki.
The insertion code consists of:
Double brackets: [[
Filename: PHIL_1181_lores.jpg
Thumbnail status: |thumb|
Pixel size: |300px|
Placement on page: |right|
Legend/credit: Electron micrograph of the Ebola Zaire virus. This was the first photo ever taken of the virus, on 10/13/1976. By Dr. F.A. Murphy, now at U.C. Davis, then at the CDC.
Closed double brackets: ]]
Other examples:
Bold
Italic
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
Introduce the topic of your paper. What is your research question? What experiments have addressed your question? Applications for medicine and/or environment?
Sample citations: [1]
[2]
A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes.
- ↑ Morris, C.E. et al. “Bioprecipitation: a feedback cycle linking Earth history, ecosystem dynamics and land use through biological ice nucleators in the atmosphere.” 2014. Global Change Biology 20: 341–351.
- ↑ Bartlett et al.: Oncolytic viruses as therapeutic cancer vaccines. Molecular Cancer 2013 12:103.
