Pseudomonas syringae: Bioprecipitation Mechanisms and Implications: Difference between revisions
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<br>By Brandon Byrd <br> | <br>By Brandon Byrd <br> | ||
Pseudomonas syringae have a significant impact on weather systems and ecosystems worldwide. This bacteria has previously been studied in depth as a plant pathogen, and it has recently been studied as a major contributor to bioprecipitation. P.syringae are rod shaped, gram-negative bacteria with polar flagella that is a plant pathogen to a wide variety of plant species at cold temperatures (Morris et al 2008). This bacteria is found in agricultural locations as well as non-agricultural locations such as clouds (Morris et al 2008). The fact that it has the capability to grow in a wide range of environments and ecosystems gives this bacteria the potential to drastically impact biogeographical systems. P.syringae also has an extraordinary ice nucleation activity which allows this bacteria to catalyze freezing water at warm temperatures which sparked interest in its role in the water cycle (Maki et al 1974). This is a major key for P.syringae’s effect on biogeographical systems. It is also important to further analyze their ice nucleation ability to understand the mechanisms in which they influence major weather systems such as the water cycle. Furthermore, how P.syringae can impact humans and biodiversity based on their influence on ecosystems and the environment. | Pseudomonas syringae have a significant impact on weather systems and ecosystems worldwide. This bacteria has previously been studied in depth as a plant pathogen, and it has recently been studied as a major contributor to bioprecipitation. P.syringae are rod shaped, gram-negative bacteria with polar flagella that is a plant pathogen to a wide variety of plant species at cold temperatures (Morris et al 2008). This bacteria is found in agricultural locations as well as non-agricultural locations such as clouds (Morris et al 2008). The fact that it has the capability to grow in a wide range of environments and ecosystems gives this bacteria the potential to drastically impact biogeographical systems. P.syringae also has an extraordinary ice nucleation activity which allows this bacteria to catalyze freezing water at warm temperatures which sparked interest in its role in the water cycle (Maki et al 1974). This is a major key for P.syringae’s effect on biogeographical systems. It is also important to further analyze their ice nucleation ability to understand the mechanisms in which they influence major weather systems such as the water cycle. Furthermore, how P.syringae can impact humans and biodiversity based on their influence on ecosystems and the environment. | ||
<ref>[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/gcb.12447/epdf Morris, C.E. et al. “Bioprecipitation: a feedback cycle linking earth history, ecosystem dynamics and land use through biological ice nucleators in the atmosphere.” 2014. Global Change Biology 20: 341–351.]</ref> | <ref>[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/gcb.12447/epdf Morris, C.E. et al. “Bioprecipitation: a feedback cycle linking earth history, ecosystem dynamics and land use through biological ice nucleators in the atmosphere.” 2014. Global Change Biology 20: 341–351.]</ref> | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
Revision as of 22:03, 28 April 2016
Overview
By Brandon Byrd
Pseudomonas syringae have a significant impact on weather systems and ecosystems worldwide. This bacteria has previously been studied in depth as a plant pathogen, and it has recently been studied as a major contributor to bioprecipitation. P.syringae are rod shaped, gram-negative bacteria with polar flagella that is a plant pathogen to a wide variety of plant species at cold temperatures (Morris et al 2008). This bacteria is found in agricultural locations as well as non-agricultural locations such as clouds (Morris et al 2008). The fact that it has the capability to grow in a wide range of environments and ecosystems gives this bacteria the potential to drastically impact biogeographical systems. P.syringae also has an extraordinary ice nucleation activity which allows this bacteria to catalyze freezing water at warm temperatures which sparked interest in its role in the water cycle (Maki et al 1974). This is a major key for P.syringae’s effect on biogeographical systems. It is also important to further analyze their ice nucleation ability to understand the mechanisms in which they influence major weather systems such as the water cycle. Furthermore, how P.syringae can impact humans and biodiversity based on their influence on ecosystems and the environment.
History
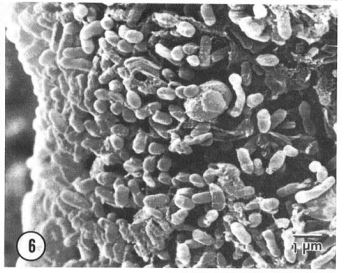
.
Every point of information REQUIRES CITATION using the citation tool shown above.
Bioprecipitation and P.syringae’s Role in Bioprecipitation
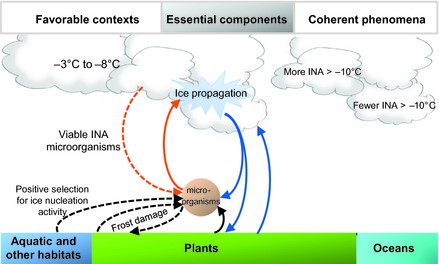
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Mechanisms for Ice Nucleation
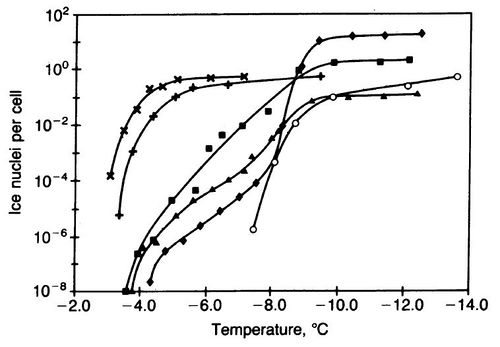
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Ecological Implications of
P.syringae Bioprecipitation
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Conclusion
References
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski, 2016, Kenyon College.
