The Monoxenous Life Cycle Of Eimeria: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<br>By Emma Stewart-Bates<br> | <br>By Emma Stewart-Bates<br> | ||
<br><i>Eimeria</i> is a genus of protozoa that are parasitic to many vertebrate animals, most often cattle, domesticated birds, goats, and sheep. These parasites contain an apical complexes and apicoplasts, organelles that allow the cell to enter a host organism. The life cycle of <i>Eimeria</i> is considered monoxenous, meaning that the cycle occurs in one host. The three stages of its life cycle include oocyst, sporozoite, and merozoite. They undergo both sexual and asexual reproduction during different stages of their life. Animals infected by <i>Eimeria</i> often develop the disease coccidiosis, which mainly causes diarrhea, fatigue, and loss of appetite. Coccidiosis is spread when an animal ingests infected tissue or is exposed to contaminated feces.<ref>[http://parasite.org.au/para-site/text/eimeria-text.html "<i>Eimeria</i>." The Australian Society for Parasitology Inc., 16 June 2010. Web. 15 Apr. 2017.]</ref> The spread of coccidiosis costs the poultry market an enormous amount of money each year. As a result, much research has been conducted on how to manage and treat the outbreak of Eimeria infections. This research includes the benefits and disadvantages of anticoccidial medications, vaccinations, and other treatment measures, as well as how those measures work within the body of the host organism.<br> | <br><i>Eimeria</i> is a genus of protozoa that are parasitic to many vertebrate animals, most often cattle, domesticated birds, goats, and sheep. These parasites contain an apical complexes and apicoplasts, organelles that allow the cell to enter a host organism. The life cycle of <i>Eimeria</i> is considered monoxenous, meaning that the cycle occurs in one host. The three stages of its life cycle include oocyst, sporozoite, and merozoite. They undergo both sexual and asexual reproduction during different stages of their life. Animals infected by <i>Eimeria</i> often develop the disease coccidiosis, which mainly causes diarrhea, fatigue, and loss of appetite. Coccidiosis is spread when an animal ingests infected tissue or is exposed to contaminated feces.<ref>[http://parasite.org.au/para-site/text/eimeria-text.html "<i>Eimeria</i>." The Australian Society for Parasitology Inc., 16 June 2010. Web. 15 Apr. 2017.]</ref> The spread of coccidiosis costs the poultry market an enormous amount of money each year. As a result, much research has been conducted on how to manage and treat the outbreak of Eimeria infections. This research includes the benefits and disadvantages of anticoccidial medications, vaccinations, and other treatment measures, as well as how those measures work within the body of the host organism.<ref>[http://cmr.asm.org/content/15/1/58.long "Recent Advances in Biology and Immunobiology of <i>Eimeria</i> Species and in Diagnosis and Control of Infection with These Coccidian Parasites of Poultry." <i>Clinical Microbiology Reviews</i> 15.1 (2002): 58-65. Web.]</ref> <br> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
==Metabolism== | ==Metabolism== | ||
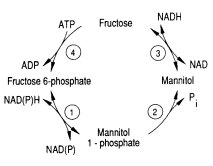
[[Image:Mannitol_Cycle.png|thumb|300px|right|<b>Figure 3.</b> The mannitol cycle occurs mainly during the sexual phase of the <i>Eimerian</i> life cycle. The conversion between fructose-6-phosphate and mannitol involves four enzymes. Among other activities, this metabolism powers oocyst sporulation for the <i>Eimeria</i>. <ref>[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0166685189900753 Schmatz, D.M., Baginsky, W.F., and Turner, M.J. “Evidence for and characterization of a mannitol cycle in Eimeria tenella.” Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology 32.2-3 (1989): 263-270.]</ref>]] | [[Image:Mannitol_Cycle.png|thumb|300px|right|<b>Figure 3.</b> The mannitol cycle occurs mainly during the sexual phase of the <i>Eimerian</i> life cycle. The conversion between fructose-6-phosphate and mannitol involves four enzymes. Among other activities, this metabolism powers oocyst sporulation for the <i>Eimeria</i>. <ref>[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0166685189900753 Schmatz, D.M., Baginsky, W.F., and Turner, M.J. “Evidence for and characterization of a mannitol cycle in <i>Eimeria tenella</i>.” <i>Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology</i> 32.2-3 (1989): 263-270.]</ref>]] | ||
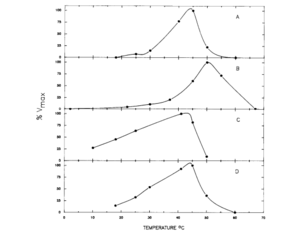
[[Image:Mannitol_enzymes.png|thumb|300px|right|<b>Figure 4.</b> The enzymes that function in the mannitol cycle appear to be the most active around the temperature level of the body of the host organisms. <ref>[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0166685189900753 Schmatz, D.M., Baginsky, W.F., and Turner, M.J. “Evidence for and characterization of a mannitol cycle in Eimeria tenella.” Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology 32.2-3 (1989): 263-270.]</ref>]] | [[Image:Mannitol_enzymes.png|thumb|300px|right|<b>Figure 4.</b> The enzymes that function in the mannitol cycle appear to be the most active around the temperature level of the body of the host organisms. <ref>[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0166685189900753 Schmatz, D.M., Baginsky, W.F., and Turner, M.J. “Evidence for and characterization of a mannitol cycle in <i>Eimeria tenella</i>.” <i>Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology</i> 32.2-3 (1989): 263-270.]</ref>]] | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
==Effects on the Body== | ==Effects on the Body== | ||
[[Image:duodenum.jpeg|thumb|300px|right|<b>Figure 5.</b> The destructive effect of an <i>Eimeria praecox</i> infection on the mucosal layer of the duodenum. One of the largest effects of <i>Eimeria</i> infection is shortening of the villi in the intestines. <ref>https://eimeriaprevention.com/news/coccidiosis-in-chickens-and-subclinical-species-of-eimeria/ “Coccidiosis in chickens: the role of subclinical species of Eimeria.” Eimeria Prevention. HIPRA, 16 Sept. 2016. Web. 19 Apr. 2017.]</ref>]] | [[Image:duodenum.jpeg|thumb|300px|right|<b>Figure 5.</b> The destructive effect of an <i>Eimeria praecox</i> infection on the mucosal layer of the duodenum. One of the largest effects of <i>Eimeria</i> infection is shortening of the villi in the intestines. <ref>https://eimeriaprevention.com/news/coccidiosis-in-chickens-and-subclinical-species-of-eimeria/ “Coccidiosis in chickens: the role of subclinical species of <i>Eimeria</i>.” <i>Eimeria Prevention</i>. HIPRA, 16 Sept. 2016. Web. 19 Apr. 2017.]</ref>]] | ||
==Treatment and Prevention== | ==Treatment and Prevention== | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
==Immunization== | ==Immunization== | ||
[[Image:Vaccination_oocysts.gif|thumb|300px|right|<b>Figure 6.</b> The mean number of oocysts per day of age for medicated and vaccinated birds in a study of 936,000 chickens.The medicated chickens showed one peak in oocyst counts around 35 days old, while the vaccinated chickens showed two peaks in oocyst counts around 21 days and 35 days. <ref>http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020751998002124 Williams, R.B., W.W.H. Carlyle, D.R. Bond, and I.A.G. Brown. “The efficacy and economic benefits of ParacoxⓇ, a live attenuated anticoccidial vaccine, in commercial trials with standard broiler chickens in the United Kingdom.” International Journal for Parasitology 29(1999): 341-355. Web..]</ref>]] | [[Image:Vaccination_oocysts.gif|thumb|300px|right|<b>Figure 6.</b> The mean number of oocysts per day of age for medicated and vaccinated birds in a study of 936,000 chickens.The medicated chickens showed one peak in oocyst counts around 35 days old, while the vaccinated chickens showed two peaks in oocyst counts around 21 days and 35 days. <ref>http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020751998002124 Williams, R.B., W.W.H. Carlyle, D.R. Bond, and I.A.G. Brown. “The efficacy and economic benefits of ParacoxⓇ, a live attenuated anticoccidial vaccine, in commercial trials with standard broiler chickens in the United Kingdom.” <i>International Journal for Parasitology</i> 29(1999): 341-355. Web..]</ref>]] | ||
==Conclusion== | ==Conclusion== | ||
Revision as of 19:05, 24 April 2017
Introduction
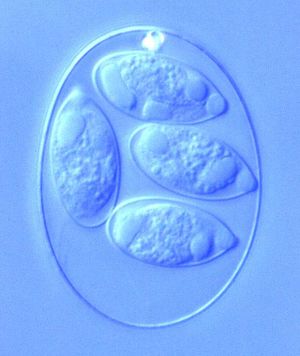
By Emma Stewart-Bates
Eimeria is a genus of protozoa that are parasitic to many vertebrate animals, most often cattle, domesticated birds, goats, and sheep. These parasites contain an apical complexes and apicoplasts, organelles that allow the cell to enter a host organism. The life cycle of Eimeria is considered monoxenous, meaning that the cycle occurs in one host. The three stages of its life cycle include oocyst, sporozoite, and merozoite. They undergo both sexual and asexual reproduction during different stages of their life. Animals infected by Eimeria often develop the disease coccidiosis, which mainly causes diarrhea, fatigue, and loss of appetite. Coccidiosis is spread when an animal ingests infected tissue or is exposed to contaminated feces.[1] The spread of coccidiosis costs the poultry market an enormous amount of money each year. As a result, much research has been conducted on how to manage and treat the outbreak of Eimeria infections. This research includes the benefits and disadvantages of anticoccidial medications, vaccinations, and other treatment measures, as well as how those measures work within the body of the host organism.[2]
Life Cycle
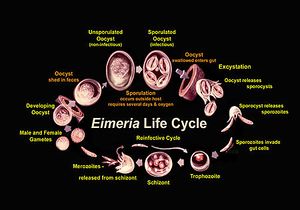
Phase Morphology
Metabolism
Infection and Diagnosis
Effects on the Body
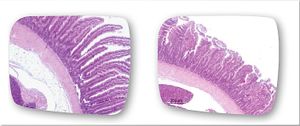
Treatment and Prevention
Impact on Poultry Market
Immunization
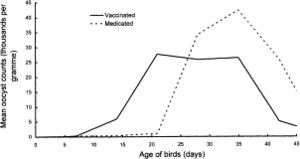
Conclusion
References
- ↑ "Eimeria." The Australian Society for Parasitology Inc., 16 June 2010. Web. 15 Apr. 2017.
- ↑ "Recent Advances in Biology and Immunobiology of Eimeria Species and in Diagnosis and Control of Infection with These Coccidian Parasites of Poultry." Clinical Microbiology Reviews 15.1 (2002): 58-65. Web.
- ↑ Schmatz, D.M., Baginsky, W.F., and Turner, M.J. “Evidence for and characterization of a mannitol cycle in Eimeria tenella.” Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology 32.2-3 (1989): 263-270.
- ↑ Schmatz, D.M., Baginsky, W.F., and Turner, M.J. “Evidence for and characterization of a mannitol cycle in Eimeria tenella.” Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology 32.2-3 (1989): 263-270.
- ↑ https://eimeriaprevention.com/news/coccidiosis-in-chickens-and-subclinical-species-of-eimeria/ “Coccidiosis in chickens: the role of subclinical species of Eimeria.” Eimeria Prevention. HIPRA, 16 Sept. 2016. Web. 19 Apr. 2017.]
- ↑ http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020751998002124 Williams, R.B., W.W.H. Carlyle, D.R. Bond, and I.A.G. Brown. “The efficacy and economic benefits of ParacoxⓇ, a live attenuated anticoccidial vaccine, in commercial trials with standard broiler chickens in the United Kingdom.” International Journal for Parasitology 29(1999): 341-355. Web..]
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski, 2017, Kenyon College.
