Bifidobacterium animalis: Difference between revisions
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
''Bifidobacterium animalis'' contains one circular chromosome consisting of 1, 943, 990 base pairs with a G-C content of 60.5% which is similar to all members of ''Bifidobacterium''[[³]] | ''Bifidobacterium animalis'' contains one circular chromosome consisting of 1, 943, 990 base pairs with a G-C content of 60.5% which is similar to all members of ''Bifidobacterium''[[³]] | ||
Revision as of 13:01, 18 April 2018
Classification
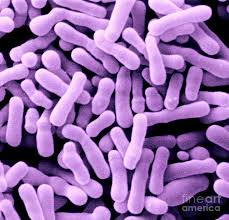
Higher Order Classification
Domain: Bacteria
Phylum: Actinobacteria
Class: Actinobacteria
Order: Bifidobacteriales
Family: Bifidobacteriaceae
Species
Bifidobacterium animalis
Description and Significance
Bifidobacterium animalis is a branched, rod-shaped (diplobicillus) gram-positive bacteria. This bacteria is generally found in the large intestines of mammals such as: cats, cows, and humans. Discovered by Henry Tissier in 1900 Bifidobacterium animalis was isolated from a breast-fed infant¹.
Although it was discovered in 1900, research on this bacterium did not ensue until the interest in probiotics in 1950. Probiotics are microorganisms that are ingested either in combination or as a single organism in an effort to normalize intestinal microbiota and potentially improve intestinal barrier function². It has long been speculation that probiotics are useful in alleviating or curing the symptoms associated with Irritable Bowel Disease (IBD) like ulcerative collitis.
Genome Structure
Bifidobacterium animalis contains one circular chromosome consisting of 1, 943, 990 base pairs with a G-C content of 60.5% which is similar to all members of Bifidobacterium³
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Ecology
Habitat; symbiosis; biogeochemical significance; contributions to environment.
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
References
¹Tissier, H. Recherches sur la flore intestinale des nourrissons:(état normal et pathologique) (Doctoral dissertation). 1900.
² Ghouri, Yezaz A et al."Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.", Clinical and Experimental Gastroenterology 7. 2014. pg 473–487. PMC. Web. 18 April 2018.
³ Bottacini, Francesca et al. "Complete Genome Sequence of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BLC1", Journal of Bacteriology. November 2011. vol 193 issue 22 pg 6387-6388. Web. 18 April. 2018.
Author
Page authored by Paul Proctor & Benjamin McKinnon-Duggins, student of Prof. Jay Lennon at IndianaUniversity.