Bordetella pertussis and the Importance of Vaccination: Difference between revisions
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- Do not edit this line-->{{Curated}} | <!-- Do not edit this line-->{{Curated}} | ||
==Introduction and History== | ==Introduction and History== | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:disease_pertussis.jpg|thumb|300px|right|This illustration depicts a three-dimensional (3D), computer-generated image, of a group of Gram-positive, Streptococcus agalactiae (group B Streptococcus) bacteria. The photo credit for this image belongs to Alissa Eckert, who is a medical illustrator at the [http://www.cdc.gov/ CDC].]] | ||
<br>By Alexandra White<br> | <br>By Alexandra White<br> | ||
<br>At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki.<br><br>The insertion code consists of: | <br>At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki.<br><br>The insertion code consists of: | ||
Revision as of 20:06, 14 April 2022
Introduction and History
By Alexandra White
At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki.
The insertion code consists of:
Double brackets: [[
Filename: download.jpg
Thumbnail status: |thumb|
Pixel size: |300px|
Placement on page: |right|
Legend/credit:
Closed double brackets: ]]
Other examples:
Bold
Italic
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
Vaccination is a widely used practice to help prevent infectious disease and commonly spread illnesses. A widely known and common vaccine is used to prevent infection of Bordetella pertussis, the causative agent of Whooping cough. Whooping cough is known as one of the most common infectious disease deaths in the world[1]. The disease results in over 50 million cases worldwide per year, with the majority being unvaccinated individuals present in Third World Countries[1].
B. pertussis is spread through coughing and sneezing and symptoms first appear seven to ten days after infection[2]. These symptoms include: fever, runny nose, coughing which develops into a whooping cough, and phenomena[2]. Those infected with pertussis are contagious for around three weeks once coughing is displayed as a symptom yet symptoms can last up to eight weeks[2].
B. pertussis was first discovered and isolated to be the cause of whooping cough in 1906 [1].Compared to human infectious diseases pertussis is a relatively recent human infectious disease that first appeared in France in 1414[3].The disease was identified in Paris, France in 1900 by Jules Bordet and Octave Gengou who obtained the sample from a 5-month-old child[1]. The bacteria was finally isolated in 1906 from Jules Bordet’s own son[1]. A vaccine for B. pertussis was developed in the early 1940s [4]. Before the development of the vaccine there were over 200,000 cases in the United States reported annually and with widespread use incidence has decreased 75% compared to the pre-vaccination era[4].
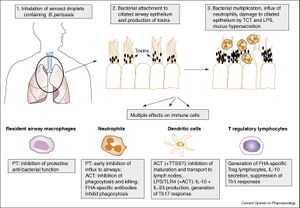
Bordetella pertussis and Infection Stages
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Every point of information REQUIRES CITATION using the citation tool shown above.
Italic
B. Pertussis Vaccine History
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Italic
Vaccine Virulence
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Why Vaccination?
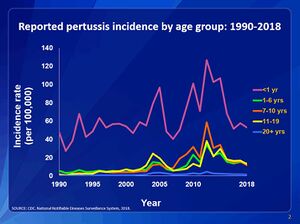
Conclusion
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Kerr, J.R. and Matthews, R.C."Bordetella pertussis Infection: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Management, and the Role of Protective Immunity." 2000. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Disease 19:77-88.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 World Health Organization: Pertussis 2018
- ↑ Guiso, N. "Bordetella pertussis and Pertussis Vaccines." 2009. Clinical infectious Diseases 49:1565-1569.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Havers et al. "Pertussis." 2021. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. 1-16.
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski, 2022, Kenyon College
