Parvovirus B19: Difference between revisions
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | ==Background== | ||
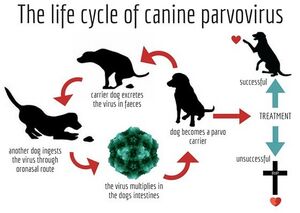
[[Image:Parvo-photo orig.jpg|thumb|300px|right|The life cycle of Canine Parvovirus. Photo credit: [https://www.azpetvet.com/canine-parvovirus-learning-how-to-prevent-is-the-key/]]] | [[Image:Parvo-photo orig.jpg|thumb|300px|right|The life cycle of Canine Parvovirus. Photo credit: [https://www.azpetvet.com/canine-parvovirus-learning-how-to-prevent-is-the-key/]]] | ||
<b>By Grace Potter <br> | <b>By Grace Potter <br> | ||
Revision as of 02:18, 19 March 2024
Background
By Grace Potter
At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki.
The insertion code consists of:
Double brackets: [[
Filename: PHIL_1181_lores.jpg
Thumbnail status: |thumb|
Pixel size: |300px|
Placement on page: |right|
Legend/credit: Magnified 20,000X, this colorized scanning electron micrograph (SEM) depicts a grouping of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria. Photo credit: CDC. Every image requires a link to the source.
Closed double brackets: ]]
Other examples:
Bold
Italic
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
Sample citations: [1]
[2]
A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes.
To repeat the citation for other statements, the reference needs to have a names: "<ref name=aa>"
The repeated citation works like this, with a forward slash.[3]
Parvovirus B19 is the only member of the Parvoviridae family that has been found to infect human hosts.[1] It was discovered in 1974, when a research group looking at hepatitis B surface antigens found a serum sample with unexpected results.[1] Another lab in Japan described a similar virus in 1979 that they called "Nakatami".[1] When compared, the two were found to be identical.[1]
In 1985 this virus was officially recognized as a member of the Parvoviridae family due to its similarities in genome size and density.[1]
Section 1
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Parvoviridae
Section 2
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 3
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 4
Conclusion
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Heegaard, E.D. and Brown, K.E. "Human Parvovirus B19." 2002. Clinical Microbiology Review 15(3):485-505.
- ↑ Bartlett et al.: Oncolytic viruses as therapeutic cancer vaccines. Molecular Cancer 2013 12:103.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedaa
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski,at Kenyon College,2024
