Infectious Disease in the Neolithic: Difference between revisions
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
These cases represent individual infections by <i>Y. pestis</i>. Based on genomic analysis of a recently discovered ancient strain of <i>Y. pestis</i>, some have argued for a plague pandemic in Eurasia near the end of the Neolithic period<ref name=Rascovan>[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.005 Rascovan, Nicolás, Karl-Göran Sjögren, Kristian Kristiansen, Rasmus Nielsen, Eske Willerslev, Christelle Desnues, and Simon Rasmussen. “Emergence and Spread of Basal Lineages of Yersinia Pestis during the Neolithic Decline.” 2019. Cell 176 (1–2): 295-305.e10.]</ref>. Several different strains, like the newly discovered Gökheim 2, would have arisen in genetically distinct and relatively isolated population<ref name=Rascovan/>. With increased trade networks that could be associated with the end of the Neolithic, these strains could have spread throughout the continent and contributed to the decline of prominent Neolithic societies <ref name=Rascovan/>. During the end of the Neolithic, <i>Y. pestis</i> may have been capable of such extensive infection. For the most part, however, genomic characterization of <i>Y. pestis</i> strains present in the Neolithic, including Scandinavia where Gökheim 2 is presumed to have originated, suggests that they were not easily transmissible. In highly transmissible strains, the <i>ymt</i> gene allows for transmission via fleas<ref name=Bergfeldt/>. In the earlier identified cases of <i>Y. pestis</i> infections, the mutation necessary for such transmission had not yet been acquired<ref name=Bergfeldt/>. | These cases represent individual infections by <i>Y. pestis</i>. Based on genomic analysis of a recently discovered ancient strain of <i>Y. pestis</i>, some have argued for a plague pandemic in Eurasia near the end of the Neolithic period<ref name=Rascovan>[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.005 Rascovan, Nicolás, Karl-Göran Sjögren, Kristian Kristiansen, Rasmus Nielsen, Eske Willerslev, Christelle Desnues, and Simon Rasmussen. “Emergence and Spread of Basal Lineages of Yersinia Pestis during the Neolithic Decline.” 2019. Cell 176 (1–2): 295-305.e10.]</ref>. Several different strains, like the newly discovered Gökheim 2, would have arisen in genetically distinct and relatively isolated population<ref name=Rascovan/>. With increased trade networks that could be associated with the end of the Neolithic, these strains could have spread throughout the continent and contributed to the decline of prominent Neolithic societies <ref name=Rascovan/>. During the end of the Neolithic, <i>Y. pestis</i> may have been capable of such extensive infection. For the most part, however, genomic characterization of <i>Y. pestis</i> strains present in the Neolithic, including Scandinavia where Gökheim 2 is presumed to have originated, suggests that they were not easily transmissible. In highly transmissible strains, the <i>ymt</i> gene allows for transmission via fleas<ref name=Bergfeldt/>. In the earlier identified cases of <i>Y. pestis</i> infections, the mutation necessary for such transmission had not yet been acquired<ref name=Bergfeldt/>. | ||
<b>Parasites</b><br> | |||
</b> | |||
In the Neolithic period, bacterial infections often occurred alongside parasitic infections by organisms like tapeworms and whipworms. These can be identified in the archaeological record without genomic analysis; eggs, most commonly of intestinal parasites, can be found within preserved soft tissue and coprolites<ref name=Maicher>[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2021.103093 Maicher, Celine, Yolaine Maigrot, Andrey Mazurkevich, Ekaterina Dolbunova, and Matthieu Le Bailly. “First Contribution of Paleoparasitology to the Study of Coprolites from the Neolithic Site Serteya II (NW Russia).” 2021. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports 38 (August): 103093.]</ref><ref name=Mitchell>[https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182022000476 Mitchell, Piers D., Evilena Anastasiou, Helen L. Whelton, Ian D. Bull, Mike Parker Pearson, and Lisa-Marie Shillito. “Intestinal Parasites in the Neolithic Population Who Built Stonehenge (Durrington Walls, 2500 BCE).” 2022. Parasitology 149 (8): 1027–33.]</ref><ref name=Nerlich>[https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1614-6_19-1 Nerlich, Andreas G., Angelika Fleckinger, and Oliver Peschel. “Life and Diseases of the Neolithic Glacier Mummy ‘Ötzi.’” 2020. In The Handbook of Mummy Studies, edited by Dong Hoon Shin and Raffaella Bianucci, 1–22. Singapore: Springer Singapore.]</ref>. Digital light microscopy on coprolites from a community near Stonehenge in 2500 BCE revealed a diverse array of parasite remnants, including helminth eggs, fish tapeworm (<i>Dibothriocephalus dendriticus</i>), and capillariid nematodes<ref name=Mitchell/>. At a Neolithic site in Russia, coprolites similarly revealed evidence of parasites including the worms <i>Diphyllobothrium</i> and <i>Dioctophyma renale</i> and two trematodes including a river lancet fluke<ref name=Maicher/>. In both studies, the coprolites were mostly attributed to canids due to the diversity of parasites and the composition of bile<ref name=Mitchell/><ref name=Maicher/>. At the Russian site, however, at least one human contributed to the sample<ref name=Mitchell/>. This suggests not only that parasites may not have been incredibly host-specific, but that humans and dogs may have had a close enough relationship to spread parasites to one another. The close relationship between humans and canines has also been cited in the spread of bacteria. For example, dogs may have acted as a transient reservoir for <i>Yersinia pestis</i><ref name=Krause/>. | |||
A particularly interesting example of parasite infection in the Neolithic comes from the so-called "Iceman," otherwise known as Ötzi, an adult male mummy recovered from a glacier in 1991 and dated to 3350-3100 BCE<ref name=Nerlich/>. Ötzi has been extensively studied over the last few decades, and research has revealed several chronic health conditions. One of these is an infection by the intestinal whipworm <i>Trichuris trichiura</i>, evidenced by many eggs found in Ötzi's intestines<ref name=Nerlich/>. These parasites are ingested and result from poor sanitation and hygienic conditions<ref name=Nerlich/>. Interestingly, Ötzi may have attempted to treat the symptoms from the <i>T. trichiura</i> by consuming the birch fungus <i>Fomitopsis betulina</i>, which was found on his person<ref name=Nerlich/>. This fungus has anti-helminitic and anti-microbial properties, including substances that inhibit multi-drug resistance<ref name=Plesz>[https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2247-0 Pleszczyńska, Małgorzata, Marta K. Lemieszek, Marek Siwulski, Adrian Wiater, Wojciech Rzeski, and Janusz Szczodrak. “Fomitopsis Betulina (Formerly Piptoporus Betulinus): The Iceman’s Polypore Fungus with Modern Biotechnological Potential.” 2017. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 33 (5): 83.]</ref>. Ötzi's intestinal problems were likely intensified by a simultaneous infection by a particularly aggressive strain of <i>Helicobacter pylori</i> that, although often asymptomatic, likely caused active gastritis for Ötzi (Figure 3)<ref name=Nerlich/>. | |||
==Section 3== | ==Section 3== | ||
Revision as of 20:36, 14 April 2024
Introduction
Methods
Major Pathogens
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Genetic evidence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative agent of tuberculosis, has been found as early as 5000 years ago [1]. It is most often identified as a Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, a larger group that is recognized by standard DNA probes [2]The complex includes M. tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. africanum, and M. microti [2]. M. tuberculosis is one of the most common causes of tuberculosis, but M. bovis and M. africanum can result in similar symptoms in humans[2]. Of these, M. bovis mostly affects cattle but can infect humans if infected meat and dairy products are ingested, while M. africanum is responsible for the majority of tuberculosis cases in Africa [2]. M. microti specifically affects mice and voles[2].
Cases of tuberculosis are often recorded in Neolithic burials. It is among the diseases most commonly reported in the archaeological record because it leaves diagnostic changes on human bone, often in the form of lesions and spinal collapse [1][3]. Calcifications in organs can also be indicative of previous tuberculosis infections [4].Individual burials in the Near East and Europe from early domestication phases in approximately 8800-7250 BCE are some of the earliest recorded cases of tuberculosis among humans [1]. In Europe, the earliest cases of skeletal tuberculosis date to about 5400-4800 BCE in Germany[1](Figure 1).
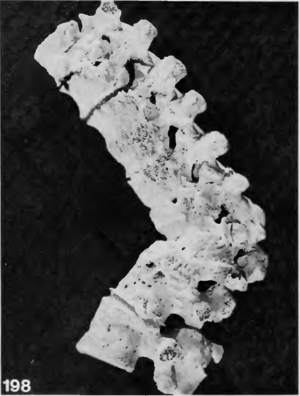
While these demonstrate that tuberculosis was present within the Neolithic period, they also suggest that microbes within the complex were capable of infecting humans before the shift away from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle. One school of thought suggests that the bacteria evolved within Pleistocene megafauna before crossing over to humans. This is partially supported by evidence of ancient M. tuberculosis complex DNA found in a North American bison from 17,830 years ago[2][5]. Others, however, suggest that the complex emerged during the Neolithic, and not before. Recently, DNA extracted from a Swedish mummy showing signs of tuberculosis contributed to a molecular clock phylogeny that placed a common ancestor to the M. tuberculosis complex as late as 2000-6000 years before present[4]. If this is the case, it would suggest that the emergence of human tuberculosis was correlated with the Neolithic revolution.
Regardless of its origin before or during the Neolithic, tuberculosis and its associated complex were likely more active once people began practicing agriculture. In a model aiming to characterize the maintenance of tuberculosis over time, researchers reinforced the claim that tuberculosis growth rates were higher in the Neolithic (0.1%/year) than they had been previously (0.003%/year)[6] . This trend may be tied to worsening living conditions that correspond with a shift to a sedentary lifestyle.
Treponema
Treponematoses, describing several diseases caused by bacteria of the genus Treponema, have been identified in individuals from Northern Vietnam in 2000 BCE [7]. Treponematoses manifests in several commonly known diseases: yaws, from T. pallidum pertenue, pinta, from T. carateum, venerial syphilis, from T. pallidum pallidum, and endemic syphilis, from T. pallidum endemicum[7]. These diseases, like tuberculosis, can be surmised from the archaeological record because late stages can leave lesions in bone[7][3]. This method is particularly important because identification of ancient Treponema DNA is relatively lacking.
Soft, tumor-like growths and lesions called gumma can develop on the face and extracranial bone and are considered diagnostic for treponematoses VLOK. Tibia deformation, called saber shin, and evidence of swelling in the digits point specifically to yaws in the two Vietnamese individuals[7]. Five additional individuals had symptoms suggesting treponematoses, but could not be confirmed as infected VLOK. Because the individuals at the site were mostly juveniles, yaws may be the most likely candidate for infection at the site. Notably, the diagnostic lesions only occur in about 1% of patients with yaws, and they mostly occur in childhood[3]. Therefore, the presence of yaws in the archaeological record, and treponematoses as a whole, is likely underrespresentative of the actual presence of infection throughout the Neolithic (Figure 2).
Salmonella enterica
Evidence of Salmonella enterica affecting Neolithic populations has been found in several agrarian communities throughout Eurasia. Unlike M. tuberculosis and Treponema, Salmonella does not usually leave distinctive marks in human skeletons[8]. Instead, it is often identified via ancient DNA analysis. This method often relies on metagenomic samples from the environment. In the case of Salmonella, however, ancient microbial DNA is collected from teeth. Teeth are often highly preserved in the archaeological record and seem to preserve bacterial DNA better than other types of bone, with reports of high microbial diversity recorded from teeth[9][10]. Because teeth are vascularized – or contain blood vessels – in life, retrieval of microbial DNA from the teeth suggests that the microbe in question was present in high levels of an individual at the time of death[8]. In 2020, a study reported that eight Salmonella enterica genomes were collected from human teeth that were up to 6,500 years old[8]. With these data, it is clear that S. enterica in one form or another has been infecting human populations for thousands of years, well within the Neolithic. However, until 3,000 years ago, S. enterica strains may have been generalists, affecting a variety of mammals, until Neolithization made specifically infecting humans advantageous for some strains of the bacteria[8]. Similarity of ancient S. enterica genomes to those infecting pigs suggests some spillover or coevolution between strains infecting pigs and humans several thousand years ago[8].
Notably, S. enterica genomes have also been found in Bronze Age Crete with limited host adaptation to humans[11]. Presence of generalist strains after the Neolithic indicate that the Neolithic may not have affected S. enterica evolution as much as some other pathogens. While the bacteria could certainly infect humans, it may not have been advantageous to do so exclusively. That said, salmonellosis was likely still a serious concern for Neolithic people. DNA extraction from Stone Age Scandinavian farmers revealed S. entericain two individuals[9]. Because these two individuals were buried in the same grave, it is possible that salmonellosis was their cause of death[9]. Regardless, people infected with S. enterica could expect symptoms like stomach cramps, fever, and diarrhea, which would seriously reduce quality of life[9].
Yersinia pestis
The plague causing bacterium Yersinia pestis is most famous for the bubonic plague pandemic of the 1300s, but it had been infecting people for thousands of years before the famous Black Death pandemic. Based on ancient DNA analysis, Yersinia pestis has been identified in Scandinavian burials over 4,800 years old, the earliest known instance of plague to date[9]. A recent study from Germany's Kiel University has identified two new Y. pestis genomes from human remains at the Warburg necropolis, a site in Germany inhabited from 5,300-4,900 years before present[12]. This suggests a comparable or even earlier case of plague, but has yet to be peer-reviewed.
These cases represent individual infections by Y. pestis. Based on genomic analysis of a recently discovered ancient strain of Y. pestis, some have argued for a plague pandemic in Eurasia near the end of the Neolithic period[13]. Several different strains, like the newly discovered Gökheim 2, would have arisen in genetically distinct and relatively isolated population[13]. With increased trade networks that could be associated with the end of the Neolithic, these strains could have spread throughout the continent and contributed to the decline of prominent Neolithic societies [13]. During the end of the Neolithic, Y. pestis may have been capable of such extensive infection. For the most part, however, genomic characterization of Y. pestis strains present in the Neolithic, including Scandinavia where Gökheim 2 is presumed to have originated, suggests that they were not easily transmissible. In highly transmissible strains, the ymt gene allows for transmission via fleas[9]. In the earlier identified cases of Y. pestis infections, the mutation necessary for such transmission had not yet been acquired[9].
Parasites
In the Neolithic period, bacterial infections often occurred alongside parasitic infections by organisms like tapeworms and whipworms. These can be identified in the archaeological record without genomic analysis; eggs, most commonly of intestinal parasites, can be found within preserved soft tissue and coprolites[14][15][16]. Digital light microscopy on coprolites from a community near Stonehenge in 2500 BCE revealed a diverse array of parasite remnants, including helminth eggs, fish tapeworm (Dibothriocephalus dendriticus), and capillariid nematodes[15]. At a Neolithic site in Russia, coprolites similarly revealed evidence of parasites including the worms Diphyllobothrium and Dioctophyma renale and two trematodes including a river lancet fluke[14]. In both studies, the coprolites were mostly attributed to canids due to the diversity of parasites and the composition of bile[15][14]. At the Russian site, however, at least one human contributed to the sample[15]. This suggests not only that parasites may not have been incredibly host-specific, but that humans and dogs may have had a close enough relationship to spread parasites to one another. The close relationship between humans and canines has also been cited in the spread of bacteria. For example, dogs may have acted as a transient reservoir for Yersinia pestis[12].
A particularly interesting example of parasite infection in the Neolithic comes from the so-called "Iceman," otherwise known as Ötzi, an adult male mummy recovered from a glacier in 1991 and dated to 3350-3100 BCE[16]. Ötzi has been extensively studied over the last few decades, and research has revealed several chronic health conditions. One of these is an infection by the intestinal whipworm Trichuris trichiura, evidenced by many eggs found in Ötzi's intestines[16]. These parasites are ingested and result from poor sanitation and hygienic conditions[16]. Interestingly, Ötzi may have attempted to treat the symptoms from the T. trichiura by consuming the birch fungus Fomitopsis betulina, which was found on his person[16]. This fungus has anti-helminitic and anti-microbial properties, including substances that inhibit multi-drug resistance[17]. Ötzi's intestinal problems were likely intensified by a simultaneous infection by a particularly aggressive strain of Helicobacter pylori that, although often asymptomatic, likely caused active gastritis for Ötzi (Figure 3)[16].
Section 3
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 4
Conclusion
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Fuchs, Katharina, Christoph Rinne, Clara Drummer, Alexander Immel, Ben Krause-Kyora, and Almut Nebel. “Infectious Diseases and Neolithic Transformations: Evaluating Biological and Archaeological Proxies in the German Loess Zone between 5500 and 2500 BCE.” 2019. The Holocene 29 (10): 1545–57.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Rothschild, Bruce M., Larry D. Martin, Galit Lev, Helen Bercovier, Gila Kahila Bar‐Gal, Charles Greenblatt, Helen Donoghue, Mark Spigelman, and David Brittain. “Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex DNA from an Extinct Bison Dated 17,000 Years before the Present.” 2001. Clinical Infectious Diseases 33 (3): 305–11.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Buikstra, J.E. ed. "Ortner's identification of pathological conditions in human skeletal remains." 2019.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Sabin et al. “A Seventeenth-Century Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Genome Supports a Neolithic Emergence of the Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex.” 2020. Genome Biology 21 (1): 201.
- ↑ Minnikin, David E, Oona Y-C Lee, Houdini Ht Wu, Gurdyal S Besra, and Helen D Donoghue. “Recognising the Broad Array of Approaches Available for the Diagnosis of Ancient Tuberculosis: Comment on ‘Infectious Diseases and Neolithic Transformations’ (Fuchs et al. 2019 The Holocene 29: 1545–1557).” 2020. The Holocene 30 (5): 781–83.
- ↑ Cardona, Pere-Joan, Martí Català, and Clara Prats. “The Origin and Maintenance of Tuberculosis Is Explained by the Induction of Smear-Negative Disease in the Paleolithic.” 2020. Pathogens 11 (3): 366
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Vlok, Melandri, Marc Oxenham, Kate Domett, Tran Thi Minh, Thi Mai Huong Nguyen, Hirofumi Matsumura, Hiep Hoang Trinh, et al. “Two Probable Cases of Infection with Treponema Pallidum during the Neolithic Period in Northern Vietnam (ca. 2000–1500 B.C.).” 2020. Bioarchaeology International 4 (1): 15–36.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Key, Felix M., Cosimo Posth, Luis R. Esquivel-Gomez, Ron Hübler, Maria A. Spyrou, Gunnar U. Neumann, Anja Furtwängler, et al. “Emergence of Human-Adapted Salmonella Enterica Is Linked to the Neolithization Process.” 2020. Nature Ecology & Evolution 4 (3): 324–33.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 Bergfeldt, Nora, Emrah Kırdök, Nikolay Oskolkov, Claudio Mirabello, Per Unneberg, Helena Malmström, Magdalena Fraser, et al. “Identification of Microbial Pathogens in Neolithic Scandinavian Humans.” 2024.Scientific Reports 14 (1): 5630.
- ↑ Margaryan, Ashot, Henrik B. Hansen, Simon Rasmussen, Martin Sikora, Vyacheslav Moiseyev, Alexandr Khoklov, Andrey Epimakhov, et al. “Ancient Pathogen DNA in Human Teeth and Petrous Bones.” 2018. Ecology and Evolution 8 (6): 3534–42.
- ↑ Neumann, Gunnar U., Eirini Skourtanioti, Marta Burri, Elizabeth A. Nelson, Megan Michel, Alina N. Hiss, Photini J.P. McGeorge, et al. “Ancient Yersinia Pestis and Salmonella Enterica Genomes from Bronze Age Crete.” 2022. Current Biology 32 (16): 3641-3649.e8.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Krause-Kyora, Ben, Julian Susat, Magdalena Haller-Caskie, Joanna Bonczarowska, Nicolas Antonio Da Silva, Kerstin Schierhold, Michael Rind, et al. “Neolithic Humans and Dogs - Transient Reservoirs for Yersinia Pestis.” 2023.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Rascovan, Nicolás, Karl-Göran Sjögren, Kristian Kristiansen, Rasmus Nielsen, Eske Willerslev, Christelle Desnues, and Simon Rasmussen. “Emergence and Spread of Basal Lineages of Yersinia Pestis during the Neolithic Decline.” 2019. Cell 176 (1–2): 295-305.e10.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 Maicher, Celine, Yolaine Maigrot, Andrey Mazurkevich, Ekaterina Dolbunova, and Matthieu Le Bailly. “First Contribution of Paleoparasitology to the Study of Coprolites from the Neolithic Site Serteya II (NW Russia).” 2021. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports 38 (August): 103093.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 Mitchell, Piers D., Evilena Anastasiou, Helen L. Whelton, Ian D. Bull, Mike Parker Pearson, and Lisa-Marie Shillito. “Intestinal Parasites in the Neolithic Population Who Built Stonehenge (Durrington Walls, 2500 BCE).” 2022. Parasitology 149 (8): 1027–33.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 Nerlich, Andreas G., Angelika Fleckinger, and Oliver Peschel. “Life and Diseases of the Neolithic Glacier Mummy ‘Ötzi.’” 2020. In The Handbook of Mummy Studies, edited by Dong Hoon Shin and Raffaella Bianucci, 1–22. Singapore: Springer Singapore.
- ↑ Pleszczyńska, Małgorzata, Marta K. Lemieszek, Marek Siwulski, Adrian Wiater, Wojciech Rzeski, and Janusz Szczodrak. “Fomitopsis Betulina (Formerly Piptoporus Betulinus): The Iceman’s Polypore Fungus with Modern Biotechnological Potential.” 2017. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 33 (5): 83.
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski,at Kenyon College,2024
