Human Astrovirus: Difference between revisions
(→Author) |
(→Author) |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
==Author== | ==Author== | ||
Page authored by Ethan Haggin and Kasia Jackowski, students of Prof. Jay Lennon at | Page authored by Ethan Haggin and Kasia Jackowski, students of Prof. Jay Lennon at Indiana University. | ||
<!-- Do not remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Jay Lennon at Indiana University]] | <!-- Do not remove this line-->[[Category:Pages edited by students of Jay Lennon at Indiana University]] | ||
Revision as of 15:32, 22 April 2024
Classification
Higher Order Taxonomy
Virus
Realm: Riboviria
Kingdom: Orthornavirae
Phylum: Pisuviricota
Class: Stelpaviricetes
Order: Stellavirales
Family: Astroviridae
Genus: Mamastrovirus
Species
Human Astrovirus 1-8
Description and Significance
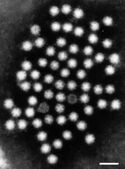
Human Astrovirus (HAstV) is a species of the genera Mamastrovirus, which are a group of enteric viruses known to be capable of causing mild symptomatic gastrointestinal infection. HAstV was first discovered as a causative agent for gastrointestinal infection among children under the age of 2. HAstV was first discovered in 1975, but the Astroviridae family was not established until 1995 [1]. In the early 2000s, three distinctive clades were discovered among the astrovirus species; VA1-VA3, VA2-VA4, and MLB [2].
Among other viruses, HAstV is notable for its resilience outside of a host environment. It has been determined that HAstV is resistant to inactivation by alcohols (including the common antiseptic ethanol), bleach, detergents, and to mild UV or heat treatments, along with being capable of staying alive in water for up to 90 days [3]. This makes HAstV commonplace in human environments, and as such HAstV has been found to responsible for roughly 4-8.6% of all diarrhea-related symptoms in young children [4]. Symptoms are relatively mild compared to other pathogens such as norovirus and rotavirus. Milder symptoms and the lack of prevalence in healthy young adults suggests that adaptive immunity is often developed in youth following a first encounter with HAstV [4].
Additionally of note are a few isolated cases associated with the HAstV serotype VA1. In 10 distinct cases, infection of the central nervous system has been noted, along with a lack of gastroenteric infection. Over half of the resulting cases were fatal [2]. It is unknown by what mechanisms these infections occur, although mink and ovine astrovirus infections have also resulted in CNS disease.
Genome Structure
Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence?
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Habitat; symbiosis; biogeochemical significance; contributions to environment.
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
References
Author
Page authored by Ethan Haggin and Kasia Jackowski, students of Prof. Jay Lennon at Indiana University.